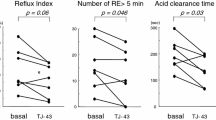
Background:
The role of reflux of duodenal contents in gastroesophageal reflux in Japanese patients, which may be different from that in Western patients, was studied. Methods: Intraesophageal pH and the bilirubin concentration were monitored, using the Bilitec 2000, in 43 patients with reflux symptoms and 10 normal volunteers. The percentage of the time that spectrophotometric absorbence was 0.15 or more and pH was less than 4.0 was defined as the holding times (HTs) of bilirubin and acid, respectively. Severity of esophagitis was classified using the Savary-Miller (S-M) classification. Results: Esophagitis was present in 37 patients; 5, 10, 13, and 9 patients had S-M grades 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Both HTs in the volunteers were less than 5%. Bilirubin HT was more than 5% in 3 of the 6 patients without esophagitis, but the acid HT was less than 5% in these 6 patients. Acid HT was less than 5% in 4, 2, 2, and 2 patients with S-M grades 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Bilirubin HT was less than 5% in 1 patient with S-M grade 2 esophagitis. Bilirubin HT in patients with S-M grades 3 and 4 esophagitis (50.9 ± 5.8%) was higher than that in grades 1 and 2 (14.9 ± 2.9%) (P < 0.0001), but this was not so for acid HT. In 32 patients, bilirubin HT exceeded acid HT. Bilirubin HT did not correlate with acid HT. Conclusions: Duodenogastroesophageal reflux occurred independently of and exceeded acid reflux. The amount of duodenogastroesophageal reflux correlated with the severity of esophagitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: October 22, 2001 / Accepted: January 25, 2002
Reprint requests to: H. Osugi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osugi, H., Higashino, M., Kaseno, S. et al. Ambulatory intraesophageal bilirubin monitoring in Japanese patients with gastroesophageal reflux. J Gastroenterol 37, 697–702 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350200114
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350200114