Abstract:
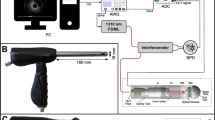
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a new imaging technology which can perform high-resolution, cross-sectional imaging of the internal microstructure of biological tissues. OCT is analogous to ultrasound, except that it measures the intensity of back-reflected infrared light rather than sound waves. OCT performs two- and three-dimensional imaging of tissue microstructure in situ and in real time. It can achieve image resolutions approaching the cellular level over approximately the same imaging depths as a conventional biopsy. In this article we examine the feasibility of OCT for high-resolution imaging of gastrointestinal malignancies with ex-vivo imaging of normal and pathologic microstructures. Tissue, both normal and neoplastic, was obtained from patients undergoing surgical resection after an initial diagnosis of a gastrointestinal malignancy. The tissue samples were imaged prior to fixation using a laboratory OCT system. The OCT system consists of a fiber optic-based Michelson interferometer, a commercially available amplified superluminscent light source, and a computer for data acquisition. The images were subsequently compared with histological cross-sections corresponding to the imaged areas. The stratified squamous epithelium of the normal esophagus was clearly visible in the OCT images and contrasted to the disorganized and non-uniform nature of the mucosal layers of Barrett's esophagus and squamous carcinoma. The columnar epithelial morphology as well as other mucosal structures in normal colon were distinctly visible using OCT. In contrast, disorganization of the normal mucosal layers and ulcerative lesions were identified in tissues from ulcerative colitis and adenocarcinoma of the colon. The ability of OCT to image tissue microstructure at high resolutions makes it a potentially powerful technology for minimally invasive assessment of the gastrointestinal tract and the evaluation of early neoplastic changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: March 25, 1999 / Accepted: July 23, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pitris, C., Jesser, C., Boppart, S. et al. Feasibility of optical coherence tomography for high-resolution imaging of human gastrointestinal tract malignancies. J Gastroenterol 35, 87–92 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350050019
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350050019