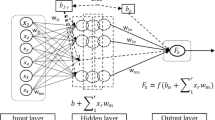
Abstract
The acoustic streaming is a key drawback and eliminates the performance of a jet pump-based thermoacoustic-Stirling heat engine. The present study deals with a new hybrid optimization approach to reduce the acoustic streaming energy. The proposed work is an integration of Taguchi method (TM), adaptive neural fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), and teaching–learning-based optimization (TLBO). The Taguchi method plays three important roles. The first role is to layout the number of experiments. The second role is to identify the most appropriate parameters for ANFIS structure regarding the number of input membership functions (MFs), types of input MFs, optimal learning method, and types of output MFs. In order to determine the optimum parameters for the ANFIS structure, the root-mean-squared error, a performance criterion, is minimized by using the TM. The final role of TM is to optimize the controllable parameters of the TLBO. Subsequently, modeling between geometric parameters and acoustic streaming is established by the built ANFIS structure. Finally, the TLBO is adopted by optimizing the design parameters. The outcomes of study revealed that the acoustic streaming is relatively reduced. Based on Wilcoxon signed-rank test and Friedman test, it proves that the effectiveness of the proposed hybrid approach is better to other evolutionary algorithms. The current approach is an efficient optimizer for complex optimization problems.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swift GW (1988) Thermoacoustic engines. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 84(4):1145–1180
Kaushik SC, Kumarm S (2000) Finite time thermodynamic analysis of endoreversible Stirling heat engine with regenerative losses. Energy 25(10):989–1003
Backhaus S, Swift GW (1999) A thermoacoustic Stirling heat engine. Nature 399(6734):335
Penelet G, Gusev V, Lotton P, Bruneau M (2006) Nontrivial influence of acoustic streaming on the efficiency of annular thermoacoustic prime movers. Phys Lett A 351(4–5):268–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2005.11.011
Biwa T, Tashiro Y, Ishigaki M, Ueda Y, Yazaki T (2007) Measurements of acoustic streaming in a looped-tube thermoacoustic engine with a jet pump. J Appl Phys 101(6):064914. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2713360
Hu JY, Luo EC, Dai W, Zhang LM (2017) Parameter sensitivity analysis of duplex Stirling coolers. Appl Energy 190:1039–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.01.022
Sun DM, Wang K, Zhang XJ, Guo YN, Xu Y, Qiu LM (2013) A traveling-wave thermoacoustic electric generator with a variable electric R-C load. Appl Energy 106:377–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.01.051
Wang K, Dubey S, Choo FH, Duan F (2016) A transient one-dimensional numerical model for kinetic Stirling engine. Appl Energy 183:775–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.09.024
Wu Z, Yu G, Zhang L, Dai W, Luo E (2014) Development of a 3 kW double-acting thermoacoustic Stirling electric generator. Appl Energy 136:866–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.04.105
Yu G, Wang X, Dai W, Luo E (2013) Study on energy conversion characteristics of a high frequency standing-wave thermoacoustic heat engine. Appl Energy 111:1147–1151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.09.050
Zhu S, Yu G, Jongmin O, Xu T, Wu Z, Dai W, Luo E (2018) Modeling and experimental investigation of a free-piston Stirling engine-based micro-combined heat and power system. Appl Energy 226:522–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.05.122
Feng Y, Tang K, Jin T, Zhang K, Yang R (2018) Performance comparison of jet pumps with round and sharp edge of small opening in oscillatory flow. Appl Therm Eng 139:562–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.05.023
Tang K, Feng Y, Jin T, Jin S, Li M, Yang R (2017) Effect of Gedeon streaming on thermal efficiency of a travelling-wave thermoacoustic engine. Appl Therm Eng 115:1089–1100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.01.054
Tijani MEH, Spoelstra S (2013) A hot air driven thermoacoustic-Stirling engine. Appl Therm Eng 61(2):866–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2013.04.052
Chen M, Ju YL (2015) Effect of different working gases on the performance of a small thermoacoustic Stirling engine. Int J Refrig 51:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2014.12.006
Ahmadi MH, Amin Nabakhteh M, Ahmadi M-A, Pourfayaz F, Bidi M (2017) Investigation and optimization of performance of nano-scale Stirling refrigerator using working fluid as Maxwell-Boltzmann gases. Physica A 483:337–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2017.04.079
Qian S, Yu J, Yan G (2017) A review of regenerative heat exchange methods for various cooling technologies. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 69:535–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.180
Wang K, Sanders SR, Dubey S, Choo FH, Duan F (2016) Stirling cycle engines for recovering low and moderate temperature heat: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 62:89–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.04.031
