Abstract
Background
In acute pancreatitis (AP), disorders of the coagulation-fibrinolysis system are closely related to the severity of the AP and to organ dysfunctions. We previously reported that plasma tissue factor (TF) levels were elevated in patients with AP, particularly in cases of alcoholic AP with pancreatic necrosis. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) is a key regulator of the extrinsic coagulation pathway, but plasma TFPI levels in AP have not yet been determined.
Methods
Plasma TFPI concentrations were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 44 patients with AP on admission. The relationships between AP severity, pancreatic necrosis, organ dysfunction, infection, and prognosis were analyzed.
Results
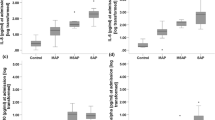
Plasma TFPI levels were increased in AP patients compared with healthy volunteers. Plasma TFPI levels in severe AP were greater than those in mild AP. Plasma TFPI levels significantly correlated with Ranson score, APACHE II score, and Japanese severity score. Plasma TFPI levels in patients with pancreatic necrosis were greater than those in patients without pancreatic necrosis. Plasma TFPI levels in patients with organ dysfunction were greater than those in patients without organ dysfunction. In patients with pancreatic necrosis, the TF/TFPI ratios in non-survivors were lower than those in survivors. Moreover, the mortality rates in patients with TF/TFPI ratios ≥ 2.0 were lower than those in patients with TF/TFPI ratios < 2.0.
Conclusions
Plasma TFPI levels were significantly increased in patients with AP, and the elevation was markedly related to the severity, pancreatic necrosis and organ dysfunctions. The imbalance of TF and TFPI may influence the disease state and thereby the prognosis in AP.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lasson A, Ohlsson K. Disseminated intravascular coagulation and antiprotease activity in acute human pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1996;126:35–9.
Tenner S, Sica G, Hughes M, Noordhoek E, Feng S, Zinner M, et al. Relationship of necrosis to organ failure in severe acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:899–903.
Foitzik T, Eibl G, Hotz B, Hotz H, Kahrau S, Kasten C, et al. Persistent multiple organ microcirculatory disorders in severe acute pancreatitis: experimental findings and clinical implications. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47:130–8.
Agarwal N, Pitchumoni CS. Acute pancreatitis: a multisystem disease. Gastroenterologist. 1993;1:115–28.
Spicer EK, Horton R, Bloem L, Bach R, Williams KR, Guha A, et al. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for human tissue factor: primary structure of the protein and cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987;84:5148–52.
ten Cate H, Bauer KA, Levi M, Edgington TS, Sublett RD, Barzegar S, et al. The activation of factor X and prothrombin by recombinant factor VIIa in vivo is mediated by tissue factor. J Clin Invest. 1993;92:1207–12.
Ruf W, Edgington TS. Structural biology of tissue factor, the initiator of thrombogenesis in vivo. Faseb J. 1994;8:385–90.
Shimura M, Wada H, Wakita Y, Nakase T, Hiyoyama K, Nagaya S, et al. Plasma tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor levels in patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Am J Hematol. 1996;52:165–70.
Gando S, Nanzaki S, Sasaki S, Aoi K, Kemmotsu O. Activation of the extrinsic coagulation pathway in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 1998;26:2005–9.
Leatham EW, Bath PM, Tooze JA, Camm AJ. Increased monocyte tissue factor expression in coronary disease. Br Heart J. 1995;73:10–3.
Sawa H, Ueda T, Takeyama Y, Yasuda T, Matsumura N, Nakajima T, et al. Elevation of plasma tissue factor levels in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:575–81.
Broze GJ Jr, Warren LA, Novotny WF, Higuchi DA, Girard JJ, Miletich JP. The lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor that inhibits the factor VII-tissue factor complex also inhibits factor Xa: insight into its possible mechanism of action. Blood. 1988;71:335–43.
Girard TJ, Warren LA, Novotny WF, Likert KM, Brown SG, Miletich JP, et al. Functional significance of the Kunitz-type inhibitory domains of lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor. Nature. 1989;338:518–20.
Novotny WF, Girard TJ, Miletich JP, Broze GJ Jr. Platelets secrete a coagulation inhibitor functionally and antigenically similar to the lipoprotein associated coagulation inhibitor. Blood. 1988;72:2020–5.
Yamamuro M, Wada H, Kumeda K, Inoue A, Tsuji I, Nakasaki T, et al. Changes in plasma tissue factor pathway inhibitor levels during the clinical course of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1998;9:491–7.
Gando S, Kameue T, Morimoto Y, Matsuda N, Hayakawa M, Kemmotsu O. Tissue factor production not balanced by tissue factor pathway inhibitor in sepsis promotes poor prognosis. Crit Care Med. 2002;30:1729–34.
Kamikura Y, Wada H, Yamada A, Shimura M, Hiyoyama K, Shiku H, et al. Increased tissue factor pathway inhibitor in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Hematol. 1997;55:183–7.
Soejima H, Ogawa H, Yasue H, Kaikita K, Nishiyama K, Misumi K, et al. Heightened tissue factor associated with tissue factor pathway inhibitor and prognosis in patients with unstable angina. Circulation. 1999;99:2908–13.
Golino P, Ravera A, Ragni M, Cirillo P, Piro O, Chiariello M. Involvement of tissue factor pathway inhibitor in the coronary circulation of patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2003;108:2864–9.
