Abstract
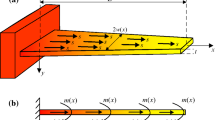
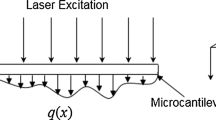
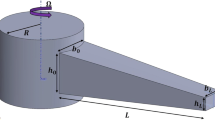
In this work, we present the design and analysis of microcantilever beams based on arrow shape. Effect of rectangular step length and width as well as free end width of beam have been investigated on various characteristics of proposed microcantilever beams. The proposed microcantilever beams were fabricated from silicon dioxide material using wet bulk micromachining in 25 wt.% TMAH at 75 °C. Vibration analysis of the microcantilever beams was carried out using a laser vibrometer. A FEM software, ANSYS, was used primarily for numerical analysis of resonance frequency, and to examine the effect of rectangular step length as well as free end width of microcantilever beam on its resonance frequency. Furthermore, ANSYS was employed to determine the maximum deflection, torsional end rotation and quality factor of proposed microcantilever beams. Additionally, effects of bottom gap and rectangular step length on quality factor of proposed microcantilever beams at lower and higher bottom gaps have also been investigated. The fundamental transverse bending mode frequency for a proposed microcantilever beam comprising rectangular step length of 50 μm and free end width 0 μm is approximately 48% higher than that of the conventional rectangular profile microcantilever beam of width 40 μm. Furthermore, maximum deflection and torsional end rotation obtained for a proposed microcantilever beam having rectangular step length 190 μm and beam free end width 40 μm are found as 680% and 800%, respectively, higher than that of the rectangular beam of length 200 μm and thickness 40 μm.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arntz Y, Seelig JD, Lang HP, Zhang J, Hunziker P, Ramseyer JP, Meyer E, Hegner M, Gerber C (2003) Label-free protein assay based on a nanomechanical cantilever array. Nanotechnology 14(1):86–90
Ashok A, Aparna G, Pal P, Pandey AK (2018a) An analysis of stepped trapezoidal-shaped microcantilever beams for MEMS-based devices. J Micromech Microeng 28:075009 (11 pp)
Ashok A, Manoj Kumar P, Singh SS, Raju P, Pal P, Pandey AK (2018b) Achieving wideband micromechanical system using coupled non-uniform beams array. Sens Actuators A Phys 273:12–18
Ashok A, Sahu NK, Pal P, Pandey AK (2018c) Arrow shaped microcantilever beams for enhancing mass sensitivity. In: 2018 IEEE sensors, New Delhi, India, 28–31 Oct 2018, pp 1–4
Cowburn RP, Moulin AM, Welland WE (1997) High-sensitivity measurement of magnetic fields using microcantilevers. Appl Phys Lett 71(15):2202–2204
Cox R, Zhang J, Josse F, Heinrich S, Dufour I, Beardslee LA, Brand O (2011) Damping and mass sensitivity of laterally vibrating resonant microcantilevers in viscous liquid media. In: Proceedings of the 2011 Joint Conference of the IEEE International Frequency Control and the European Frequency and Time Forum (FCS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–5 May 2011, pp 1–6
Datskos PG, Oden PI, Thundat T, Wachter EA, Warmack RJ, Hunter RS (1996) Remote infrared radiation detection using piezoresistive microcantilevers. Appl Phys Lett 69(20):2986–2988
Decuzz P, Granaldi A, Pascazio G (2007) Dynamic response of microcantilever-based sensors in a fluidic chamber. J Appl Phys 101(2):024303 (6 pp)
Dong Y, Gao W, Zhou Q, Zheng Y, You Z (2010) Characterization of the gas sensors based on Polymer coated resonant microcantilevers for the detection of volatile organic compounds. Anal Chim Acta 671:85–91
Finot E, Lesniewska E, Goudonnet JP, Thundat T (2001) Measuring magnetic susceptibilities of nanogram quantities of materials using microcantilevers. Ultramicroscopy 86(1–2):175–180
Hawari HF, Wahab Y, Azmi MT, Shakaff Md AY, Hashim U, Johari S (2014) Design and analysis of various microcantilever shapes for MEMS based sensing. J Phys Conf Ser 495:012045 (9 pp)
Jin D, Li X, Liu J, Zuo G, Wang Y, Liu M, Yu H (2006) High-mode resonant piezoresistive cantilever sensors for tens-femtogram resoluble mass sensing in air. J Micromech Microeng 16(5):1017–1023
Kooser A, Gunter RL, Delinger WD, Porter TL, Eastman MP (2004) Gas sensing using embedded piezoresistive microcantilever sensors. Sens Actuators B Chem 99:474–479
