Abstract
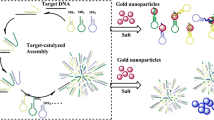
An ultrasensitive method for colorimetric and fluorometric determination of Hg(II) is described. It involves a dual signal detection strategy based on the use of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and of a catalytic hairpin self-assembly. Three fluorophore-labeled metastable hairpin DNA probes were adsorbed on AuNPs to quench the fluorescence of the labels. The addition of Hg(II) causes catalytic self-assembly of the hairpins due to formation of T-Hg(II)-T base pairs with the aid of helper DNA to form a branched junction. The branched junction is a dsDNA that is released from the surface of the AuNPs. As a result, fluorescence recovers. Its intensity, best measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 492/517 nm, increases linearly in the 0.2 to 100 nM of Hg(II) concentration range. The limit of detection is 0.1 nM. This is comparable to, or better than in other amplification based methods. The detection scheme offers both colorimetric (visual) and fluorescent read-out.

The fluorescence of labelled hairpins adsorbed on AuNPs is quenched in the absence of Hg(II) ions and the AuNPs shows red color with the protection of hairpins. However, Hg(II) ions can induce hairpins to be released by the AuNPs. As a result, fluorescence pops up and a red-blue color change occurs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nie SM, Emery SR (1997) Probing single molecules and single nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Science 275(5303):1102–1106
Chai X, Chang X, Hu Z, He Q, Tu Z, Li Z (2010) Solid phase extraction of trace hg (II) on silica gel modified with 2-(2-oxoethyl) hydrazine carbothioamide and determination by ICP-AES. Talanta 82(5):1791–1796
Hu Q, Yang G, Yin J, Yao Y (2002) Determination of trace lead, cadmium and mercury by on-line column enrichment followed by RP-HPLC as metal-tetra-(4-bromophenyl)-porphyrin chelates. Talanta 57(4):751–756
Hight SC, Cheng J (2006) Determination of methylmercury and estimation of total mercury in seafood using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS): method development and validation. Anal Chim Acta 567(2):160–172
Miyake Y, Togashi H, Tashiro M, Yamaguchi H, Oda S, Kudo M, Tanaka Y, Kondo Y, Sawa R, Fujimoto T (2006) MercuryII-mediated formation of thymine-HgII-thymine base pairs in DNA duplexes. J Am Chem Soc 128(7):2172–2173
Tanaka Y, Oda S, Yamaguchi H, Kondo Y, Kojima C, Ono A (2007) 15N-15N J-coupling across HgII: direct observation of HgII-mediated TT base pairs in a DNA duplex. J Am Chem Soc 129(2):244–245
Zhu Y, Cai Y, Zhu Y, Zheng L, Ding J, Quan Y, Wang L, Qi B (2015) Highly sensitive colorimetric sensor for hg 2+ detection based on cationic polymer/DNA interaction. Biosens Bioelectron 69:174–178
Jeong J-E, Kim B, Lee J, Kyhm K, Woo HY (2017) Inhibitor effects on molecular beacon-based mercury assays for tuning of detection range. Sensors Actuators B Chem 240:810–817
Zarlaida F, Adlim M (2016) Gold and silver nanoparticles and indicator dyes as active agents in colorimetric spot and strip tests for mercury (II) ions: a review. Microchim Acta 184(1):45–58
Li M, Wang Q, Shi X, Hornak LA, Wu N (2011) Detection of mercury (II) by quantum dot/DNA/gold nanoparticle ensemble based nanosensor via nanometal surface energy transfer. Anal Chem 83(18):7061–7065
Stobiecka M, Molinero AA, Chałupa A, Hepel M (2012) Mercury/homocysteine ligation-induced ON/OFF-switching of a T–T mismatch-based oligonucleotide molecular beacon. Anal Chem 84(11):4970–4978
Yuan M, Zhu Y, Lou X, Chen C, Wei G, Lan M, Zhao J (2012) Sensitive label-free oligonucleotide-based microfluidic detection of mercury (II) ion by using exonuclease I. Biosens Bioelectron 31(1):330–336
