Abstract.
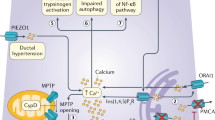
Efforts to unravel the events in the evolution of tissue damage in acute pancreatitis have shown a number of inflammatory mediators to be involved. The pathways of damage are similar, whatever the etiology of pancreatitis, with three phases of progression: local acinar injury, systemic response, and generalized sepsis. The proinflammatory response is countered by an anti-inflammatory response, and an imbalance between these two systems leads to localized tissue destruction and distant organ damage. Cytokines lie at the heart of the problem and are involved in all aspects of the cascade leading to systemic inflammatory response syndrome and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. This review discusses the present knowledge about the role of various mediators in this process, their genetic control, and the effects of their modulation. The major proinflammatory mediators are tumor necrosis factor, interleukins 1, 6, and 8, platelet activation factor, and the chemokines. The major anti-inflammatory factors include interleukin 10, and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. Emerging knowledge of new mediators as well as future strategy of damage control is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: February 19, 2002 / Accepted: March 8, 2002
Offprint requests to: A.N. Kingsnorth
About this article
Cite this article
Makhija, R., Kingsnorth, A. Cytokine storm in acute pancreatitis. J Hep Bil Pancr Surg 9, 401–410 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005340200049
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005340200049