Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to investigate the correlation between precore (PC)/basal core promoter (BCP) mutations and the viral loads or activity of hepatitis in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
Methods
HBV genotypes, PC mutations, BCP mutations, HBV DNA levels, and serological markers of HBV were analyzed in all the patients with chronic HBV infection seen in Fujita Health University Hospital from June 2004 to November 2008 (n = 215).
Results
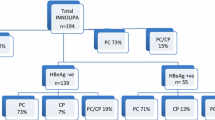
HBV genotype was C in 169 patients, B in 16, A in 3, F in 1, and unclassifiable in 5. Among the patients with genotype C, the prevalence of PC wild type was significantly lower in hepatitis B envelope antigen (HBeAg)(−) patients than in HBeAg(+) patients (9.5% versus 49.0%, P < 0.0001). Among HBeAg(−) patients, the patients with PC wild type had significantly lower serum viral loads and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels compared with those with PC mutant (P < 0.001). Among HBeAg(−) patients, the patients with genotype B had lower serum viral loads compared with those with genotype C (3.6 ± 0.9 versus 4.6 ± 1.6, P < 0.05), and the prevalence of BCP wild type was significantly higher in those with genotype B than in those with genotype C (58.3% versus 10.8%, P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Among HBeAg(−) patients with genotype C, the patients with PC wild type had significantly lower viral loads and ALT levels than those with PC mutant. This suggests that the patients with PC wild type may have better prognosis than those with PC mutant among HBeAg(−) patients with genotype C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lavanchy D. Hepatitis B virus epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging prevention and control measures. J Viral Hepat. 2004;11:97–107.
Custer B, Sullivan SD, Hazlet TK, Iloeje U, Veenstra DL, Kowdley KV. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004;38:S158–68.
van Zonneveld M, Honkoop P, Hansen BE, Niesters HGM, Murad SD, de Man RA, et al. Long-term follow-up of alpha-interferon treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2004;39:804–10.
Ganem D, Prince AM. Hepatitis B virus infection-natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1118–29.
Lin CL, Liao LY, Liu CJ, Chen PJ, Lai MY, Kao JH, et al. Hepatitis B genotypes and precore/basal core promoter mutants in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol. 2002;37:283–7.
Schiefke I, Klecker C, Maier M, Oesen U, Etzrodt G, Tannapfel A, et al. Sequential combination therapy of HBe antigen-negative/virus-DNA-positive chronic hepatitis B with famciclovir or lamivudine and interferon-alpha-2a. Liver Int. 2004;24:98–104.
Carman WF, Jacyna MR, Hadziyannis S, Karayiannis P, McGarvey MJ, Makris A, et al. Mutation preventing formation of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet. 1989;2:588–91.
Okamoto H, Tsuda F, Akahane Y, Sugai Y, Yoshiba M, Moriyama K, et al. Hepatitis B virus with mutations in the core promoter for an e antigen-negative phenotype in carriers with antibody to e antigen. J Virol. 1994;68:8102–10.
Takahashi K, Aoyama K, Ohno N, Iwata K, Akahane Y, Baba K, et al. The precore/core promoter mutant (T1762A1764) of hepatitis B virus: clinical significance and an easy method for detection. J Gen Virol. 1995;76:3159–64.
Liang TJ, Hasegawa K, Rimon N, Wands JR, Ben-Porath E. A hepatitis B virus mutant associated with an epidemic of fulminant hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1705–9.
Aritomi T, Yatsuhashi H, Fujino T, Yamasaki K, Inoue O, Koga M, et al. Association of mutations in the core promoter and precore region of hepatitis virus with fulminant and severe acute hepatitis in Japan. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;13:1125–32.
Chen CH, Lee CM, Lu SN, Changchien CS, Eng HL, Huang CM, et al. Clinical significance of hepatitis B virus (HBV) genotypes and precore and core promoter mutations affecting HBV e antigen expression in Taiwan. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:6000–6.
