Abstract
Aim
Arterial stiffness is an important feature of diabetic macrovascular complications. Activin receptor-like kinase 7 (ALK7), a member of type I transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) receptors, is correlated with pathogenic risks of type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases and may be involved in cardiovascular remodeling. We aimed to investigate whether ALK7 is implicated in diabetes-induced aortic stiffness.
Methods
Type 2 diabetes was induced by high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin (STZ; 27.5 mg/kg). Forty rats were separated into four groups: control, diabetes, diabetes with empty virus and diabetes treated with ALK7-shRNA. The metabolic index, ALK 7 expression and aortic stiffness were evaluated. We used gene silencing method to investigate the role of ALK7 in the pathological development.
Results
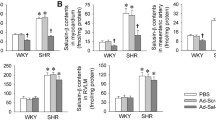
Diabetic rats showed increased blood glucose, cholesterol, triglyceride levels, severe insulin resistance and ALK7 overexpression. Diabetes enhanced aortic stiffness, as demonstrated by the loss and disruption of elastic fibers as well as by an increase in collagen fibers in the aortic media. ALK7 gene silencing ameliorated metabolic hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance. With ALK7 gene silencing, collagen content, elastin to collagen ratio, as well as collagen I-to-collagen III content ratio in diabetic rats were significantly decreased. Moreover, the phosphorylation level of Smad2/3 was markedly decreased after ALK7 gene silencing.
Conclusions
ALK7 gene silencing has a protective effect on diabetes-induced aortic stiffness, insulin resistance and hyperlipidemia, thus implicating a new potential therapeutic approach to diabetic macrovascular stiffness.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bozorgmanesh M, Hadaegh F, Azizi F (2010) Transportability of the updated diabetes prediction model from Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study to a Middle Eastern adult population: community-based cohort study. Acta Diabetol 50(2):175–181. doi:10.1007/s00592-010-0241-1
Law B, Fowlkes V, Goldsmith JG, Carver W, Goldsmith EC (2012) Diabetes-induced alterations in the extracellular matrix and their impact on myocardial function. Microsc Microanal 18(1):22–34. doi:10.1017/s1431927611012256
Srikanth S, Deedwania P (2011) Primary and secondary prevention strategy for cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Cardiol Clin 29(1):47–70. doi:10.1016/j.ccl.2010.11.004
Salminen M, Kuoppamäki M, Vahlberg T, Räihä I, Irjala K, Kivelä S-L (2011) Metabolic syndrome and vascular risk: a 9-year follow-up among the aged in Finland. Acta Diabetol 48(2):157–165. doi:10.1007/s00592-010-0251-z
Sesti G, Andreozzi F, Fiorentino TV, Mannino GC, Sciacqua A, Marini MA, Perticone F (2014) High circulating irisin levels are associated with insulin resistance and vascular atherosclerosis in a cohort of nondiabetic adult subjects. Acta Diabetol 51(5):705–713. doi:10.1007/s00592-014-0576-0
Tauzin L (2014) Alterations in viscoelastic properties following premature birth may lead to hypertension and cardiovascular disease development in later life. Acta Paediatr. doi:10.1111/apa.12815
Tang A, Eng JJ, Brasher PM, Madden KM, Mohammadi A, Krassioukov AV, Tsang TS (2014) Physical activity correlates with arterial stiffness in community-dwelling individuals with stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 23(2):259–266. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.01.020
Miyamoto M, Kotani K, Okada K, Fujii Y, Konno K, Ishibashi S, Taniguchi N (2011) The correlation of common carotid arterial diameter with atherosclerosis and diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol 49(1):63–68. doi:10.1007/s00592-011-0287-8
Jung C-H, Lee W-Y, Kim S-Y, Jung J-H, Rhee E-J, Park C-Y, Mok J-O, Oh K-W, Kim C-H, Park S-W, Kim S-W (2009) The relationship between coronary artery calcification score, plasma osteoprotegerin level and arterial stiffness in asymptomatic type 2 DM. Acta Diabetol 47(S1):145–152. doi:10.1007/s00592-009-0154-z
Xu J (1842) Shi GP (2014) Vascular wall extracellular matrix proteins and vascular diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 11:2106–2119. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.07.008
Lan TH, Huang XQ, Tan HM (2013) Vascular fibrosis in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Pathol 22(5):401–407. doi:10.1016/j.carpath.2013.01.003
Li L, Fan D, Wang C, Wang JY, Cui XB, Wu D, Zhou Y, Wu LL (2011) Angiotensin II increases periostin expression via Ras/p38 MAPK/CREB and ERK1/2/TGF-beta1 pathways in cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovasc Res 91(1):80–89. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvr067
Kamato D, Burch ML, Piva TJ, Rezaei HB, Rostam MA, Xu S, Zheng W, Little PJ, Osman N (2013) Transforming growth factor-beta signalling: role and consequences of Smad linker region phosphorylation. Cell Signal 25(10):2017–2024. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.001
Ryden M, Imamura T, Jornvall H, Belluardo N, Neveu I, Trupp M, Okadome T, ten Dijke P, Ibanez CF (1996) A novel type I receptor serine-threonine kinase predominantly expressed in the adult central nervous system. J Biol Chem 271(48):30603–30609
Zhao F, Huang F, Tang M, Li X, Zhang N, Amfilochiadis A, Li Y, Hu R, Jin T, Peng C, Wang Q (2012) Nodal induces apoptosis through activation of the ALK7 signaling pathway in pancreatic INS-1 beta-cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 303(1):E132–E143. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00074.2012
Bertolino P, Holmberg R, Reissmann E, Andersson O, Berggren PO, Ibanez CF (2008) Activin B receptor ALK7 is a negative regulator of pancreatic beta-cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(20):7246–7251. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801285105
