Abstract
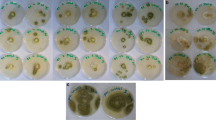
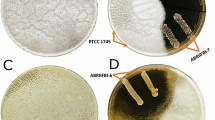
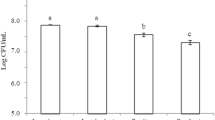
In the present study, after molecular identification of dominant lactic acid bacteria (LAB) isolated from traditional fermented foods, antifungal activity of the isolates was investigated against aflatoxigenic Aspergillus spp. Based on screening results, among the isolated LAB, Pediococus lolii had the highest inhibitory effect against Aspergillus flavus (70.32%) and Aspergillus niger (98.8%). Furthermore, antifungal activity of P. lolii stationary phase cell-free supernatant (CFS) was significantly (P < 0.05) higher than the effect of the logarithmic phase CFS. MIC values of P. lolii CFSs from logarithmic and stationary phases against A. flavus were 2 and 1%, and against A. niger were 4 and 1% (v/v), respectively. The media containing ≥4% of CFSs from logarithmic and stationary phases (v/v) had also totally inhibited from germination of A. flavus and A. niger spores. Safety assessment during 28-day oral administration of P. lolii revealed that there was no noticeable difference in specific growth rate, activity, behavior, hair luster, clinical chemistry, and hematological indices in treated rats in comparison to control group.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annan NT, Poll L, Sefa-Dedeh S, Plahar WA, Jakobsen M (2003) Volatile compounds produced by Lactobacillus fermentum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida krusei in single starter culture fermentations of Ghanaian maize dough. J Appl Microbiol 94:462–474
Avis TJ, Belanger RR (2001) Specificity and mode of action of the antifungal fatty acid cis-9-heptadecenoic acid produced by Pseudozyma flocculosa. Appl Environ Microb 67:956–960
Belguesmia Y, Choiset Y, Rabesona H, Baudy-Floc'h M, Le Blay G, Haertle T, Chobert JM (2013) Antifungal properties of durancins isolated from Enterococcus durans A5-11 and of its synthetic fragments. Lett Appl Microbiol 56:237–244
Bian X, Muhammad Z, Evivie SE, Luo WXM, Huo GC (2016) Screening of antifungal potentials of Lactobacillus helveticus KLDS 1.8701 against spoilage microorganism and their effects on physicochemical properties and shelf life of fermented soybean milk during preservation. Food Control 66:183–189
Calvo AM, Gardner HW, Keller NP (2001) Genetic connection between fatty acid metabolism and sporulation in Aspergillus nidulans. J Biol Chem 276:25766–25774
Dalie DKD, Deschamps AM, Atanasova-Penichon V, Richard-Forget F (2010) Potential of Pediococcus pentosaceus (L006) isolated from maize leaf to suppress fumonisin-producing fungal growth. J Food Protect 73:1129–1137
Damodharan K, Lee YS, Palaniyandi SA, Yang SH, Suh JW (2015) Preliminary probiotic and technological characterization of Pediococcus pentosaceus strain KID7 and in vivo assessment of its cholesterol-lowering activity. Front Microbiol 6. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00768
Delavenne E, Cliquet S, Trunet C, Barbier G, Mounier J, Blay GL (2015) Characterization of the antifungal activity of Lactobacillus harbinensis K.V9.3.1Np and Lactobaciilus rhamnosus K.C8.3.11 in yogurt. Food Microbiol 45:10–17
Digaitiene A, Hansen AS, Juodeikiene G, Eidukonyte D, Josephsen J (2012) Lactic acid bacteria isolated from rye sourdoughs produce bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances active against Bacillus subtilis and fungi. J Appl Microbiol 112:732–742
Dong AR, Ho TT, Lo R, Bansal N, Turner MS (2017) A genetic diversity study of antifungal Lactobacillus plantarum isolates. Food Control 72:83–89
Gerbaldo GA, Barberis C, Pascual L, Dalcero A, Barberis L (2012) Antifungal activity of two Lactobacillus strains with potential probiotic properties. FEMS Microbiol Lett 332:27–33