Li T, Li B, Wang E, Dong S (2009) G-quadruplex-based DNAzyme for sensitive mercury detection with the naked eye. Chem Commun 24:3551–3553
Xia F, Zuo X, Yang R, Xiao Y, Kang D, Vallée-Bélisle A, Gong X, Yuen JD, Hsu BB, Heeger AJ (2010) Colorimetric detection of DNA, small molecules, proteins, and ions using unmodified gold nanoparticles and conjugated polyelectrolytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(24):10837–10841
Zhu Z, Su Y, Li J, Li D, Zhang J, Song S, Zhao Y, Li G, Fan C (2009) Highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for mercury (II) ions by using a mercury-specific oligonucleotide probe and gold nanoparticle-based amplification. Anal Chem 81(18):7660–7666
Xuan F, Luo X, Hsing I-M (2013) Conformation-dependent exonuclease III activity mediated by metal ions reshuffling on thymine-rich DNA duplexes for an ultrasensitive electrochemical method for Hg2+ detection. Anal Chem 85(9):4586–4593
Xue X, Wang F, Liu X (2008) One-step, room temperature, colorimetric detection of mercury (Hg2+) using DNA/nanoparticle conjugates. J Am Chem Soc 130(11):3244–3245
Li Z, Ni Y, Kokot S (2015) A new fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dot system modified by the fluorophore-labeled ssDNA for the analysis of 6-mercaptopurine and hg (II). Biosens Bioelectron 74:91–97
Khani H, Rofouei MK, Arab P, Gupta VK, Vafaei Z (2010) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes-ionic liquid-carbon paste electrode as a super selectivity sensor: application to potentiometric monitoring of mercury ion (II). J Hazard Mater 183(1):402–409
Dinda D, Shaw BK, Saha SK (2015) Thymine functionalized Graphene oxide for fluorescence “turn-off-on” sensing of Hg2+ and I–in aqueous medium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(27):14743–14749
Zhang Y, Yuan Q, Chen T, Zhang X, Chen Y, Tan W (2012) DNA-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an ion-responsive release system to determine the presence of mercury in aqueous solutions. Anal Chem 84(4):1956–1962
Wang G, Xu G, Zhu Y, Zhang X (2014) A “turn-on” carbon nanotube–Ag nanoclusters fluorescent sensor for sensitive and selective detection of hg 2+ with cyclic amplification of exonuclease III activity. Chem Commun 50(6):747–750
Li Q, Zhou X, Xing D (2010) Rapid and highly sensitive detection of mercury ion (Hg2+) by magnetic beads-based electrochemiluminescence assay. Biosens Bioelectron 26(2):859–862
Huang D, Niu C, Wang X, Lv X, Zeng G (2013) “Turn-on” fluorescent sensor for Hg2+ based on single-stranded DNA functionalized Mn: CdS/ZnS quantum dots and gold nanoparticles by time-gated mode. Anal Chem 85(2):1164–1170
Zhu X, Zhou X, Xing D (2011) Ultrasensitive and selective detection of mercury (II) in aqueous solution by polymerase assisted fluorescence amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 26(5):2666–2669
Zhou X, Su Q, Xing D (2012) An electrochemiluminescent assay for high sensitive detection of mercury (II) based on isothermal rolling circular amplification. Anal Chim Acta 713:45–49
Wang Q, Yang X, Yang X, Liu P, Wang K, Huang J, Liu J, Song C, Wang J (2015) Colorimetric detection of mercury ion based on unmodified gold nanoparticles and target-triggered hybridization chain reaction amplification. Spectrochim. Acta. Part A 136:283–287
Li Y, Chen X, Wang B, Liu G, Tang Y, Miao P (2016) DNA tetrahedron and star trigon nanostructures for target recycling detection of nucleic acid. Analyst 141(11):3239–3241
Huang J, Gao X, Jia J, Kim J-K, Li Z (2014) Graphene oxide-based amplified fluorescent biosensor for Hg2+ detection through hybridization chain reactions. Anal Chem 86(6):3209–3215
