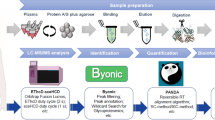
Abstract
Aims
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is associated with an increased risk of serious complications for mother and child during pregnancy. The main option for diagnosis of GDM is 75 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) at 24–28 gestation weeks, when harms to both mother and child have already potentially occurred. The aim of this study was to investigate new biomarkers for earlier detection and assessment of GDM at early second trimester (16–18 gestation weeks).
Methods
We systematically used multiplexed isobaric tandem mass tag labeling combined with liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) to screen differentially expressed proteins in plasma collected at 16–18 gestational weeks between pregnant women with and without GDM outcome.
Results
A total of 828 proteins were identified, of which 36 proteins implicated in immune response, inflammation, transport, platelet aggregation, catalyze and defense response were identified as differentially regulated proteins in GDM. To assess the validity of the results, four selected proteins including C-reactive protein, sex hormone-binding globulin, Ficolin 3 and pregnancy-specific beta-1-glycoprotein 4 were selected for subsequent Western blot analysis.
Conclusions
This is the first comprehensive study that integrates multiple state-of-the-art proteomic technologies to discover the earlier potential plasma biomarkers for GDM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coustan DR (2013) Gestational diabetes mellitus. Clin Chem 59(9):1310–1321
Ruchat SM, Mottola MF (2013) The important role of physical activity in the prevention and management of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 29(5):334–346
Wahabi HA, Alzeidan RA, Esmaeil SA (2012) Pre-pregnancy care for women with pre-gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 12:792
Buchanan TA, Xiang AH, Page KA (2012) Gestational diabetes mellitus: risks and management during and after pregnancy. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8(11):639–649
Metzger BE, Gabbe SG, Persson B, Buchanan TA, Catalano PM, Damm P, Dyer AR, Hod M, Kitzmiller JL, Lowe LP, McIntyre HD, Oats JJ, Omori Y (2012) The diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus: new paradigms or status quo? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 25(12):2564–2569
Oostdam N, van Poppel MN, Wouters MG, van Mechelen W (2011) Interventions for preventing gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 20(10):1551–1563
Mirabelli P, Incoronato M (2013) Usefulness of traditional serum biomarkers for management of breast cancer patients. Biomed Res Int 2013:685641
Elvidge T, Matthews IP, Gregory C, Hoogendoorn B (2013) Feasibility of using biomarkers in blood serum as markers of effect following exposure of the lungs to particulate matter air pollution. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 31(1):1–44
Liu B, Xu Y, Voss C, Qiu FH, Zhao MZ, Liu YD, Nie J, Wang ZL (2012) Altered protein expression in gestational diabetes mellitus placentas provides insight into insulin resistance and coagulation/fibrinolysis pathways. PLoS ONE 7(9):e44701
Oliva K, Barker G, Rice GE, Bailey MJ, Lappas M (2013) 2d-DIGE to identify proteins associated with gestational diabetes in omental adipose tissue. J Endocrinol 218(2):165–178
Adkins JN, Varnum SM, Auberry KJ, Moore RJ, Angell NH, Smith RD, Springer DL, Pounds JG (2002) Toward a human blood serum proteome analysis by multidimensional separation coupled with mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 1(12):947–955
Antoniewicz MR (2013) Tandem mass spectrometry for measuring stable-isotope labeling. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24(1):48–53
Ong SE, Blagoev B, Kratchmarova I, Kristensen DB, Steen H, Pandey A, Mann M (2002) Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture, silac, as a simple and accurate approach to expression proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 1(5):376–386
Wiese S, Reidegeld KA, Meyer HE, Warscheid B (2007) Protein labeling by itraq: a new tool for quantitative mass spectrometry in proteome research. Proteomics 7(3):340–350
