Abstract
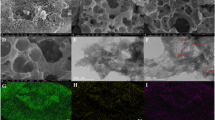
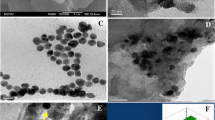
A 3D nanocomposite consisting of porous graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets (p-g-C3N4-NSs) and oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (O-MWCNTs) was prepared by simultaneous chemical oxidation of bulk g-C3N4 and bulk MWCNTs. This one-step oxidation results in the formation of acidic functional groups on the basal surfaces of both g-C3N4 and MWCNTs. Simultaneously, the O-MWCNTs are incorporated in-situ on the porous structure of p-g-C3N4. The acid functionalization and surface morphology of the nanocomposite were examined using attenuated total reflectance infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. The nanocomposite was used to modify a screen-printed electrode (SPE) which then was studied by using cyclic voltammetry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and differential pulse voltammetry. The modified SPE exhibits excellent sensitivity and selectivity towards the simultaneous detection of the heavy metal ions Cd(II), Hg(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II), typically at −0.78, +0.35, −0.5 and − 1.16 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). The detection limits (at S/N = 3) range between 8 and 60 ng L−1 under conditions of stripping analysis. The method was applied to the simultaneous detection of these ions in various (spiked) food samples. The results demonstrated the good accuracy and reproducibility of the method.

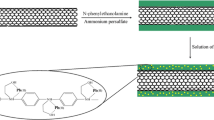
Schematic of a highly sensitive and selective electrochemical method for the simultaneous detection of four heavy metals. It is based on the use of a screen printed electrode (SPE) modified with 3D porous g-C3N4 and O-MWCNTs, and of anodic stripping voltammetry.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng H, Hu Y (2010) Lead (Pb) isotopic fingerprinting and its applications in lead pollution studies in China: a review. Environ Pollut 158:1134–1146
Navas-Acien A, Guallar E, Silbergeld EK, Rothenberg S (2007) J Environ Health Perspect 115:472–476
World Health Organization Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th edn, 2011. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241548151_eng.pdf
Seiler HG, Sigel A, Sigel H (1998) Handbook on toxicity of inorganic compounds. Marcel-Dekker, New York
Tarighat MA (2016) Orthogonal projection approach and continuous wavelet transform-feed forward neural networks for simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of some heavy metals in diet samples. Food Chem 192:548–556
Cui L (2016) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for identification of heavy metal arsenic (V)-mediated enhancing effect on antibiotic resistance. Anal Chem 88:3164–3170
Dico G, Galvano ML, Dugo F, D'ascenzi G, Macaluso C, Vella A, Ferrantelli V (2018) Toxic metal levels in cocoa powder and chocolate by ICP-MS method after microwave-assisted digestion. Food Chem 245:1163–1168
Chen J, Chakravarty P, Davidson GR, Wren DG, Locke MA, Zhou Y, Brown G Jr, Cizdziel JV (2015) Simultaneous determination of mercury and organic carbon in sediment and soils using a direct mercury analyzer based on thermal decomposition–atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Anal Chim Acta 871:9–17
Solovyev N, Vinceti M, Grill P, Mandrioli J, Michalke B (2017) Redox speciation of iron, manganese, and copper in cerebrospinal fluid by strong cation exchange chromatography–sector field inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 973:25–33
Daňhel A, Havran L, Trnková L, Fojta M (2016) Hydrogen evolution facilitates reduction of DNA guanine residues at the hanging mercury drop electrode: evidence for a chemical mechanism. Electroanalysis 28:2785–2790
Brett CM, Fungaro DA (2000) Poly (ester sulphonic acid) coated mercury thin film electrodes: characterization and application in batch injection analysis stripping voltammetry of heavy metal ions. Talanta 50:1223–1231
Wang J (2005) Stripping analysis at bismuth electrodes: a review. Electroanalysis 17:1341–1346
Gan X, Zhao H, Schirhagl R, Quan X (2018) Microchim Acta 185:478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3005-1
Lv H, Teng Z, Wang S, Feng K, Wang X, Wang C, Wang G (2018) Voltammetric simultaneous ion flux measurements platform for Cu2+, Pb2+ and Hg2+ near rice root surface: utilizing carbon nitride heterojunction film modified carbon fiber microelectrode. Sensors Actuators B 256:98–106
Gao W, Wang X, Li P, Wu Q, Qi F, Wu S, Ding K (2016) Highly sensitive and selective detection of cadmium with a graphite carbon nitride nanosheets/Nafion electrode. RSC Adv 6:113570–113575
Teng Z, Lv H, Wang L, Liu L, Wang C, Wang G (2016) Voltammetric sensor modified by EDTA-immobilized graphene-like carbon nitride nanosheets: preparation, characterization and selective determination of ultra-trace Pb (II) in water samples. Electrochim Acta 212:722–733
Balasubramanian P, Settu R, Chen SM, Chen TW (2018) Voltammetric sensing of sulfamethoxazole using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a graphitic carbon nitride and zinc oxide nanocomposite. Microchim Acta 185(8):396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2934-z