Andersson O, Korach-Andre M, Reissmann E, Ibanez CF, Bertolino P (2008) Growth/differentiation factor 3 signals through ALK7 and regulates accumulation of adipose tissue and diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(20):7252–7256. doi:10.1073/pnas.0800272105
Liu L, Ding WY, Zhao J, Wang ZH, Zhong M, Zhang W, Chen YG, Zhang Y, Li L, Tang MX (2013) Activin receptor-like kinase 7 mediates high glucose-induced H9c2 cardiomyoblast apoptosis through activation of Smad2/3. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45(9):2027–2035. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2013.06.018
Shen N, Lin H, Wu T, Wang D, Wang W, Xie H, Zhang J, Feng Z (2013) Inhibition of TGF-beta1-receptor posttranslational core fucosylation attenuates rat renal interstitial fibrosis. Kidney Int 84(1):64–77. doi:10.1038/ki.2013.82
Carlsson LMS, Jacobson P, Walley A, Froguel P, Sjöström L, Svensson P-A, Sjöholm K (2009) ALK7 expression is specific for adipose tissue, reduced in obesity and correlates to factors implicated in metabolic disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 382(2):309–314. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.03.014
Zhang W, Wang H, Lv R, Wang Z, Shang Y, Zhang Y, Zhong M, Chen Y, Tang M (2013) ALK7 gene polymorphism is associated with metabolic syndrome risk and cardiovascular remodeling. Arq Bras Cardiol 101(2):134–140. doi:10.5935/abc.20130148
Ti Y, Xie GL, Wang ZH, Bi XL, Ding WY, Wang J, Jiang GH, Bu PL, Zhang Y, Zhong M, Zhang W (2011) TRB3 gene silencing alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy in a type 2 diabetic rat model. Diabetes 60(11):2963–2974. doi:10.2337/db11-0549
Stehouwer CD, Henry RM, Ferreira I (2008) Arterial stiffness in diabetes and the metabolic syndrome: a pathway to cardiovascular disease. Diabetologia 51(4):527–539. doi:10.1007/s00125-007-0918-3
Salum E, Butlin M, Kals J, Zilmer M, Eha J, Avolio AP, Arend A, Aunapuu M, Kampus P (2014) Angiotensin II receptor blocker telmisartan attenuates aortic stiffening and remodelling in STZ-diabetic rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr 6:57. doi:10.1186/1758-5996-6-57
Pyeritz RE (2014) Heritable thoracic aortic disorders. Curr Opin Cardiol 29(1):97–102. doi:10.1097/hco.0000000000000023
Yogosawa S, Izumi T (2013) Roles of activin receptor-like kinase 7 signaling and its target, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, in lean and obese adipocytes. Adipocyte 2(4):246–250. doi:10.4161/adip.24974
Yogosawa S, Mizutani S, Ogawa Y, Izumi T (2013) Activin receptor-like kinase 7 suppresses lipolysis to accumulate fat in obesity through downregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and C/EBPalpha. Diabetes 62(1):115–123. doi:10.2337/db12-0295
Byfield SDC, Major C, Laping NJ, Roberts AB (2004) SB-505124 is a selective inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta type I receptors ALK4, ALK5, and ALK7. Mol Pharmacol 65(3):744–752. doi:10.1124/mol.65.3.744
Akpan I, Goncalves MD, Dhir R, Yin X, Pistilli EE, Bogdanovich S, Khurana TS, Ucran J, Lachey J, Ahima RS (2009) The effects of a soluble activin type IIB receptor on obesity and insulin sensitivity. Int J Obes 33(11):1265–1273. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.162
Mita T, Watada H, Shimizu T, Tamura Y, Sato F, Watanabe T, Choi JB, Hirose T, Tanaka Y, Kawamori R (2007) Nateglinide reduces carotid intima-media thickening in type 2 diabetic patients under good glycemic control. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27(11):2456–2462. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.107.152835
Searls Y, Smirnova IV, Vanhoose L, Fegley B, Loganathan R, Stehno-Bittel L (2012) Time-dependent alterations in rat macrovessels with type 1 diabetes. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:278620. doi:10.1155/2012/278620
Agabiti-Rosei E, Porteri E, Rizzoni D (2009) Arterial stiffness, hypertension, and rational use of nebivolol. Vasc Health Risk Manag 5(1):353–360
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the research grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, Grant No. 2013CB530700), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81070192, 81070141, 81100605, 81270352, 81270287, 81300168, 81471036 and 81470560), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (BS2013YY017), the Independent Innovation Foundation of Shandong University (2012JC034), the cardiovascular exploration research foundation of Chinese Medical Doctor Association (DFCMDA201320) and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (SRFDP 20130131120065).
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported. W.-B.L. and J.Z. researched data and wrote the manuscript; L.L. and Z.-H.W. researched data and contributed to discussion; L.H. researched data; M.Z., W.Z. and M.-X.T. wrote, reviewed and edited the manuscript; and Y.Z. reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Ethical standard
All the animal experimental protocol complied with the ethical standards of Animal Management Rules of the Chinese Ministry of Health (Document NO. 55, 2001). Ethics approval was obtained from Animal Care and Use Committee of Shandong University, China.
Informed consent disclosure
No human studies were carried out in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Managed by Antonio Secchi.
Wen-bo Li and Jing Zhao have contributed equally to the article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Wb., Zhao, J., Liu, L. et al. Silencing of activin receptor-like kinase 7 alleviates aortic stiffness in type 2 diabetic rats. Acta Diabetol 52, 717–726 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0706-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0706-8