Abstract
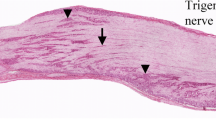
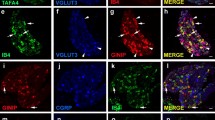
Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons with dichotomizing axons have been reported in several species and are thought to be related to referred pain. However, these neurons, which have dichotomizing axons to the lumbar muscles and to the knee, have not been investigated. Clinically, pain from the lumbar muscles is sometimes referred to the lower extremities. Two kinds of neurotracers [1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethyl-indocarbocyanine perchlorate (DiI) and fluoro-gold (FG)] were used in the present double-labelling study. DiI crystals were placed in the left lower back muscle, and FG was applied to the medial side of the knee. Bilateral DRGs from L1 through L6 were immunoreacted with calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antibodies and observed under a fluorescence microscope. DRG neurons double-labelled with DiI and FG were recognized only in the ipsilateral DRGs from levels L1 to L6. Approximately 1% of DRG neurons innervating the low back muscles had other axons to the medial side of the knee. In double-labelled neurons, the ratio of CGRP-immunoreactive DRG neurons was 60%. This finding provides a possible neuroanatomical explanation for referred knee pain from the lower back since CGRP is a marker of sensory neurons typically involved with pain perception. However, these neurons are rare, and mechanisms of referred pain may be explained by the convergence–projection hypothesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alles A, Dom RM (1985) Peripheral sensory nerve fibers that dichotomize to supply the brachium and the pericardium in the rat: a possible morphological explanation for referred cardiac pain? Brain Res 342:382–385
Ashton IK, Ashton BA, Gibson SJ, Polak JM, Jaffray DC, Eisenstein SM (1992) Morphological basis for back pain: the demonstration of nerve fibers and neuropeptides in the lumbar facet joint capsule but not in ligamentum flavum. J Orthop Res 10:72–78
Ashton IK, Roberts S, Jaffray DC, Polak M, Eisenstein SM (1994) Neuropeptides in the human intervertebral disc. J Orthop Res 12:186–192
Beaman DN, Graziano GP, Glover RA, Wojtys EM, Chang V (1993) Substance P innervation of lumbar spine facet joints. Spine 18:1044–1049
Fairbank JC, Park WM, McCall IW, O’Brien JP (1981) Apophyseal injection of local anesthetic as a diagnostic aid in primary low-back pain syndromes. Spine 6:598–605
Feinstein B, Langton JNK, Jameson RM, et al (1954) Experiments pain referred from deep somatic tissues. J Bone Joint Surg 36-A:981–997
Graven-Nielsen T, Babenko V, Svensson P, Jensen TS (1998) Experimentally induced muscle pain induces hypoalgesia in heterotopic deep tissues, but not in homotopic deep tissues. Brain Res 787:203–210
Graven-Nielsen T, Babenko V, Svensson P, Arendt-Nielsen L (1998) Experimentally induced muscle pain induces hypoalgesia in heterotopic deep tissues, but not in homotopic deep tissues. Brain Res 787:203–210
Greene EC, (1963) Anatomy of the rat. Hafner, New York
Habler HJ, Janig W, Koltzenburg M (1988) Dichotomizing unmyelinated afferents supplying pelvic viscera and perineum are rare in the sacral segments of the cat. Neurosci Lett 94:119–124
Hökfelt T (1991) Neuropeptides in perspective: the last ten years. Neuron 7:867–879
Jensen K, Tuxen C, Pedersen-Bjergaard U, Jansen I, Edvinsson L, Olesen J (1990) Pain and tenderness in human temporal muscle induced by bradykinin and 5-hydroxytryptamine. Peptides 11:1127–1132
Kellgren JH (1938) Observation on referred pain arising from muscle. Clin Sci 3:175–190
Kellgren JH (1939) On the distribution of pain arising from deep somatic structures with charts of segmental pain areas. Clin Sci 4:35–46
Laursen RJ, Graven-Nielsen T, Jensen TS, Arendt-Nilsen L (1997) Quantification of local and referred pain in humans induced by intramuscular electrical stimulation. Eur J Pain 1:105–113
