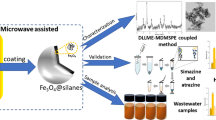
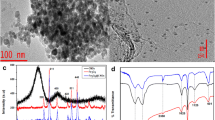
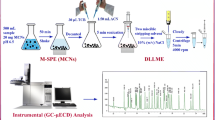
Abstract
Magnetic matrix solid phase dispersion (MMSPD) assisted dispersive liquid liquid microextraction (DLLME) was applied to extract ultra traces of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) from water samples prior to gas chromatography with electron capture detection. PCBs in water were adsorbed by micro particles of magnetic bamboo charcoal and then transferred into the elution solvent. PCBs in the elution solvent of the MMSPD were further concentrated into trace volume extraction solvent of the DLLME procedure. Under optimized conditions, good linearity in the range of 0.2–100 ng L−1 was obtained with regression coefficients (r) higher than 0.9987. Based on a signal-noise ratio of 3, the limits of detection (LODs) range from 0.05–0.1 ng L−1. These LODs are much lower than those of MMSPD or DLLME alone. Relative standard deviations are between 4.9–8.2 %. The method was successfully applied to the determination of PCBs in lake and river water. Relative recoveries were 85.5–117.4 % for the spiked environmental water samples.

Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) were adsorbed by micro particles of magnetic bamboo charcoal (MBC) and then eluted. PCBs were further concentrated into a trace volume of the extraction solvent used in dispersive liquid liquid microextraction.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kluwe WM, Hook JB (1981) Comparative induction of xenobiotic metabolism in rodent kidney, testis and liver by commercial mixtures of polybrominated biphenyls and polychlorinated biphenyls, phenobarbital and 3-methylcholanthrene: absolute and temporal effects. Toxicology 20:259
Murugesan P, Muthusamy T, Balasubramanian K, Arunakaran J (2007) Effects of vitamins C and E on steroidogenic enzymes mRNA expression in polychlorinated biphenyl (aroclor 1254) exposed adult rat leydig cells. Toxicology 232:170
Hori S, Obana H, Kashimoto T, Otake T, Nishimura H, Ikegami N, Kunita N, Uda H (1982) Effect of polychlorinated biphenyls and polychlorinated quaterphenyls in cynomolgus monkey (Macaca fascicularis). Toxicology 24:123
Popp P, Keil P, Montero L, Ruckert M (2005) Optimized method for the determination of 25 polychlorinated biphenyls in water samples using stir bar sorptive extraction followed by thermodesorption-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1071:155
Li K, Zhao GF, Zhou HD, Zeng M, Liao BH, Wu ZY, Zhang PW, Hao H (2012) Distribution characteristics and potential risk of PCBs in surface water from 22 tributaries and mainstream in middle reaches of Yangtze river. Chinese J Environ sci 5:1677
Sobek A, Gustafsson Ö (2014) Deep water masses and sediments are main compartments for polychlorinated biphenyls in the Arctic ocean. Environ Sci Technol 48:6719
Galbán-Malagón CJ, Vento SD, Berrojalbiz N, Ojeda MJ, Dachs J (2013) Polychlorinated biphenyls, hexachlorocyclohexanes and hexachlorobenzene in seawater and phytoplankton from the southern ocean (Weddell, south scotia, and Bellingshausen seas). Environ Sci Technol 47:5578
Zare F, Ghaedi M, Daneshfar A (2015) Solid phase extraction of antidepressant drugs amitriptyline and nortriptyline from plasma samples using core-shell nanoparticles of the type Fe3O4@ZrO2@N-cetylpyridinium, and their subsequent determination by HPLC with UV detection. Microchim Acta 182:1893
Wang RL, Yuan YN, Yang X, Han YH, Yan HY (2015) Polymethacrylate microparticles covalently functionalized with an ionic liquid for solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Microchim Acta 182:2201
Tao YF, Zhu FW, Chen DM, Xie SY, Hu PY, Wang X, Liu ZL, Peng DP, Yuan ZH (2014) Evaluation of matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction for 11 β-agonists in swine feed by liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 37:2574
Yan S, Qi TT, Chen DW, Li Z, Li XJ, Pan SY (2014) Magnetic solid phase extraction based on magnetite/reduced graphene oxide nanoparticles for determination of trace isocarbophosresidues in different matrices. J Chromatogr A 1347:30
Ye Q, Liu LH, Chen ZB, Hong LM (2014) Analysis of phthalate acid esters in environmental water by magneticgraphene solid phase extraction coupled with gaschromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1329:24
Taghizadeh M, Asgharinezhad AA, Samkhaniany N, Tadjarodi A, Abbaszadeh A, Pooladi M (2014) Solid phase extraction of heavy metal ions based on a novel functionalized magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotube composite with the aid of experimental design methodology. Microchim Acta 181:597
Zheng HB, Mo JZ, Zhang Y, Gao Q, Ding J, Yu QW, Feng YQ (2014) Facile synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers and itsapplication in magnetic solid phase extraction for fluoroquinolones inmilk samples. J Chromatogr A 1329:17
