Abstract
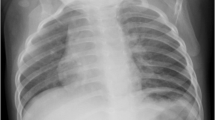
We provided anesthetic management during a tracheotomy procedure for a child who demonstrated labored respiration during inspiration because of severe glottic stenosis and bilateral vocal cord paralysis caused by tracheal intubation. A 4-year-old boy developed acute respiratory depression associated with influenza pneumonia and had been under respiratory management with mechanical ventilation with tracheal intubation for 3 days. Following extubation, an upper-airway obstruction immediately appeared. The symptoms later worsened because of development of a common cold, and the patient underwent an emergency tracheotomy. For anesthetic management, we used a combination of ketamine with low-concentration sevoflurane inhalation. The tracheotomy was performed safely without respiratory complications by employing manual-assisted ventilation, while spontaneous breathing was preserved by use of a face mask.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meneghini L, Zadra N, Metrangolo S, Narne S, Giusti F. Post-intubation subglottal stenosis in children: risk factors and prevention in pediatric intensive care. Minerva Anesthesiol. 2000;66:467–71.
Yang LK. Tracheal stenosis after a brief intubation. Anesth Analg. 1995;80:625–7.
Motoyama EK. The shape of the pediatric larynx: cylindrical or funnel shaped? Anesth Analg. 2009;108:1379–81.
George M, Jaquet Y, Ikonomidis C, Monnier P. Management of severe pediatric subglottic stenosis with glottic involvement. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;139:411–7.
Bordet F, Allaouchiche B, Lansiaux S, Combet S, Pouyau A, Taylor P, Bonnard C, Chassard D. Risk factors for airway complications during general anaesthesia in paediatric patients. Paediatr Anaesth. 2002;12:762–9.
Greene CA, Gillette PC, Fyfe DA. Frequency of respiratory compromise after ketamine sedation for cardiac catheterization in patients less than 21 years of age. Am J Cardiol. 1991;68:1116–7.
Green WB. The ventilatory effects of sevoflurane. Anesth Analg. 1995;81(suppl 6):S23–6.
Kawabata T, Nitta K, Sugahara K. A case of difficult intubation with congenital subglottic stenosis. Clin Pediatr Anesth. 2006;12:108–13.
American Heart Association. Part 12. Pediatric advanced life support. Circulation. 2005;94:80–7.
James I. Cuffed tubes in children: 3-year experience in a single institution. Paediatr Anaesth. 2001;11:259–63.
Weiss M, Dullenkopf A, Gysin C, Dillier CM, Gerber AC. Shortcomings of cuffed paediatric tracheal tubes. Br J Anaesth. 2004;92:78–88.
Ho AM, Aun CS, Karmakar MK. The margin of safety associated with the use of cuffed paediatric tracheal tubes. Anesthesia. 2002;57:173–5.
Fine GF, Borland LM. The future of the cuffed endotracheal tube. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004;14:38–42.
Dullenkopf A, Gerber AC, Weiss M. Fit and seal characteristics of a new pediatric tracheal tube with high volume-low pressure polyurethane cuff. Acta Anesthesiol Scand. 2005;49:232–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, M., Okutani, R., Nakada, K. et al. Anesthetic management during tracheotomy in a child with respiratory distress caused by severe intubation-induced glottic stenosis. J Anesth 26, 449–452 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-012-1324-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-012-1324-7