Lee Y, Takami K, Kawai Y, Girgis S, Hillyard CJ, MacIntyre I, Emson PC, Tohyama M (1985) Distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the rat peripheral nervous system with reference to its coexistence with substance P. Neurosci 15:1227–1237
Lippitt AB (1984) The facet joint and its role in spine pain: Management with facet joint injections. Spine 9:746–750
McCarthy PW, Lawson SN (1990) Cell type and conduction velocity of rat primary sensory neurons with calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity. Neuroscience 34:623–632
Mooney V, Robertson J (1976) The facet syndrome. Clin Orthop Res 149–156
Ohtori S, Takahashi K, Chiba T, Yamagata M, Sameda H, Moriya H (2000) Substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactive sensory DRG neurons innervating the lumbar facet joints in rats. Auton Neurosci Basic Clin 86:13–17
Ohtori S, Takahashi K, Chiba T, Yamagata M, Sameda H, Moriya H (2001) Sensory innervation of the dorsal portion of the lumbar intervertebral discs in rats. Spine 26:946–950
Ohtori S, Takahashi K, Chiba T, Yamagata M, Sameda H, Moriya H (2000) Sensory innervation of the cervical facet joints in rats. Spine 26:147–150
Ohtori S, Takahashi K, Chiba T, Yamagata M, Sameda H, Moriya H (2000) Substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactive sensory DRG neurons innervating the lumbar intervertebral discs in rats. Ann Anat 184:235-240
Pierau FK, Taylor DC, Abel W, Friedrich B (1982) Dichotomizing peripheral fibers revealed by intracellular recording from rat sensory neurones. Neurosci Lett 31:123–128
Pierau FK, Fellmer G, Taylor DCM (1984) Somato-visceral convergence in cat dorsal root ganglion neurones demonstrated by double-labelling with fluorescent tracers. Brain Res 321:63–70
Ruch TC (1946) Visceral sensation and referred pain. In: Fulton JF (ed) Howell’s textbook of physiology, 15th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 385–401
Rucker HK, Holloway JA (1982) Viscerosomatic convergence onto spinothalamic tract neurons in the cat. Brain Res 243:155–157
Sameda H, Takahashi Y, Takahashi K, Chiba T, Ohtori S, Moriya H (2001) Primary sensory neurons with dichotomizing axons projecting to the facet joint and the sciatic nerve in rats. Spine 26:1105–1109
Schmid H, Taylor DCM, Pierau FK (1983) Tracing of sensory neurones and spinal motoneurones of the pigeon by injection of fluorescent dyes into peripheral nerves. Cell Tissue Res 232:9–19
Selzer M, Spencer WA (1969) Convergence of visceral and cutaneous afferent pathways in the lumbar spinal cord. Brain Res 14:331–348
Simone DA, Marchettini P, Caputi G, Ochoa JL (1994) Identification of muscle afferents subserving sensation of deep pain in humans. J Neurophysiol 72:883–889
Sinclair DC, Weddell G, Feindel WH (1948) Referred pain and associated phenomena. Brain 71:184–211
Suseki K, Takahashi Y, Takahashi K, Chiba T, Tanaka K, Morinaga T, Nakamura S, Moriya H (1997) Innervation of the lumbar facet joints. Spine 22:477–485
Taylor DCM, Pierau,FK (1982) Double fluorescence labelling supports electrophysiological evidence for dichotomizing peripheral sensory nerve fibers in rats. Neurosci Lett 33:1–6
Taylor DCM, Pierau,FK, Schmid H (1983) The use of fluorescent tracers in the peripheral sensory nervous system. J Neurosci Methods 8:211–224
Wiberg G (1949) Back pain in relation to the nerve supply of the intervertebral disc. Acta Orthop Scand 19:211–221
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohtori, S., Takahashi, K., Chiba, T. et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactive neurons with dichotomizing axons projecting to the lumbar muscle and knee in rats. Eur Spine J 12, 576–580 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-003-0573-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-003-0573-4