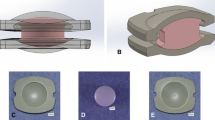
Abstract
Introduction
The objective of our in vitro study was to introduce a test method to evaluate impingement in lumbar spinal disc arthroplasty in terms of wear, contact pattern, metal ion concentration and particle release.
Material and Method
Impingement wear simulation was performed on a 6-station spinal wear simulator (Endolab, Germany) on a lumbar spinal disc system (activ® L Aesculap AG, Germany) using four different protocols specific to impingement in flexion, in extension, in lateral bending and in combined flexion bending. Impingement contact stress is intentionally created by applying an angular displacement of +2° in addition to the intended range of motion in the impingement direction, whereas a bending moment of 8 Nm remains constant during the impingement phase (plateau).
Results
An average volumetric wear rate of 0.67 mm3/million cycles was measured by impingement under flexion, of 0.21 mm3/million cycles under extension, of 0.06 mm3/million cycles under lateral bending and of 1.44 mm3/million cycles under combined flexion bending. The particle size distribution of the cobalt-chromium wear particles released by impingement in flexion (anterior), extension (posterior), lateral bending (lateral) and combined flexion bending (antero-lateral) revealed that most of the detected cobalt-chromium particles were in a size range between 0.2 and 2 µm.
Conclusion
The impingement wear simulation introduced here proved to be suitable to predict in vivo impingement behaviour in regard to contact pattern seen on retrieved devices of the activ® L lumbar disc arthroplasty design in a pre-clinical test.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affatato S, Fernandes B, Tucci A, Esposito L, Toni A (2001) Isolation and morphological characterisation of UHMWPE wear debris generated in vitro. Biomaterials 22:2325–2331
Amstutz HC, Campbell PA, Dorey FJ, Johnson AJ, Skipor AK, Jacobs JJ (2013) Do ion concentrations after metal-on-metal hip resurfacing increase over time? A prospective study. J Arthroplasty 28(4):695–700
Austen S, Punt IM, Cleutjens JPM, Willems PC, Kurtz SM, MacDonald DW, van Rhijn LW, van Ooij A (2012) Clinical, radiological, histological and retrieval findings of Activ-L and Mobidisc total disc replacements—a study of two patients. Eur Spine J 21(4):S51–S520
Baxter RM, MacDonald DW, Kurtz SM, Steinbeck MJ (2013) Severe impingement of lumbar disc replacements increases the functional biological activity of polyethylene wear debris. J Bone Joint Surg 95A(e75):1–9
Blumenthal S, McAfee PC, Guyer RD, Hochschuler SH, Geisler FH, Holt RT, Garcia R, Regan JJ, Ohnmeiss DD (2005) A prospective, randomized, multicenter food and drug administration investigational device exemptions study of lumbar total disc replacement with the Charité artificial disc versus lumbar fusion. Spine 30(14):1565–1575
Catelas I, Wimmer MA, Utzschneider S (2011) Polyethylene and metal wear particles: characteristics and biological effects. Semin Immunopathol 33(3):257–271
Cavanaugh DA, Nunley PD, Kerr EJ III, Werner DJ, Jawahar A (2009) Delayed hyper-reactivity to metal ions after cervical disc arthroplasty—a case report and literature review. Spine 34(7):E262–E265
Cunningham BW, Gordon JD, Dmitriev AE, Hu N, McAfee PC (2003) Biomechanical evaluation of total disc replacement arthroplasty: an in vitro human cadaveric model. Spine 28(20S):110–117
Cunningham BW, Hu N, Hallab NJ, McAfee PC (2007) Epidural application of particular wear debris—a comprehensive analysis of ten different implant materials using an in vivo animal model. 7th Annual Meeting of the Spine Arthroplasty Society May 1–4, 2007 Berlin Abstract PA-WE10
David T (2007) Long-term results of one-level lumbar arthroplasty. Minimum 10-year follow-up of the Charité artificial disc in 106 patients. Spine 32(6):661–666
de Souza RM, Parsons NR, Oni T, Dalton P, Costa M, Krikler S (2010) Metal ion levels following resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip—serial results over a ten-year period. J Bone Joint Surg 92B:1642–1647
Devin CJ, Myers TG, Kang JD (2008) Chronic failure of a lumbar total disc replacement with osteolysis. Report of a case with nineteen-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg 90A:2230–2234
Golish SR, Anderson PA (2012) Bearing surfaces for total disc arthroplasty: metal-on-metal versus metal-on-polyethylene and other biomaterials. Spine J 12(8):693–701