Lavrik NV, Sepaniak MJ, Datskos PG (2004) Cantilever transducers as a platform for chemical and biological sensors. Rev Sci Instrum 75:2229–2253
Lim YC, Kouzani AZ, Duan W, Kaynak A (2010) Effects of design parameters on sensitivity of microcantilever biosensors. In: IEEE/ICME international conference on complex medical engineering, Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 13–15 July 2010, pp 177–181
Liu Y, Wang H, Qin H, Zhao W, Wang P (2017) Geometry and profile modification of microcantilevers for sensitivity enhancement in sensing applications. Sens Mater 29(6):689–698
Nordstrom M, Keller S, Lillemose M, Johansson A, Dohn S, Haefliger D, Blagoi G, Havsteen-Jakobsen M, Boisen A (2008) SU-8 cantilevers for bio/chemical sensing; fabrication, characterisation and development of novel read-out methods. Sensors 8(3):1595–1612
Nugaeva N, Gfeller KY, Backman N, Lang HP, Duggelin M, Hegner M (2005) Micromechanical cantilever array sensors for selective fungal immobilization and fast growth detection. Biosens Bioelectron 21(6):849–856
Pandey AK, Pratap R (2007) Effect of flexural modes on squeeze film damping in MEMS cantilever resonators. J Micromech Microeng 17(12):2475–2484
Pandey AK, Pratap R, Chau FS (2007) Influence of boundary conditions on the dynamic characteristics of squeeze films in MEMS device. J Microelectromech Syst 16(4):893–903
Parsediya DK, Singh J, Kankar PK (2014) Simulation and analysis of highly sensitive MEMS cantilever designs for in vivo label free biosensing. Procedia Technol 14:85–92
Parsediya DK, Singh J, Kankar PK (2015) Variable width based stepped MEMS cantilevers for micro or pico level biosensing and effective switching. J Mech Sci Technol 29(11):4823–4832
Purohit B, Jain PC, Pandey AK (2016) Modal analysis of monolithic and jointed type cantilever beams with non-uniform section. Exp Mech 56(6):1083–1094
Shih WY, Li XP, Gu HM, Shih WH, Aksay IA (2001) Simultaneous liquid viscosity and density determination with piezoelectric unimorph cantilevers. J Appl Phys 89:1497–1505
Singh SS, Pal P, Pandey AK (2016) Mass sensitivity of non-uniform microcantilever beams. J Vib Acoust 138(6):064502 (7 pp)
Spletzer M, Raman A, Sumali H, Sullivan JP (2008) Highly sensitive mass detection and identification using vibration localization in coupled microcantilever arrays. Appl Phys Lett 92(11):114102 (3 pp)
Subramanian S, Gupta N (2009) Improved V-shaped microcantilever width profile for sensing applications. J Phys D Appl Phys 42(18):185501 (6 pp)
Suri CR, Kaur J, Gandhi S, Shekhawat GS (2008) Label-free ultra-sensitive detection of atrazine based on nanomechanics. Nanotechnology 19(23):235502–235600
Vidic A, Then D, Ziegler Ch (2003) A new cantilever system for gas and liquid sensing. Ultramicroscopy 97:407–416
Wachter EA, Thundat T, Oden PI (1996) Remote optical detection using micro-cantilevers. Rev Sci Instrum 67(10):3434–3439
Wang DF, Li X, Yang X, Ikehara T, Maeda R (2015) Enhancing amplitude changes by mode localization in trio cantilevers with mass perturbation. J Micromech Microeng 25(9):095017 (8 pp)
Xia X, Li X (2008) Resonance-mode effect on microcantilever mass-sensing performance in air. Rev Sci Instrum 79(7):074301 (8 pp)
Yue M, Lin H, Dedrick DE, Satyanaayana S, Majumda A, Bedekar AS, Jenkins JW, Sundaram S (2004) A 2-D microcantilever array for multiplexed biomolecular analysis. J Microelectromech Syst 13(2):290–299
Zahid Ansari M, Cho C (2008) A study on increasing sensitivity of rectangular microcantilevers used in biosensors. Sensors 8(11):7530–7544
Zahid Ansari M, Cho C (2009) Deflection, frequency and stress characteristics of rectangular, triangular and step profile microcantilevers for biosensors. Sensors 9(8):6046–6057
Zahid Ansari M, Cho C, Kim J, Bang B (2009) Comparison between deflection and vibration characteristics of rectangular and trapezoidal profile microcantilevers. Sensors 9:2706–2718
Acknowledgements
This research work is supported in part by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India (22(0696)/15/EMR-II).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashok, A., Nighot, R.P., Sahu, N.K. et al. Design and analysis of microcantilever beams based on arrow shape. Microsyst Technol 25, 4379–4390 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04555-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04555-4