Abraham E, Reinhart K, Svoboda P, Seibert A, Olthoff D, Dal Nogare A, et al. Assessment of the safety of recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor in patients with severe sepsis: a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blind, dose escalation study. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:2081–9.
Carraway MS, Welty-Wolf KE, Miller DL, Ortel TL, Idell S, Ghio AJ, et al. Blockade of tissue factor: treatment for organ injury in established sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:1200–9.
LaRosa SP, Opal SM. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor and antithrombin trial results. Crit Care Clin. 2005;21:433–48.
Ogawa M, Hirota M, Hayakawa T, Matsuno S, Watanabe S, Atomi Y, et al. Development and use of a new staging system for severe acute pancreatitis based on a nationwide survey in Japan. Pancreas. 2002;25:325–30.
Ueda T, Takeyama Y, Yasuda T, Kamei K, Satoi S, Sawa H, et al. Utility of new Japanese severity score and indication for special therapies in acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol 2009; Mar 25 (Epub ahead of print).
Ranson JH, Rifkind KM, Roses DF, Fink SD, Eng K, Spencer FC. Prognostic signs and the role of operative management in acute pancreatitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1974;139:69–81.
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985;13:818–29.
Balthazar EJ, Robinson DL, Megibow AJ, Ranson JH. Acute pancreatitis: value of CT in establishing prognosis. Radiology. 1990;174:331–6.
Novotny WF, Palmier M, Wun TC, Broze GJ Jr, Miletich JP. Purification and properties of heparin-releasable lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor. Blood. 1991;78:394–400.
Warn-Cramer BJ, Rao LV, Maki SL, Rapaport SI. Modifications of extrinsic pathway inhibitor (EPI) and factor Xa that affect their ability to interact and to inhibit factor VIIa/tissue factor: evidence for a two-step model of inhibition. Thromb Haemost. 1988;60:453–6.
Novotny WF, Girard TJ, Miletich JP, Broze GJ Jr. Purification and characterization of the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:18832–7.
Lindahl AK, Jacobsen PB, Sandset PM, Abildgaard U. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor with high anticoagulant activity is increased in post-heparin plasma and in plasma from cancer patients. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1991;2:713–21.
Nordfang O, Bjorn SE, Valentin S, Nielsen LS, Wildgoose P, Beck TC, et al. The C-terminus of tissue factor pathway inhibitor is essential to its anticoagulant activity. Biochemistry. 1991;30:10371–6.
Hansen JB, Huseby KR, Huseby NE, Ezban M, Nordoy A. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor in complex with low density lipoprotein isolated from human plasma does not possess anticoagulant function in tissue factor-induced coagulation in vitro. Thromb Res. 1997;85:413–25.
Bendz B, Andersen TO, Sandset PM. A new sensitive chromogenic substrate assay of tissue factor pathway inhibitor type 1. Thromb Res. 2000;97:463–72.
Dahm AE, Andersen TO, Rosendaal F, Sandset PM. A novel anticoagulant activity assay of tissue factor pathway inhibitor I (TFPI). 2005;3:651–8.
Novotny WF, Brown SG, Miletich JP, Rader DJ, Broze GJ Jr. Plasma antigen levels of the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor in patient samples. Blood. 1991;78:387–93.
Broze GJ Jr. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor and the current concept of blood coagulation. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1995;6:S7–13.
Lupu C, Lupu F, Dennehy U, Kakkar VV, Scully MF. Thrombin induces the redistribution and acute release of tissue factor pathway inhibitor from specific granules within human endothelial cells in culture. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995;15:2055–62.
Lupu C, Kruithof EK, Kakkar VV, Lupu F. Acute release of tissue factor pathway inhibitor after in vivo thrombin generation in baboons. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82:1652–8.
Drew AF, Davenport P, Apostolopoulos J, Tipping PG. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor expression in atherosclerosis. Lab Invest. 1997;77:291–8.
Tang H, Ivanciu L, Popescu N, Peer G, Hack E, Lupu C, et al. Sepsis-induced coagulation in the baboon lung is associated with decreased tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Am J Pathol. 2007;171:1066–77.
Foitzik T, Eibl G, Hotz HG, Faulhaber J, Kirchengast M, Buhr HJ. Endothelin receptor blockade in severe acute pancreatitis leads to systemic enhancement of microcirculation, stabilization of capillary permeability, and improved survival rates. Surgery. 2000;128:399–407.
Badimon JJ, Lettino M, Toschi V, Fuster V, Berrozpe M, Chesebro JH, et al. Local inhibition of tissue factor reduces the thrombogenicity of disrupted human atherosclerotic plaques: effects of tissue factor pathway inhibitor on plaque thrombogenicity under flow conditions. Circulation. 1999;99:1780–7.
Westrick RJ, Bodary PF, Xu Z, Shen YC, Broze GJ, Eitzman DT. Deficiency of tissue factor pathway inhibitor promotes atherosclerosis and thrombosis in mice. Circulation. 2001;103:3044–6.
Acknowledgments
This investigation was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan, and from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasuda, T., Ueda, T., Kamei, K. et al. Plasma tissue factor pathway inhibitor levels in patients with acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol 44, 1071–1079 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0096-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0096-9