Abstract
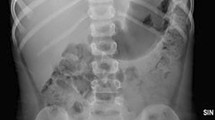
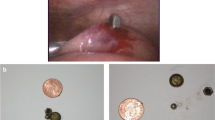
Ingested magnets can cause intestinal fistulas, perforation, and obstruction. There have been reports of magnet ingestion causing intestinal volvulus, but multiple magnet ingestion causing perforation and intestinal volvulus in a child is very unusual. We report the case of a 4-year-old girl, who ingested four magnets she acquired as toys, which caused intestinal volvulus and perforation as a result of pressure necrosis, several days after ingestion. At surgery we repaired two perforations, but additional bowel resection was not required. The patient was discharged on postoperative day 10. If multiple magnet ingestion is suspected in a child, the child must be monitored carefully. If there are signs of obstruction, emergency surgery is mandatory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S Hachimi-Idrissi S Corne Y Vandenplas (1998) ArticleTitleManagement of ingested foreign bodies in childhood: our experience and review of the literature Eur J Emerg Med 5 319–23 Occurrence Handle9827834 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2FktlGgtA%3D%3D
L Spitz (1971) ArticleTitleManagement of ingested foreign bodies in childhood BMJ 4 469–72 Occurrence Handle5125285 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE38%2FlsFaitA%3D%3D
DE McCause A Kurchin JR Hinshaw (1981) ArticleTitleGastrointestinal foreign bodies Am J Surg 142 335–7 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0002-9610(81)90342-1
V Selivanov GF Sheldon (1984) ArticleTitleManagement of foreign body ingestion Ann Surg 199 187–91 Occurrence Handle6696536 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000658-198402000-00010 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2c7islSmtA%3D%3D
JK Kim SS Kim JI Kim SW Kim YS Yang SH Cho et al. (1999) ArticleTitleManagement of foreign bodies in the gastrointestinal tract: an analysis of 104 cases Endoscopy 31 302–4 Occurrence Handle10376456 Occurrence Handle10.1055/s-1999-13 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1Mzgt12nuw%3D%3D
JA Cauchi RN Shawis (2002) ArticleTitleMultiple magnet ingestion and gastrointestinal morbidity Arch Dis Child 87 539–40 Occurrence Handle12456561 Occurrence Handle10.1136/adc.87.6.539 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38npsFKktw%3D%3D
L Suk-Koo B Nam-Seon K Hyun-Hahk (1996) ArticleTitleMischievous magnets: unexpected health hazard in children J Pediatr Surg 31 1694–5 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-3468(96)90053-6
M Honzumi C Shigemori H Ito Y Mohri H Urata T Yamamoto (1995) ArticleTitleAn intestinal fistula in a 3-year-old child caused by the ingestion of magnets: report of a case Surg Today 25 552–3 Occurrence Handle7579965 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00311314 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28%2Fot12luw%3D%3D
A Nui T Hirama T Katsuramaki T Maeda M Meguro M Nagayama et al. (2005) ArticleTitleAn intestinal volvulus caused by multiple magnet ingestion: an unexpected risk in children J Pediatr Surg 40 e9–11 Occurrence Handle16150334 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2005.05.065
Y Kubota K Tokiwa S Tanaka N Iwai (1995) ArticleTitleIntestinal obstruction in an infant due to magnet ingestion Eur J Pediatr Surg 5 119–21 Occurrence Handle7612582 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2MzjslSmug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1055/s-2008-1066183
S Suita H Ohgami S Yakabe A Nagasaki (1990) ArticleTitleThe fate of swallowed button batteries in children Z Kinderchir 45 212–4 Occurrence Handle2238845 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3M%2FkvF2hsA%3D%3D
SE Morrow SW Bickler AP Kennedy CL Snyder RJ Sharp KW Ashcraft (1998) ArticleTitleBalloon extraction of esophageal foreign bodies in children J Pediatr Surg 33 266–70 Occurrence Handle9498399 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-3468(98)90444-4 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7lvVWltg%3D%3D
E Volle P Beyer HJ Kaufmann D Hanel (1987) ArticleTitleMagnetic removal of metal foreign bodies from the esophagus and stomach Z Kinderchir 42 346–9 Occurrence Handle3439355 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c7kslWlsg%3D%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
İlçe, Z., Samsum, H., Mammadov, E. et al. Intestinal Volvulus and Perforation Caused by Multiple Magnet Ingestion: Report of a Case. Surg Today 37, 50–52 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-006-3330-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-006-3330-6