Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of verapamil on the prevention of epidural fibrosis in laminectomy rats.
Methods
A controlled double-blinded study was conducted in sixty healthy adult Wistar rats that underwent laminectomy at the L1–L2 levels. All rats were divided randomly into three groups according to the treatment method, with 20 in each group: (1) VP treatment group; (2) vehicle treatment group; and (3) sham group (laminectomy without treatment). All rats were killed 4 weeks post-laminectomy. The hydroxyproline content, Rydell score, vimentin cells density, fibroblasts density, inflammatory cells density and inflammatory factors expressions were evaluated.
Results
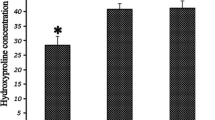
The histological evaluation showed less epidural scar adhesions in verapamil group than other two groups. The hydroxyproline content, Rydell score, vimentin cells density, fibroblasts density, inflammatory cells density and inflammatory factors expressions all suggested better results in verapamil group than other two groups.
Conclusion
Topical application of verapamil could inhibit fibroblasts proliferation and TGF-β1 and IL-6 expressions and prevent epidural scar adhesion in post-laminectomy rat model.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guyer RD, Patterson M, Ohnmeiss DD (2006) Failed back surgery syndrome: diagnostic evaluation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 14:534–543
Burton CV, Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Yong-Hing K, Heithoff KB (1981) Causes of failure of surgery on the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res 157:191–199
Siqueira EB, Kranzler LI, Dharkar DD (1983) Fibrosis of the dura mater: a cause of “failed back” syndrome. Surg Neurol 19:168–170
Cokluk C, Aydi K (2005) Experimental rabbit hemilaminotomy model in the evaluation of peridural fibrosis: a minimally invasive peridural fibrosis model. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 48:235–239
Sandoval MA, Hernandez-Vaquero D (2008) Preventing peridural fibrosis with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur Spine J 17:451–455
Henderson R, Weir B, Davis L, Mielke B, Grace M (1993) Attempted experimental modification of the postlaminectomy membrane by local instillation of recombinant tissue-plasminogen activator gel. Spine 18:1268–1272
Xu Q, Zhou W, Kong HY, Li L, Zhang YD, Zhang ZJ, Liu C, Wang RG (2010) The effect of the Sanqi qisodium hyaluronate gel on the collagen of epidural scar after rabbits laminectomy. Zhongguo Gu Shang 23:278–281
Copcu E, Sivrioglu N, Oztan Y (2004) Combination of surgery and intralesional verapamil injection in the treatment of the keloid. J Burn Care Rehabil 25:1–7
Giugliano G, Pasquali D, Notaro A, Brongo S, Nicoletti G, D’Andrea F, Bellastella A, Sinisi AA (2003) Verapamil inhibits interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor production in primary cultures of keloid fibroblasts. Br J Plast Surg 56:804–809
Margaret Shanthi FX, Ernest K, Dhanraj P (2008) Comparison of intralesional verapamil with intralesional triamcinolone in the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 74:343–348
Lee RC, Doong H, Jellema AF (1994) The response of burn scars to intralesional verapamil: report of five cases. Arch Surg 129:107–111
Singh DP, Chopra K (2013) Verapamil augments the neuroprotectant action of berberine in rat model of transient global cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol 720(1–3):98–106
Ning Z, Chen D, Liu A, Fan P, Duan Q, Zhang T, Fan G (2013) Efficacy of chemotherapy combined with targeted arterial infusion of verapamil in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys. doi:10.1007/s12013-013-9689-2
D’Andrea F, Brongo S, Ferraro G, Baroni A (2002) Prevention and treatment of keloids with intralesional verapamil. Dermatology 204:60–62
Skaria AM (2004) Prevention and treatment of keloids with intralesional verapamil. Dermatology 209:71
Dematte MF, Gemperli R, Salles AG, Dolhnikoff M, Lanças T, Saldiva PH, Ferreira MC (2011) Mechanical evaluation of the resistance and elastance of post-burn scars after topical treatment with tretinoin. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 66:1949–1954
Zhang C, Kong X, Zhou H, Liu C, Zhao X, Zhou X, Su Y, Sharma HS, Feng S (2013) An experimental novel study: Angelica sinensis prevents epidural fibrosis in laminectomy rats via downregulation of hydroxyproline, IL-6, and TGF-β 1. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. doi:10.1155/2013/291814
Liu C, Chang R, Yao X, Qiao WT, Geng YQ (2009) ISG15 expression in response to double-stranded RNA or LPS in cultured Fetal bovine lung(FBL) cells. Vet Res Commun 33:723–733
Zhang C, Kong X, Ning G, Liang Z, Qu T, Chen F, Cao D, Wang T, Sharma HS, Feng S (2013) All-trans retinoic acid prevents epidural fibrosis through NF-κB signaling pathway in post-laminectomy rats. Neuropharmacology. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm
Liu J, Ni B, Zhu L, Yang J, Cao X, Zhou W (2010) Mitomycin C-polyethylene glycol controlled-release film inhibits collagen secretion and induces apoptosis of fibroblasts in the early wound of a postlaminectomy rat model. Spine J 10:441–447
Su C, Yao C, Lu S, Zhang A, Cao X, Teng G, Zang F (2010) Study on the optimal concentration of topical mitomycin-C in preventing postlaminectomy epidural adhesion. Eur J Pharmacol 640:63–66
Lee JY, Stenzel W, Ebel H, Wedekind C, Ernestus RI, Klug N (2004) Mitomycin C in preventing spinal epidural fibrosis in a laminectomy model in rats. J Neurosurg 100:52–55
Rabb CH (2010) Failed back syndrome and epidural fibrosis. Spine J 10:454–455
Liu L, Sui T, Hong X, Wu X, Cao X (2013) Inhibition of epidural fibrosis after microendoscopic discectomy with topical application of mitomycin C: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. J Neurosurg Spine 18:421–427
Hayashi M, Yamaji Y, Nakazato Y, Saruta T (2000) The effects of calcium channel blockers on nuclear factor kappa B activation in the mesangium cells. Hypertens Res 23:521–525
Lee RC, Ping JA (1990) Calcium antagonists retard extracellular matrix production in connective tissue equivalent. J Surg Res 49:463–466
Lawrence WT (1996) Treatment of earlobe keloids with surgery plus adjuvant intralesional verapamil and pressure earrings. Ann Plast Surg 37:167–169
Ahuja RB, Chatterjee P (2013) Comparative efficacy of intralesional verapamil hydrochloride and triamcinolone acetonide in hypertrophic scars and keloids. Burns. doi:10.1016/j.burns
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Xie, P. et al. Calcium channel blockers in reduction of epidural fibrosis and dural adhesions in laminectomy rats. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24 (Suppl 1), 293–298 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-013-1395-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-013-1395-7