Xu S, Jiang C, Lin YX, Jia L (2012) Magnetic nanoparticles modified with polydimethylsiloxane and multi-walled carbon nanotubes for solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones. Microchim Acta 179:257
Wang X, Zhang LL, Diao CP, Zhao RS (2009) Bamboo charcoal as a solid phase extraction adsorbent for enrichment and determination of triclosan in environmental water samples. Chinese J Anal Lab 28:72
Wang XJ, Wu Z, Wang Y, Wang W, Wang X, Bu YJ, Zhao JF (2013) Adsorption-photodegradation of humic acid in water by using ZnO coupled TiO2/bamboo charcoal under visible light irradiation. J Hazard Mater 262:16
Wang XJ, Wang Y, Wang X, Liu M, Xia SQ, Yin DQ, Zhang YL, Zhao JF (2011) Microwave-assisted preparation of bamboo charcoal-based iron-containing adsorbents for Cr(VI) removal. Chem Eng J 174:326
Diao CP, Wei CH (2012) Rapid determination of anilines in water samples by dispersive liquid liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic drop prior to gas chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 403:877
Diao CP, Wei CH, Feng CH (2012) Rapid determination of benzene derivatives in water samples by trace volume solvent dispersive liquid Liquid microextraction prior to gas chromatography-flame ionization Detector. Chromatographia 75:551
Zgoła-Grześkowiak A, Grześkowiak T (2012) Solid-phase extraction combined with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction, fast derivatisation and high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis for trace determination of short-chained dodecyl alcohol ethoxylates and dodecyl alcohol in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1251:40
Samadi S, Sereshti H, Assadi Y (2012) Ultra-preconcentration and determination of thirteen organophosphorus pesticides in water samples using solid-phase extraction followed by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and gas chromatography with flame photometric detection. J Chromatogr A 1219:61
Zhao RS, Diao CP, Chen QF, Wang X (2009) Sensitive determination of amide herbicides in environmental water samples by a combination of solid-phase extraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction prior to GC-MS. J Sep Sci 32:1069
Zhao RS, Diao CP, Wang X, Jiang T, Yuan JP (2008) Rapid determination of amide herbicides in environmental water samples with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction prior to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:2915
Yang N, Zhu SM, Zhang D, Xu S (2008) Synthesis and properties of magnetic Fe3O4-activated carbon nanocomposite particles for dye removal. Mater Lett 62:645
Zanjani MRK, Yamini Y, Shariati S, Jonsson JA (2007) A new liquid-phase microextraction method based on solidification of floating organic drop. Anal Chim Acta 585:286
Dai LP, Cheng J, Matsadiq G, Liu L, Li JK (2010) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on the solidification of floating organic droplet for the determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in aqueous samples. Anal Chim Acta 674:201
Lee HK, Obbard JP (2004) Application of liquid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in blood plasma. J Chromatogr A 1022:161
Li GH, Zhang LJ, Zhang ZE (2008) Determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in water using dynamic hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1204:119
Joshi MD, Ho TD, Cole WTS, Anderson JL (2014) Determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in ocean water and bovine milk using cross linked polymeric ionic liquid sorbent coatings by solid-phase microextraction. Talanta 118:172
Wu YY, Yang CX, Yan XP (2014) Fabrication of metal-organic framework MIL-88B films on stainlesssteel fibers for solid-phase microextraction of polychlorinatedbiphenyls. J Chromatogr A 1334:1
Rezaei F, Bidari A, Birjandi AP, Hosseini MRM, Assadi Y (2008) Development of a dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method for the determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in water. J Hazard Mater 158:621
Cao XJ, Chen JY, Ye XM, Zhang FF, Shen LX, Mo WM (2013) Ultrasound-assisted magnetic SPE based on Fe3O4-grafted graphene for the determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in water samples. J Sep Sci 36:3579
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Program of National Natural Science of China (No. 31170110), Research Encouragement Foundation of Excellent Midlife-Youth Scientists of Shandong Province (No. BS2015HZ014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 797 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diao, C., Li, C., Yang, X. et al. Magnetic matrix solid phase dispersion assisted dispersive liquid liquid microextraction of ultra trace polychlorinated biphenyls in water prior to GC-ECD determination. Microchim Acta 183, 1261–1268 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1761-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1761-3