Gulahmadov SG, Abdullaeva NF, Guseinova NF, Kuliev AA, Ivanova IV, Dalgalarondo M, Chobert JM, Haertlee T (2009) Isolation and characterization of bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances from lactic acid bacteria isolated from Azerbaijan cheeses. Appl Biochem Microbiol 45:266–271
Jones ML, Martoni CJ, Tamber S, Parent M, Prakash S (2012) Evaluation of safety and tolerance of microencapsulated Lactobacillus reuteri NCIMB 30242 in a yogurt formulation: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Food Chem Toxicol 50:2216–2223
Ju H, Youn H, Kwon J, Hong W, Song C (2016) Protective efficacy of Pediococcus lolii against Influenza a virus. Conference proceeding. Paper presented at International Scientific Conference on Probiotics and Prebiotics 2016, Budapest. In Kysucke Nove Mesto, by PAMIDA International. ISBN-978-80-89589-14-2
Kabak B, Brandon EFA, Var I, Blokland M, Sips AJAM (2009) Effects of probiotic bacteria on the bioaccessibility of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A using an in vitro digestion model under fed conditions. Journal of Environmental Science and Health 44:472–480
Kato N, Suyama S, Shirokane M, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Tsukagoshi T (2002) Novel α-glucosidase from Aspergillus nidulans with strong transglycosylation activity. Appl Environ Microb 68:1250–1256
Khanafari A, Soudi H, Miraboulfathi M (2007) Biocontrol of Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin B1 production corn. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 4:163–168
Kohl J, Postma J, Nicot P, Ruocco M, Blum B (2011) Stepwise screening of microorganisms for commercial use in biological control of plant-pathogenic fungi and bacteria. Biol Control 57:1–12
Lara-Villoslada F, Sierra S, Martín R, Delgado S, Rodríguez JM, Olivares M, Xaus J (2007) Safety assessment of two probiotic strains, Lactobacillus coryniformis CECT5711 and Lactobacillus gasseri CECT5714. J Appl Microbiol 103:175–184
Lavermicocca P, Valerio F, Evidente A, Lazzaroni S, Corsetti A, Gobbetti M (2000) Purification and characterization of novel antifungal compounds from the sourdough Lactobacillus plantarum strain 21B. Appl Environ Microb 66:4084–4090
Lee JY, Nguyenb DT, Parka YS, Hwanga KY, Choa YS, Kanga KD, Yoonb J, Yuc J, Yeed SD, Ahne YH, Leeb G, Seonga SL, Paikd MJ (2012) Organic acid profiling analysis in culture media of lactic acid bacteria by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom Lett 3:74–77
Li H, Liu L, Zhang S, Cui W, Lv J (2012) Identification of antifungal compounds produced by Lactobacillus casei AST18. Curr Microbiol 65:156–161
Magnusson J, Schnurer J (2001) Lactobacillus coryniformis subsp. coryniformis strain Si3 produces a broad-spectrum proteinaceous antifungal. Appl Environ Microb 67:1–5
Muhialdin BJ, Hassan Z, Bakar FA, Saari N (2016) Identification of antifungal peptides produced by Lactobacillus plantarum IS10 grown in the MRS broth. Food Control 59:27–30
Özcelik S, Kuley E, Özogul F (2016) Formation of lactic, acetic, succinic, propionic, formic and butyric acid by lactic acid bacteria. LWT - Food Sci Technol 73:536–542
Quiles JM, Saladino F, Manes J, Fernandez-Franzon M, Meca G (2016) Occurrence of mycotoxins in refrigerated pizza dough and risk assessment of exposure for the Spanish population. Food Chem Toxicol 94:19–24
Rather IA, Seo BJ, Kumar VJR, Choi UH, Choi KH, Lim J, Park YH (2014) Biopreservative potential of Lactobacillus plantarum YML007 and efficacy as a replacement for chemical preservatives in animal feed. Food Sci Biotechnol 23:195–200