Zhang F, Zhong H, Lin Y, Chen M, Wang Q, Lin Y, Huang J (2018) A nanohybrid composed of Prussian blue and graphitic C3N4 nanosheets as the signal-generating tag in an enzyme-free electrochemical immunoassay for the neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. Microchim Acta 185(7):327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2865-8
Gooding JJ (2005) Nanostructuring electrodes with carbon nanotubes: a review on electrochemistry and applications for sensing. Electrochim Acta 50:3049–3060
Morton J, Havens N, Mugweru A, Wanekaya AK (2009) Detection of trace heavy metal ions using carbon nanotube-modified electrodes. Electroanalysis 21:1597–1603
Tian J, Liu Q, Ge C, Xing Z, Asiri AM, Al-Youbi AO, Sun X (2013) Ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets: a low-cost, green, and highly efficient electrocatalyst toward the reduction of hydrogen peroxide and its glucose biosensing application. Nanoscale 5:8921–8924
Xu H, Zeng L, Huang D, Xian Y, Jin L (2008) A Nafion-coated bismuth film electrode for the determination of heavy metals in vegetable using differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry: an alternative to mercury-based electrodes. Food Chem 109:834–839
Zhang H, Huang Y, Hu S, Huang Q, Wei C, Zhang W, Hao A (2015) Self-assembly of graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets–carbon nanotube composite for electrochemical simultaneous determination of catechol and hydroquinone. Electrochim Acta 176:28–35
Seenivasan R, Chang WJ, Gunasekaran S (2015) Highly sensitive detection and removal of lead ions in water using cysteine-functionalized graphene oxide/polypyrrole nanocomposite film electrode. Appl Mater Interfaces 7:15935–15943
Lu Z, Zhang J, Dai W, Lin X, Ye J, Ye J (2017) A screen-printed carbon electrode modified with a bismuth film and gold nanoparticles for simultaneous stripping voltammetric determination of Zn (II), Pb (II) and cu (II). Microchim Acta 184:4731–4740
Lee S, Park SK, Choi E, Piao Y (2016) Voltammetric determination of trace heavy metals using an electrochemically deposited graphene/bismuth nanocomposite film-modified glassy carbon electrode. J Electroanal Chem 766:120–127
Guo Z, Luo XK, Li YH, Zhao QN, Li MM, Zhao YT, Ma C (2017) Simultaneous determination of trace Cd (II), Pb (II) and Cu (II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry using a reduced graphene oxide-chitosan/poly-l-lysine nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. J Colloid Interface Sci 490:11–22
Lin H, Li M, Mihailovič D (2015) Simultaneous determination of copper, lead, and cadmium ions at a Mo6S9-xIx nanowires modified glassy carbon electrode using differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry. Electrochim Acta 154:184–189
Ruecha N, Rodthongkum N, Cate DM, Volckens J, Chailapakul O, Henry CS (2015) Sensitive electrochemical sensor using a graphene–polyaniline nanocomposite for simultaneous detection of Zn (II), Cd (II), and Pb (II). Anal Chim Acta 874:40–48
Sahoo PK, Panigrahy B, Sahoo S, Satpati AK, Li D, Bahadur D (2013) In situ synthesis and properties of reduced graphene oxide/Bi nanocomposites: as an electroactive material for analysis of heavy metals. Biosens Bioelectron 43:293–296
Lee S, Oh J, Kim D, Piao Y (2016) A sensitive electrochemical sensor using an iron oxide/graphene composite for the simultaneous detection of heavy metal ions. Talanta 160:528–536
Wang WJ, Cai YL, Li BC, Zeng J, Huang ZY, Chen XM (2018) A voltammetric sensor for simultaneous determination of lead, cadmium and zinc on an activated carbon fiber rod. Chin Chem Lett 29:111–114
Devadas B, Sivakumar M, Chen SM, Rajkumar M, Hu CC (2015) Simultaneous and selective detection of environment hazardous metals in water samples by using flower and Christmas tree like cerium hexacyanoferrate modified electrodes. Electroanalysis 27:2629–2636
Prabakar SR, Sakthivel C, Narayanan SS (2011) Hg (II) immobilized MWCNT graphite electrode for the anodic stripping voltammetric determination of lead and cadmium. Talanta 85:290–297
Lezi N, Economou A, Dimovasilis PA, Trikalitis PN, Prodromidis MI (2012) Disposable screen-printed sensors modified with bismuth precursor compounds for the rapid voltammetric screening of trace Pb (II) and Cd (II). Anal Chim Acta 728:1–8
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Ministry of Science and Technology-Taiwan (MOST105-2113-M-037-019-MY2), Kaohsiung Medical University (KMU)-Taiwan and Research Center for Environmental Medicine-KMU, Taiwan for research grant supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 853 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramalingam, M., Ponnusamy, V. & Sangilimuthu, S. A nanocomposite consisting of porous graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets and oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes for simultaneous stripping voltammetric determination of cadmium(II), mercury(II), lead(II) and zinc(II). Microchim Acta 186, 69 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3178-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3178-7