Gornet MF, Burkus JK, Harper ML, Chan FW, Skipor AK, Jacobs JJ (2012) Prospective study on serum metal levels in patients with metal-on-metal lumbar disc arthroplasty. Eur Spine J 22(4):741–746
Grupp TM, Yue JJ, Garcia R, Basson J, Schwiesau J, Fritz B, Blömer W (2009) Biotribological evaluation of artificial disc arthroplasty devices: influence on loading and kinematic patterns during in vitro wear simulation. Eur Spine J 18(1):98–108
Guyer RD, Shellock J, MacLennan B, Hanscom D, Knight RQ, McCombe P, Jacobs JJ, Urban RM, Bradford D, Ohnmeiss DD (2011) Early failure of metal-on-metal artificial disc prostheses associated with lymphocytic reaction—diagnosis and treatment experience in four cases. Spine 36(4):E492–E497
Hallab NJ, Chan FW, Harper ML (2012) Quantifying subtle but persistent peri-spine inflammation in vivo to submicron cobalt-chromium alloy particles. Eur Spine J 21:2649–2658
Hallab NJ, Cunningham BW, Jacobs JJ (2003) Spinal implant debris-induced osteolysis. Spine 28(20S):125–138
Hannemann F, Hartmann A, Schmitt J, Lützner J, Seidler A, Campbell P, Delaunay CP, Drexler H, Ettema HB, García-Cimbrelo E, Huberti H, Knahr K, Kunze J, Langton DJ, Lauer W, Learmonth I, Lohmann CH, Morlock M, Wimmer MA, Zagra L, Günther KP (2013) European multidisciplinary consensus statement on the use and monitoring of metal-on-metal bearings for total hip replacement and hip resurfacing. Orthop Trauma Surg Res. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2013.01.005
Hedman TP, Kostuik JP, Fernie GR, Heller WG (1991) Design of an intervertebral disc prosthesis. Spine 16(6):S256–S260
Kaddick C, Hintner M, Wimmer MA (2010) Standardized wear testing of intervertebral spinal disc prostheses—a summary of 9 years of testing experience. In: Cobb (ed) Modern trends in THA bearings—material and clinical performance. Springer, New York, pp 131–138
Kaefer W, Clessienne CB, Daexle M, Kocak T, Reichel H, Cakir B (2008) Posterior component impingement after lumbar total disc replacement—a radiographic analysis of 66 ProDisc-L prostheses in 56 patients. Spine 33(22):2444–2449
Kurtz SM, Patwardhan A, MacDonald D, Ciccarelli L, van Ooij A, Lorenz M, Zindrick M, O’Leary P, Isaza J, Ross R (2008) What is the correlation of in vivo wear and damage patterns with in vitro TDR motion response. Spine 33(5):481–489
Kurtz SM, von Ooij A, Ross ER, de Waal Malefijt J, Ciccarelli L, Villarraga ML (2007) Polyethylene wear and rim fracture in total disc arthroplasty. Spine J 7(1):12–21
Langton DJ, Sprowson AP, Joyce TJ, Reed M, Carluke I, Partington P, Nargol AVF (2009) Blood metal ion concentrations after hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 91B:1287–1295
Lebl DR, Cammisa FP Jr, Girardi FP, Wright T, Abjornson C (2012) The mechanical performance of cervical total disc replacements in vivo—prospective retrieval analysis of ProDisc-C devices. Spine 37(26):2151–2160
Lebl DR, Cammisa FP, Girardi FP, Wright T, Abjornson C (2012) In vivo functional performance of failed ProDisc-L devices. Spine 37(19):E1209–E1217
Lee JL, Billi F, Sangiorgio SN, McGarry W, Krueger DJ, Miller PT, McKellop H, Ebramzadeh E (2008) Wear of an experimental metal-on-metal artificial disc for the lumbar spine. Spine 33(6):597–606
Maezawa K, Nozawa M, Yuasa T, Aritomi K, Matsuda K, Shitoto K (2010) Seven years of chronological changes of serum chromium levels after Metasul metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 25(8):695–700
Marker M, Grübl A, Riedl O, Heinze G, Pohanka E, Kotz R (2008) Metal-on-metal hip implants: do they impair renal function in the long-term? A 10-year follow-up study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128:915–919
Mathews HH, LeHuec JC, Friesem T, Zdeblick T, Eisermann L (2004) Design rationale and biomechanics of Maverick total disc arthroplasty with early clinical results. Spine J 4:268S–275S
Merritt K, Brown SA (1996) Distribution of cobalt chromium wear and corrosion products and biologic reactions. Clin Orth Rel Res 329S:S233–S234
Niedzwiecki S, Klapperich C, Short J, Jani S, Ries M, Pruitt L (2001) Comparison of three joint simulator wear debris isolation techniques: acid digestion, base digestion, and enzymatic cleavage. J Biomed Mater Res 56:245–249
Paré PE, Chan FW, Powell ML (2007) Wear characterization of the A-MAVTM anterior motion replacement using a spine wear simulator. Wear 263:1055–1059
Polyzois I, Nikolopoulos D, Michos I, Patsouris E, Theocharis S (2012) Local and systemic toxicity of nanoscale debris particles in total hip arthroplasty. J Appl Toxicol 32(4):255–269
