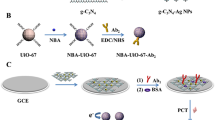
Abstract
An enzyme-free electrochemical immunoassay is described for the neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL; a biomarker of kidney disease). Prussian Blue (PB) nanoparticles with redox activity were deposited on graphitic C3N4 nanosheets (g-C3N4) by in-situ reduction. A screen printed electrode (SPCE) was modified with antibody against NGAL, and the PB-g-C3N4 nanohybrid was used as the signal-generating tag for the secondary antibody against NGAL. Upon addition of target NGAL and of secondary antibody, a sandwich is formed on the SPCE. At an applied potential of typically 0.13 V (vs. Ag/AgCl), a well-defined voltammetric peak is observed that results from the presence of PB on the secondary antibody. Under optimal conditions, the peak current increases linearly in the 0.01 to 10 ng·mL−1 NGAL concentration range, and the detection limit is 2.8 pg·mL−1. An average precision of <12% was accomplished in the batch-to-batch mode. Other disease-related biomarkers do not interfere. The accuracy and inter-laboratory validation of this method were evaluated for target NGAL detection in spiked human serum by using a commercial ELISA. The results obtained by the two methods are in good accordance.

An enzyme-free electrochemical immunoassay was used for detection of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin by Prussian blut/graphitic-C3N4 nanohybrids as the signal-generation tags.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pisano D, Joyce M (2018) Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: biomarker of the future or just another test? J Clin Anesthesia 45:37–38
Hraba-Renevey S, Turler H, Kress M, Salomon C, Weil R (1989) SV40-induced expression of mouse gene 243 involves a post-transcriptional mechanism. Oncogene 4:601–608
Mori K, Nakao K (2007) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as the real-time indicator of active kidney damage. Kidney Int 71:967–970
Deverajan P (2010) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a promising biomarker for human acute kidney injury. Biomark Med 4(2):265–280
Sellmer A, Bech B, Bjerre J, Schmidt M, Hjortdal V, Esberg G, Rttig S, Henriksen T (2017) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in the evaluation of patent ductus arteriosus and AKI in very preterm neonates: a cohort study. BMC Pediatr 17:art. ID 7
Devarajan P (2008) Neutrophil genlatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL): a new maker of kidney disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl 241:89–94
Lei L, Zhu J, Xia G, Feng F, Zhang H, Han Y (2017) A rapid and user-friendly assay to detect the neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) using up-converting nanoparticles. Talanta 162:339–344
Shukla K, Badgujar S, Bhanushali P, Sabharwal S (2017) Simplified purification approach of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-association lipocalin by tangential flow filtration and ion exchange chromatography. J Chromatogr B 1051:68–74
Mu Y, Xie H, Wan Y (2015) Sensitive and specific neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin detection by solid-phase proximity ligation assay. Anal Sci 31:475–479
Li H, Mu Y, Yan J, Cui D, Ou W, Wan Y, Liu S (2015) Label-free photoelectrochemical immunosensor for neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin based on the use of nanobodies. Anal Chem 87:2007–2015
Kannan P, Tiong H, Kim D (2012) Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for acute kidney injury. Biosens Bioelectron 31:32–36
Qiu Z, Shu J, Tang D (2018) Near-infrared-to-ultraviolet light-mediated photoelectrochemical aptasensing platform for cancer biomarker based on core-shell NaYF4:Yb,tm@TiO2 upconversion microrods. Anal Chem 90:1021–1028
Shu J, Tang D (2017) Current advances in quantum-dots-based photoelectrochemical immunoassay. Chem Asian J 12:2780–2789
Zhang K, Lv S, Lin Z, Li M, Tang D (2018) Bio-bar-code-based photoelectrochemical immunoassay for sensitive detection of prostate-specific antigen using rolling circle amplification and enzymatic biocatalytic precipitation. Biosens Bioelectron 101:159–166