Yun W, Jiang J, Cai D, Zhao P, Liao J, Sang G (2016) Ultrasensitive visual detection of DNA with tunable dynamic range by using unmodified gold nanoparticles and target catalyzed hairpin assembly amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 77:421–427
Zhang JF, Zhou Y, Yoon J, Kim JS (2011) Recent progress in fluorescent and colorimetric chemosensors for detection of precious metal ions (silver, gold and platinum ions). Chem Soc Rev 40(7):3416–3429
Oh E, Hong M-Y, Lee D, Nam S-H, Yoon HC, Kim H-S (2005) Inhibition assay of biomolecules based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 127(10):3270–3271
Doron A, Katz E, Willner I (1995) Organization of au colloids as monolayer films onto ITO glass surfaces: application of the metal colloid films as base interfaces to construct redox-active monolayers. Langmuir 11(4):1313–1317
Demers LM, Mirkin CA, Mucic RC, Reynolds RA, Letsinger RL, Elghanian R, Viswanadham G (2000) A fluorescence-based method for determining the surface coverage and hybridization efficiency of thiol-capped oligonucleotides bound to gold thin films and nanoparticles. Anal Chem 72(22):5535–5541
Jung C, Ellington AD (2014) Diagnostic applications of nucleic acid circuits. Acc Chem Res 47(6):1825–1835
Tan D, He Y, Xing X, Zhao Y, Tang H, Pang D (2013) Aptamer functionalized gold nanoparticles based fluorescent probe for the detection of mercury (II) ion in aqueous solution. Talanta 113:26–30
Liu C-W, Hsieh Y-T, Huang C-C, Lin Z-H, Chang H-T (2008) Detection of mercury (II) based on hg 2+–DNA complexes inducing the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Chem Commun 19:2242–2244
Alvand M, Shemirani F (2017) A Fe3O4@ SiO2@ graphene quantum dot core-shell structured nanomaterial as a fluorescent probe and for magnetic removal of mercury (II) ion. Microchim Acta 184(6):1621–1629
Deng L, Zhou Z, Li J, Li T, Dong S (2011) Fluorescent silver nanoclusters in hybridized DNA duplexes for the turn-on detection of hg 2+ ions. Chem Commun 47(39):11065–11067
Zhang L, Li T, Li B, Li J, Wang E (2010) Carbon nanotube–DNA hybrid fluorescent sensor for sensitive and selective detection of mercury (II) ion. Chem Commun 46(9):1476–1478
Li Q, Zhou X, Xing D (2010) Rapid and highly sensitive detection of mercury ion (hg 2+) by magnetic beads-based electrochemiluminescence assay. Biosens Bioelectron 26(2):859–862
Zhan L, Yang T, Zhen SJ, Huang CZ (2017) Cytosine triphosphate-capped silver nanoparticles as a platform for visual and colorimetric determination of mercury (II) and chromium (III). Microchim Acta 184(9):3171–3178
Zhang Y, Tang L, Yang F, Sun Z, Zhang G-J (2015) Highly sensitive DNA-based fluorometric mercury (II) bioassay based on graphene oxide and exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Microchim Acta 182(7–8):1535–1541
Acknowledgments
This work is sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31300819), Open Research Fund (CQCM-2016-05), the Opening Project of Zhejiang Provincial Top Key Discipline of Pharmaceutical Sciences (Grant No.201712), the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. KJ1706156), the Project of Wenzhou Science &Technology Bureau (S20150012) and Open Research Fund Program of Key Laboratory of Reservoir Aquatic Environment of CAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 0.99 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Yun, W., Chen, Y. et al. Ultrasensitive colorimetric and fluorometric detection of Hg(II) based on the use of gold nanoparticles and a catalytic hairpin assembly. Microchim Acta 184, 4741–4747 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2516-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2516-5