Roy U, Batish VK, Grover S, Neelakantan S (1996) Production of antifungal substance by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis CHD-28.3. Int J Food Microbiol 32:27–34
Russo P, Arena MP, Fiocco D, Capozzi V, Drider D, Spano G (2016) Lactobacillus plantarum with broad antifungal activity: a promising approach to increase safety and shelf-life of cereal-based products. Int J Food Microbiol In Press, Corrected Proof
Sadeghi A, Raeisi M, Ebrahimi M, Sadeghi B (2016) Antifungal activity of Pediococcus pentosaceus isolated from whole barley sourdough. J Food Qual Hazards Control 3:30–36
Sangmanee P, Hongpattarakere T (2014) Inhibitory of multiple antifungal components produced by Lactobacillus plantarum K35 on growth, aflatoxin production and ultrastructure alterations of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Food Control 40:224–233
Sellamani M, Kalagatur NK, Siddaiah C, Mudili V, Krishna K, Natarajan G, Rao Putcha VL (2016) Antifungal and zearalenone inhibitory activity of Pediococcus pentosaceus isolated from dairy products on Fusarium graminearum. Front Microbiol 7: doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00890
Sjogren J, Magnusson J, Broberg A, Schnürer J, Kenne L (2003) Antifungal 3-hydroxy fatty acids from Lactobacillus plantarum MiLAB 14. Appl Environ Microb 69:7554–7557
Strom K, Sjogren J, Broberg A, Schnurer J (2002) Lactobacillus plantarum MiLAB 393 produces the antifungal cyclic dipeptides cyclo(L-Phe-L-Pro) and cyclo(L-Phe-trans-4-OH-L-Pro) and 3-phenyllactic acid. Appl Environ microb 68:4322–4327
Sulemankhil I, Parent M, Jones ML, Feng Z, Labbe A, Prakash S (2012) In vitro and in vivo characterization and strain safety of Lactobacillus reuteri NCIMB 30253 for probiotic applications. Can J Microbiol 58:776–787
Szabo NJ, DolanLC BGA, Shibano T, Sato S, Suzuki H, Uesugi T, Yamahira S, Toba M, Ueno H (2011) Safety evaluation of Lactobacillus pentosus strain b240. Food Chem Toxicol 49:251–258
Tsai CC, Liu TH, Chen MH, Tsen HY (2004) Toxicity evaluation for an Enterococcus faecium strain TM39 in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem Toxicol 42:1601–1609
Tsai CC, Leu SF, Huang QR, Chou LC, Huang CC (2014) Safety evaluation of multiple strains of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus pentosaceus in Wistar rats based on the Ames test and a 28-day feeding study. Scientific World J 2014: Article ID 928652, doi:10.1155/2014/928652
Varsha KK, Nishant G, Sneha SM, Shilpa G, Devendra L, Priya S, Nampoothiri KM (2016) Antifungal, anticancer and aminopeptidase inhibitory potential of a Phenazine compound produced by Lactococcus BSN307. Indian J Microbiol 56:411–416
Wang H, Yan Y, Wang J, Zhang H, Qi W (2012) Production and characterization of antifungal compounds produced by Lactobacillus plantarum IMAU10014. PLoS One 7:e29452
Yang EJ, Chang HC (2010) Purification of a new antifungal compound produced by Lactobacillus plantarum AF1 isolated from kimchi. Int J Food Microbiol 139:56–63
Yang E, Fan L, Yueming J, Doucette C, Fillmore S (2012) Antimicrobial activity of bacteriocin-producing lactic acid bacteria isolated from cheeses and yogurts. AMB Express 2:48–60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Funding
This work is part of a PhD thesis supported by Gorgan University of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources and the authors thank the financial support.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimi, M., Khomeiri, M., Masoudi-Nejad, A. et al. Inhibitory effects of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional fermented foods against aflatoxigenic Aspergillus spp.. Comp Clin Pathol 26, 1083–1092 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2489-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2489-0