Gao Z, Lv S, Xu M, Tang D (2017) High-index: HK0 faceted platinum concave nanocubes with enhanced peroxidase-like activity for an ultrasensitive colorimetric immunoassay of the human prostate-specific antigen. Analyst 142:911–917
He L, Guo C, Song Y, Zhang S, Yang M, Peng D, Fang S, Zhang Z, Liu C (2017) Chitosan stabilized gold nanoparticle based electrochemical ractopamine immunoassay. Microchim Acta 184:2919–2924
Shu J, Qiu Z, Lv S, Zhang K, Tang D (2018) Plasmonic enhancement coupling with defect-engineered TiO2-x: a mode for sensitive photoelectrochemical biosensing. Anal Chem 90:2425–2429
Qin Z, Xu W, Chen S, Chen J, Qiu J, Li C (2018) Electrochemical immunoassay for the carcinoembryonic antigen based on the use of a glassy carbon electrode modified with an octahedral Cu2O-gold nanocomposite and staphylococcal protein for signal amplification. Microchim Acta 185:266
Yin S, Zhao L, Ma Z (2018) Label-free electrochemical immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of neuron-specific enolase based on enzyme-free catalytic amplification. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:1279–1286
Felix F, Angnes L (2018) Electrochemical immunosensors-a powerful tool for analytical applications. Biosens Bioelectron 102:470–478
Chu Z, Liu Y, Jin W (2017) Recent progress in Prussian blue films: methods used to control regular nanostructures for electrochemical biosensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron 96:17–25
Wen S, Wang Y, Yuan Y, Liang R, Qiu J (2018) Electrochemical sensor for arsenite detection using graphene oxide assisted generation of Prussian blue nanoparticles as enhanced signal label. Anal Chim Acta 1002:82–89
Aguila D, Prado Y, Koumousi E, Mathoniere C, Clerac R (2016) Switchable Fe/co Prussian blue networks and molecular analogues. Chem Soc Rev 45:203–224
Moritomo Y, Takachi M, Kuihara Y, Matsuda T (2013) Synchrotron-radiation X-ray investigation of li+/Na+ intercalation into Prussian blue analogues. Adv mater Sci Engin 2013: art. ID 967285
Mollarasouli F, Serafin V, Campuzano S, Yanez-Sedeno P, Pingarron J, Asadpour-Zeynali K (2018) Ultrasensitive determination of receptor tyrosine kinase with a label-free electrochemical immunosensor using graphene quantum dots-modified screen-printed electrodes. Anal Chim Acta 1011:28–34
Molinero-Abad B, Izquierdo D, Perez L, Escudero I, Arcos-Martinez M (2018) Comparison of backing materials of screen printed electrochemical sensors for direct determination of the subnanomolar concentration of lead in seawater. Talanta 182:549–557
Lv S, Li Y, Zhang K, Lin Z, Tang D (2017) Carbon dots/g-C3N4 nanoheterostructures-based signal-generation tags for photoelectrochemical immunoassay of cancer biomarkers coupling with copper nanoclusters. ACS Appl Mater Interface 9:38336–38343
Ouyang H, Tu X, Fu Z, Wang W, Fu S, Zhu C, Du D, Lin Y (2018) Colorimetric and chemiluminescent dual-readout immunochromatographic assay for detection of pesticide utilizing g-C3N4/BiFeO3 nanocomposites. Biosens Bioelectron 106:43–49
Wasilewaka A, Zoch-Zwierz W, Taranta-Janusz K, Michaluk-Skutnik J (2010) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL): a new marker of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity? Pediatr Nephrol 25:889–897
Zheng Y, Jiao Y, Jaroniec M, Jin Y, Qiao S (2012) Nanostrucrued metal-free electrochemical catalysts for highly efficient oxygen reduction. Small 8:3550–3566
Gong Y, Li M, Wang Y (2015) Carbon nitride in energy conversion and storage: recent advances and future prospects. ChemSusChem 8:931–946
Funding
Support by the Health Science Research Personnel Training Program of Fujian Province (Grant no.: 2017-CXB-22) and the Scientific Research Innovation Team Construction Program of Fujian Normal University (Grant no.: IRTL1702) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 397 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Zhong, H., Lin, Y. et al. A nanohybrid composed of Prussian Blue and graphitic C3N4 nanosheets as the signal-generating tag in an enzyme-free electrochemical immunoassay for the neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. Microchim Acta 185, 327 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2865-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2865-8