Okamoto H, Tsuda F, Sakugawa H, Sastrosoewignjo RI, Imai M, Miyakawa Y, et al. Typing hepatitis B virus by homology in nucleotide sequence: comparison of surface antigen subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1988;69:2575–83.
Stuyver LS, De Gendt S, Van Geyt C, Zoulim F, Fried M, Schinazi RF, et al. A new genotype of hepatitis B virus: complete genome a phylogenetic relatedness. J Gen Virol. 2000;81:67–74.
Orito E, Ichida T, Sakugawa H, Sata M, Horiike N, Hino K, et al. Geographic distribution of hepatitis B virus (HBV) genotype in patients with chronic HBV infection in Japan. Hepatology. 2001;34:590–4.
Chu CJ, Keeffe EB, Han SH, Perrillo RP, Min AD, Soldevila-Pico C, et al. Hepatitis B virus genotypes in the United States: results of a nationwide study. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:444–51.
Kao JH, Chen PJ, Lai MY, Chen DS. Hepatitis B genotypes correlate with clinical outcomes in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:554–9.
Lindh M, Hannoun C, Dhillon AP, Norkrans G, Horal P. Core promotor mutations and genotypes in relation to viral replication and liver damage in East Asian hepatitis B virus carriers. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:775–82.
Orito E, Mizokami M, Sakugawa H, Michitaka K, Ishikawa K, Ichida T, et al. A case–control study for clinical and molecular biological differences between hepatitis B viruses of genotype B and C. Hepatology. 2001;33:218–23.
Ding X, Mizokami K, Yao G, Xu B, Orito E, Ueda R, et al. Hepatitis B virus genotype distribution among chronic hepatitis B virus carriers in Shanghai, China. Intervirology. 2001;44:43–7.
Lindh M, Andersson A. Gusdal. Genotypes, nt 1858 variants, and geographic origin of hepatitis B virus—large-scale analysis using a new genotyping method. J Infect Dis. 1997;175:1285–93.
Lindh M, Gustavson K, Mardberg G, Norkrans AP, Dhillon PH. Mutation of nucleotide 1762 in the core promoter region during hepatitis B e seroconversion and its relation to liver damage in hepatitis B e antigen carriers. J Med Virol. 1998;55:185–90.
Kessler HH, Pierer K, Dragon E, Lackner H, Santner B, Stünzner D, et al. Evaluation of a new assay for HBV DNA quantitation in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Clin Diagn Virol. 1998;9:37–43.
Misawa N, Matsumoto A, Tanaka E, Rokuhara A, Yoshizawa K, Umemura T, et al. Patients with and without loss of hepatitis B virus DNA after hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion have different virological characteristics. J Med Virol. 2006;78:68–73.
Yoo BC, Park JW, Kim HJ, Lee DH, Cha YJ, Park SM. Precore and core promoter mutations of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B in Korea. J Hepatol. 2003;38:98–103.
Chu CJ, Keeffe EB, Han SH, Perrillo RP, Min AD, Soldevila-Pico C, et al. U.S. HBV Epidemiology Study Group. Prevalence of HBV precore/core promoter variants in the United States. Hepatology. 2003;38:619–28.
Lindh M, Horal P, Dhillon AP, Norkrans G. Hepatitis B virus DNA levels, precore mutations, genotypes and histological activity in chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat. 2000;7:258–67.
Sugauchi F, Kumada H, Sakugawa H, Komatsu M, Niitsuma H, Watanabe H, et al. Two subtypes of genotype B (Ba and Bj) of hepatitis B virus in Japan. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:1222–8.
Sugauchi F, Orito E, Ichida T, Kato H, Sakugawa H, Kakumu S, et al. Epidemiologic and virologic characteristics of hepatitis B virus genotype B having the recombination with genotype C. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:925–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawabe, N., Hashimoto, S., Harata, M. et al. The loss of HBeAg without precore mutation results in lower HBV DNA levels and ALT levels in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Gastroenterol 44, 751–756 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0061-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0061-7