Punt IM, Cleutjens JPM, de Bruin T, Willems PC, Kurtz SM, van Rhijn LW, Schurink GWH, van Ooij A (2009) Periprosthetic tissue reactions observed at revision of total intervertebral disc arthroplasty. Biomaterials 30:2079–2084
Punt IM, Willems P, Kurtz SM, van Rhijn LW, van Ooij A (2012) Clinical outcomes of two revision strategies for failed total disc replacements. Eur Spine J 21:2558–2564
Rohlmann A, Bergmann G, Graichen F (1999) Loads on internal spinal fixators measured in different body positions—SSE Basic Science Award 1999. Eur Spine J 8:354–359
Rundell SA, Day JS, Isaza J, Guillory S, Kurtz SM (2012) Lumbar total disc replacement impingement sensitivity to disc height distraction, spinal sagittal orientation, implant position, and implant lordosis. Spine 37(10):E590–E598
Rundell SA, Day JS, Isaza J, Siskey R, MacDonald D, Kurtz SM (2011) Derivation of clinically relevant boundary conditions suitable for evaluation of chronic impingement of lumbar total disk replacement: application to standard development. J ASTM Int 8(5):1–14, JAI103556
Simonsen LO, Harbak H, Bennekou P (2012) Cobalt metabolism and toxicology—a brief update. Sci Total Environ 432:210–215
Tropiano P, Huang RC, Girardi FP, Cammisa FP, Marnay T (2005) Lumbar total disc replacement—seven to eleven-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg 87A(3):490–496
Tumialán LM, Gluf WM (2011) Progressive vertebral body osteolysis after cervical disc arthroplasty. Spine 36(14):E973–E978
van den Eerenbeemt KD, Ostelo RW, van Royen BJ, Peul WC, van Tulder MW (2010) Total disc replacement surgery for symptomatic degenerative lumbar disc disease—a systematic review of the literature. Eur Spine J 19(8):1262–1280
van Ooij A, Kurtz SM, Stessels F, Noten H, van Rhijn L (2007) Polyethylene wear debris and long-term clinical failure of the Charité disc prosthesis. Spine 32(2):223–229
Wilke HJ, Wenger K, Claes L (1998) Testing criteria for spinal implants—recommendations for the standardization of in vitro stability testing of spinal implants. Eur Spine J 7(2):148–154
Wooley PH, Morren R, Andary J, Sud S, Yang SY, Mayton L, Markel D, Sieving A, Nasser S (2002) Inflammatory responses to orthopaedic biomaterials in the murine air pouch. Biomaterials 23:517–526
Zeh A, Planert M, Siegert G, Lattke P, Held A, Hein W (2007) Release of cobalt and chromium ions into the serum following implantation of the metal-on-metal Maverick-type artificial lumbar disc. Spine 32(3):348–352
Zigler J, Delamarter R, Spivak JM, Linovitz RJ, Danielson III GO, Haider TT, Cammisa F, Zuchermann J, Balderston R, Kitchel S, Foley K, Watkins R, Bradford D, Yue J, Yuan H, Herkowitz H, Geiger D, Bendo J, Peppers T, Sachs B, Girardi F, Kropf M, Goldstein J (2007) Results of the prospective, randomized, multicenter FDA IDE study of the ProDisc-L total disc replacement versus circumferential fusion for the treatment of 1-level degenerative disc disease. Spine 32(11):1155–1162
Zigler JE, Delamarter RB (2012) Five-year results of the prospective, randomized, multicenter, FDA IDE study of the ProDisc-L total disc replacement versus circumferential arthrodesis for the treatment of single-level degenerative disc disease. J Neurosurg Spine 17:493–501
Zigler JE, Glenn J, Delamarter RB (2012) Five-year adjacent-level degenerative changes in patients with single-level disease treated using lumbar total disc replacement with ProDisc-L versus circumferential fusion. J Neurosug Spine 17:504–511
Zysk SP, Gebhard H, Plitz W, Buchhorn GH, Sprecher CM, Jansson V, Messmer K, Veihelmann A (2004) Influence of orthopedic particulate biomaterials on inflammation and synovial microcirculation in the murine knee joint. J Biomed Mater Res Appl Biomater 71B:108–115
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Sarah Mattes and Ricardo Smits Serena for their work on part of the particle analysis.
Conflict of interest
Five of the authors (TG, BF, CS, JS, WB) are employees of Aesculap Tuttlingen a manufacturer of orthopaedic implants. Two of the authors (JY, RG) are advising surgeons in Aesculap R&D projects. One of the authors (CK) is getting research funding in correlation with Aesculap R&D projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grupp, T.M., Yue, J.J., Garcia, R. et al. Evaluation of impingement behaviour in lumbar spinal disc arthroplasty. Eur Spine J 24, 2033–2046 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3381-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3381-0