Abstract:
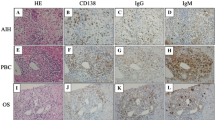
Autoimmune cholangitis (AIC) has been proposed as a distinct disease entity from primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), without antimitochondrial antibody (AMA) and anti-M2 antibody but with a high titer of antinuclear antibody (ANA) in the serum. However, negativity for AMA and anti-M2 antibody was determined by different methods in different studies. We hypothesized that anti-M2 antibody negativity in AIC resulted from methodological differences, including selection of the immunoglobulin subclass of the autoantibody. Twenty-three patients compatible with AIC whose serum tested negative for AMA and positive for ANA (≧1 : 80) were compared with 71 AMA-positive PBC patients. Laboratory findings, histology, and the pattern of anti-M2 antibody assessed by immunoblotting were compared. Alkaline phosphatase, total bilirubin, total cholesterol, and IgM values were lower in patients with AIC (P < 0.05, 0.01, respectively). Anti-smooth muscle antibody was detected more frequently in patients with AIC (P < 0.01). However, anti-M2 antibody was detected using immunoblotting not only in PBC but also in AIC cases. IgA class alone, IgM class alone, or both IgA and IgM classes of anti-M2 antibody were detected in 13%, 17%, and 22% of AIC patients, respectively, whereas they were not detected in PBC patients (P < 0.05, P < 0.01, P < 0.01). IgG class anti-M2 was detected in all patients with PBC, whereas it was detected in 48% of patients with AIC (P < 0.01). Histological evaluation showed that the early stages of disease were found more frequently in AIC (78%) than in PBC patients (39%) (P < 0.01). Anti-M2 antibody was detected by immunoblotting in all AIC patients. Hence, AIC is not a distinct disease from PBC. For diagnosing AIC and/or PBC, anti-M2 antibody should be examined by the immunoblotting assay to detect not only IgG but also IgA and IgM subclasses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: December 17, 1998 / Accepted: May 28, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakajima, M., Shimizu, H., Miyazaki, A. et al. Detection of IgA, IgM, and IgG subclasses of anti-M2 antibody by immunoblotting in autoimmune cholangitis: Is autoimmune cholangitis an early stage of primary biliary cirrhosis?. J Gastroenterol 34, 607–612 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350050380
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350050380