Abstract
Aims
Severe hypoglycemia is one of the strongest predictors of adverse clinical outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Our study addressed the question whether there is a relationship between hypoglycemic events (HE) and severe cardiac arrhythmias in type 2 diabetic patients with established clinical risk factors under real-world conditions.
Methods
We included 94 patients with type 2 diabetes and documented cardiovascular disease, in which interstitial glucose values and Holter ECG were recorded for 5 days in parallel. Patients received a stable treatment with insulin and/or sulfonylurea and were instructed to record symptoms of hypoglycemia or arrhythmias.
Results
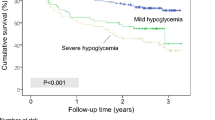
Continuous glucose monitoring revealed 54 HE (interstitial glucose <3.1 mmol/l) in a total of 26 patients. Patients perceived only 39 % of HE during the day and 11 % of HE during the night. Patients with HE had a significantly higher number of severe ventricular arrhythmias [ventricular tachycardia (VT) 32.8 ± 60 vs. 0.9 ± 4.2, p = 0.019], and multivariate regression analysis revealed the duration of severe HE and TSH level as independent predictors of the occurrence of a VT.
Conclusions
In conclusion, our study suggests that hypoglycemia might be able to trigger at least under certain circumstances, such as low TSH, ventricular arrhythmias under real-world conditions. The large number of unrecognized HE and VT in vulnerable patients treated with insulin or sulfonylurea should encourage the practitioner to focus on stable glucose control and to search for silent HE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bedenis R, Price AH, Robertson CM, Morling JR, Frier BM, Strachan MW, Price JF (2014) Association between severe hypoglycemia, adverse macrovascular events, and inflammation in the Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 37(12):3301–3308
McCoy RG, Van Houten HK, Ziegenfuss JY, Shah ND, Wermers RA, Smith SA (2012) Increased mortality of patients with diabetes reporting severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 35(9):1897–1901
Mellbin LG, Ryden L, Riddle MC, Probstfield J, Rosenstock J, Diaz R, Yusuf S, Gerstein HC (2013) Does hypoglycaemia increase the risk of cardiovascular events? A report from the ORIGIN trial. Eur Heart J 34(40):3137–3144
Nordin C (2014) The proarrhythmic effect of hypoglycemia: evidence for increased risk from ischemia and bradycardia. Acta Diabetol 51(1):5–14
Zoungas S, Patel A, Chalmers J, de Galan BE, Li Q, Billot L, Woodward M, Ninomiya T, Neal B, MacMahon S, Grobbee DE, Kengne AP, Marre M, Heller S (2010) Severe hypoglycemia and risks of vascular events and death. N Engl J Med 363(15):1410–1418
Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, Woodward M, Marre M, Cooper M, Glasziou P, Grobbee D, Hamet P, Harrap S, Heller S, Liu L, Mancia G, Mogensen CE, Pan C, Poulter N, Rodgers A, Williams B, Bompoint S, de Galan BE, Joshi R, Travert F (2008) Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 358(24):2560–2572
Clark AL, Best CJ, Fisher SJ (2014) Even silent hypoglycemia induces cardiac arrhythmias. Diabetes 63(5):1457–1459
Chow E, Bernjak A, Williams S, Fawdry RA, Hibbert S, Freeman J, Sheridan PJ, Heller SR (2014) Risk of cardiac arrhythmias during hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk. Diabetes 63(5):1738–1747
Gill GV, Woodward A, Casson IF, Weston PJ (2009) Cardiac arrhythmia and nocturnal hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes—the ‘dead in bed’ syndrome revisited. Diabetologia 52(1):42–45
Nordin C (2010) The case for hypoglycaemia as a proarrhythmic event: basic and clinical evidence. Diabetologia 53(8):1552–1561
Stahn A, Pistrosch F, Ganz X, Teige M, Koehler C, Bornstein S, Hanefeld M (2014) Relationship between hypoglycemic episodes and ventricular arrhythmias in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases: silent hypoglycemias and silent arrhythmias. Diabetes Care 37(2):516–520
Hay LC, Wilmshurst EG, Fulcher G (2003) Unrecognized hypo- and hyperglycemia in well-controlled patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the results of continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Technol Ther 5(1):19–26
Curione M, Di Bona S, Amato S, Turinese I, Tarquini G, Gatti A, Mandosi E, Rossetti M, Varrenti M, Salvatore S, Baiocco E, Morano S (2014) Lack of the QTc physiologic decrease during cardiac stress test in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with secretagogues. Acta Diabetol 51(1):31–33
Dumotier BM (2014) A straightforward guide to the basic science behind arrhythmogenesis. Heart 100(24):1907–1915
Collet TH, Gussekloo J, Bauer DC, den Elzen WP, Cappola AR, Balmer P, Iervasi G, Asvold BO, Sgarbi JA, Volzke H, Gencer B, Maciel RM, Molinaro S, Bremner A, Luben RN, Maisonneuve P, Cornuz J, Newman AB, Khaw KT, Westendorp RG, Franklyn JA, Vittinghoff E, Walsh JP, Rodondi N (2012) Subclinical hyperthyroidism and the risk of coronary heart disease and mortality. Arch Intern Med 172(10):799–809
Cooper DS, Biondi B (2012) Subclinical thyroid disease. Lancet 379(9821):1142–1154
Monnier L, Mas E, Ginet C, Michel F, Villon L, Cristol JP, Colette C (2006) Activation of oxidative stress by acute glucose fluctuations compared with sustained chronic hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. JAMA 295(14):1681–1687
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Medtronic for supplying the CGM equipment.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Ethical standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Human and Animal Rights disclosure
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Managed by Massimo Federici.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pistrosch, F., Ganz, X., Bornstein, S.R. et al. Risk of and risk factors for hypoglycemia and associated arrhythmias in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: a cohort study under real-world conditions. Acta Diabetol 52, 889–895 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-015-0727-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-015-0727-y