Sui P, Watanabe H, Ossipov MH, Porreca F, Bakalkin G, Bergquist J, Artemenko K (2013) Dimethyl-labeling-based protein quantification and pathway search: a novel method of spinal cord analysis applicable for neurological studies. J Proteome Res 12(5):2245–2252
Rayavarapu S, Coley W, Cakir E, Jahnke V, Takeda S, Aoki Y, Grodish-Dressman H, Jaiswal JK, Hoffman EP, Brown KJ, Hathout Y, Nagaraju K (2013) Identification of disease specific pathways using in vivo silac proteomics in dystrophin deficient mdx mouse. Mol Cell Proteomics 12(5):1061–1073
Dayon L, Sanchez JC (2012) Relative protein quantification by ms/ms using the tandem mass tag technology. Methods Mol Biol 893:115–127
Tsuchida S, Satoh M, Kawashima Y, Sogawa K, Kado S, Sawai S, Nishimura M, Ogita M, Takeuchi Y, Kobyashi H, Aoki A, Kodera Y, Matsushita K, Izumi Y, Nomura F (2013) Application of quantitative proteomic analysis using tandem mass tags for discovery and identification of novel biomarkers in periodontal disease. Proteomics 13(15):2339–2350
Maes E, Valkenborg D, Mertens I, Broeckx V, Baggerman G, Sagaert X, Landuyt B, Prenen H, Schoofs L (2013) Proteomic analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded colorectal cancer tissue using tandem mass tag protein labeling. Mol BioSyst 9(11):2686–2695
Ruckhaberle E, Karn T, Hanker L, Schwarz J, Schulz-Knappe P, Kuhn K, Bohm G, Selzer S, Erhard N, Engels K, Holtrich U, Kaufmann M, Rody A (2010) Breast cancer proteomics—differences in protein expression between estrogen receptor-positive and -negative tumors identified by tandem mass tag technology. Breast Care (Basel) 5(1):7–10
Georgiou HM, Lappas M, Georgiou GM, Marita A, Bryant VJ, Hiscock R, Permezel M, Khalil Z, Rice GE (2008) Screening for biomarkers predictive of gestational diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol 45(3):157–165
Farrah T, Deutsch EW, Omenn GS, Campbell DS, Sun Z, Bletz JA, Mallick P, Katz JE, Malmstrom J, Ossola R, Watts JD, Lin B, Zhang H, Moritz RL, Aebersold R (2011) A high-confidence human plasma proteome reference set with estimated concentrations in peptideatlas. Mol Cell Proteomics 10(9):M110–M006353
Maged AM, Moety GA, Mostafa WA, Hamed DA (2013) Comparative study between different biomarkers for early prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 27(11):1108–1112
D’Anna R, Baviera G, De Vivo A, Facciola G, Di Benedetto A, Corrado F (2006) C-reactive protein as an early predictor of gestational diabetes mellitus. J Reprod Med 51(1):55–58
Caglar GS, Ozdemir ED, Cengiz SD, Demirtas S (2012) Sex-hormone-binding globulin early in pregnancy for the prediction of severe gestational diabetes mellitus and related complications. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 38(11):1286–1293
Li RX, Chen HB, Tu K, Zhao SL, Zhou H, Li SJ, Dai J, Li QR, Nie S, Li YX, Jia WP, Zeng R, Wu JR (2008) Localized-statistical quantification of human serum proteome associated with type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 3(9):e3224
Fuchtenbusch M, Bonifacio E, Lampasona V, Knopff A, Ziegler AG (2004) Immune responses to glutamic acid decarboxylase and insulin in patients with gestational diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol 135(2):318–321
Han S, Middleton P, Crowther CA (2012) Exercise for pregnant women for preventing gestational diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 7:CD009021
Kim SY, England JL, Sharma JA, Njoroge T (2011) Gestational diabetes mellitus and risk of childhood overweight and obesity in offspring: a systematic review. Exp Diabetes Res 2011:541308
Aguiar FJ, Ferreira-Junior M, Sales MM, Cruz-Neto LM, Fonseca LA, Sumita NM, Duarte NJ, Lichtenstein A, Duarte AJ (2013) C-reactive protein: clinical applications and proposals for a rational use. Rev Assoc Med Bras 59(1):85–92
Gabay C, Kushner I (1999) Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med 340(6):448–454
Szalai AJ, Agrawal A, Greenhough TJ, Volanakis JE (1999) C-reactive protein: structural biology and host defense function. Clin Chem Lab Med 37(3):265–270
Le TN, Nestler JE, Strauss JF 3rd, Wickham EP 3rd (2012) Sex hormone-binding globulin and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Trends Endocrinol Metab 23(1):32–40
Chen C, Smothers J, Lange A, Nestler JE, Strauss Iii JF, Wickham Iii EP (2010) Sex hormone-binding globulin genetic variation: associations with type 2 diabetes mellitus and polycystic ovary syndrome. Minerva Endocrinol 35(4):271–280
Kopp HP, Festa A, Krugluger W, Schernthaner G (2001) Low levels of sex-hormone-binding globulin predict insulin requirement in patients with gestation diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 109(7):365–369
Martinez FF, Cervi L, Knubel CP, Panzetta-Dutari GM, Motran CC (2013) The role of pregnancy-specific glycoprotein 1a (psg1a) in regulating the innate and adaptive immune response. Am J Reprod Immunol 69(4):383–394
Grudzinskas JG, Gordon YB, Menabawey M, Lee JN, Wadsworth J, Chard T (1983) Identification of high-risk pregnancy by the routine measurement of pregnancy-specific beta 1-glycoprotein. Am J Obstet Gynecol 147(1):10–12
Zhang XL, Ali MA (2008) Ficolins: structure, function and associated diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol 632:105–115
Szala A, Sawicki S, Swierzko AS, Szemraj J, Sniadecki M, Michalski M, Kaluzynski A, Lukasiewicz J, Maciejewska A, Wydra D, Kilpatrick DC, Matsushita M, Cedzynski M (2013) Ficolin-2 and ficolin-3 in women with malignant and benign ovarian tumours. Cancer Immunol Immunother 62(8):1411–1419
Halmos A, Rigo J Jr, Szijarto J, Fust G, Prohaszka Z, Molvarec A (2012) Circulating ficolin-2 and ficolin-3 in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Clin Exp Immunol 169(1):49–56
Chen H, Lu J, Chen X, Yu H, Zhang L, Bao Y, Lu F, Tang J, Gu C, Jia W (2012) Low serum levels of the innate immune component ficolin-3 is associated with insulin resistance and predicts the development of type 2 diabetes. J Mol Cell Biol 4(4):256–257
Rho JH, Roehrl MH, Wang JY (2009) Tissue proteomics reveals differential and compartment-specific expression of the homologs transgelin and transgelin-2 in lung adenocarcinoma and its stroma. J Proteome Res 8(12):5610–5618
Zhang Y, Ye Y, Shen D, Jiang K, Zhang H, Sun W, Zhang J, Xu F, Cui Z, Wang S (2010) Identification of transgelin-2 as a biomarker of colorectal cancer by laser capture microdissection and quantitative proteome analysis. Cancer Sci 101(2):523–529
De Seymour JV, Conlon CA, Sulek K, Villas Bôas SG, McCowan LM, Kenny LC, Baker PN (2014) Early pregnancy metabolite profiling discovers a potential biomarker for the subsequent development of gestational diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol 51(5):887–890
He X, de Seymour JV, Sulek K, Qi H, Zhang H, Han TL, Villas-Bôas SG, Baker PN (2015) Maternal hair metabolome analysis identifies a potential marker of lipid peroxidation in gestational diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol [Epub ahead of print]. (http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00592-015-0737-9)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81000258, 81100436), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2010586), the Bureau of Nanjing City Science and Technology Development Fund (201104014), the Open topic of State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine (SKLRM-KF-201109, SKLRM-B12) and the Nanjing Medical Technology Development Project [Grant Numbers YKK14126, QRX11210, QRX11211].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical standard
This study was performed in accordance with the Ethics Committee of Nanjing Medical University with an Institutional Review Board Number of 2012-NFLZ-32, the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Human and animal rights
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanjing Medical University with an Institutional Review Board (IRB) Number of 2012-NFLZ-32. The blood sample-collection was performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the revised Helsinki Declaration in 2008.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Additional information
Managed by Massimo Porta.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Wang, F., Wang, P. et al. Early second-trimester plasma protein profiling using multiplexed isobaric tandem mass tag (TMT) labeling predicts gestational diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol 52, 1103–1112 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-015-0796-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-015-0796-y