Yang P, Fang M, Liu YW (2014) Optimization of a Phase Adjuster in a Thermo-acoustic Stirling Engine Using Response Surface Methodology. Energy Procedia 61:1772–1775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.12.209
Tijani MEH, Spoelstra S (2011) A high performance thermoacoustic engine. J Appl Phys 110(9):093519. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3658872
<backhaus2000-[8].pdf>
Pillai MA, Deenadayalan E (2014) A review of acoustic energy harvesting. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing 15(5):949–965. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0422-x
Chaitou H, Nika P (2012) Exergetic optimization of a thermoacoustic engine using the particle swarm optimization method. Energy Convers Manag 55:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2011.10.024
Babaei H, Siddiqui K (2008) Design and optimization of thermoacoustic devices. Energy Convers Manag 49(12):3585–3598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2008.07.002
Tang K, Feng Y, Jin SH, Jin T, Li M (2015) Performance comparison of jet pumps with rectangular and circular tapered channels for a loop-structured traveling-wave thermoacoustic engine. Appl Energy 148:305–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.03.092
Liu Y-W, Yang P (2014) Influence of inner diameter and position of phase adjuster on the performance of the thermo-acoustic Stirling engine. Appl Therm Eng 73(1):1141–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.09.002
Yang P, Liu Y-W, Zhong G-Y (2016) Prediction and parametric analysis of acoustic streaming in a thermoacoustic Stirling heat engine with a jet pump using response surface methodology. Appl Therm Eng 103:1004–1013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.04.157
Yang P, Chen H, Y-w Liu (2017) Application of response surface methodology and desirability approach to investigate and optimize the jet pump in a thermoacoustic Stirling heat engine. Appl Therm Eng 127:1005–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.08.077
Rout SK, Choudhury BK, Sahoo RK, Sarangi SK (2014) Multi-objective parametric optimization of Inertance type pulse tube refrigerator using response surface methodology and non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm. Cryogenics 62:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cryogenics.2014.03.019
Rao RV, Waghmare GG (2015) Multi-objective design optimization of a plate-fin heat sink using a teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm. Appl Therm Eng 76:521–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.11.052
Rao RV, Savsani VJ, Vakharia DP (2011) Teaching–learning-based optimization: a novel method for constrained mechanical design optimization problems. Comput Aided Des 43(3):303–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2010.12.015
Dao T-P, Huang S-C (2016) Design and analysis of a compliant micro-positioning platform with embedded strain gauges and viscoelastic damper. Microsyst Technol 23(2):441–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3048-3
Dao T-P, Huang S-C (2017) Design and multi-objective optimization for a broad self-amplified 2-DOF monolithic mechanism. Sādhanā 42(9):1527–1542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-017-0714-9
Dao T-P, Huang S-C (2017) Optimization of a two degrees of freedom compliant mechanism using Taguchi method-based grey relational analysis. Microsyst Technol 23(10):4815–4830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3292-1
Dao T-P, Huang S-C, Thang PT (2017) Hybrid Taguchi-cuckoo search algorithm for optimization of a compliant focus positioning platform. Appl Soft Comput 57:526–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.04.038
Galankashi MR, Fallahiarezoudar E, Moazzami A, Helmi SA, Rohani JM, Yusof NM (2016) An efficient integrated simulation–Taguchi approach for sales rate evaluation of a petrol station. Neural Comput Appl 29(4):1073–1085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2491-5
Bayca SU, Kisik H (2018) Optimization of leaching parameters of aluminum hydroxide extraction from bauxite waste using the Taguchi method. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy 37(1):196–202. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12654
Brahmeswara Rao D, Venkata Rao K, Gopala Krishna A (2018) A hybrid approach to multi response optimization of micro milling process parameters using Taguchi method based graph theory and matrix approach (GTMA) and utility concept. Measurement 120:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.02.005
Celik N, Pusat G, Turgut E (2018) Application of Taguchi method and grey relational analysis on a turbulated heat exchanger. Int J Therm Sci 124:85–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2017.10.007
Hong Y-Y, Beltran AA, Paglinawan AC (2018) A robust design of maximum power point tracking using Taguchi method for stand-alone PV system. Appl Energy 211:50–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.11.041
Kotcioglu I, Khalaji MN, Cansiz A (2018) Heat transfer analysis of a rectangular channel having tubular router in different winglet configurations with Taguchi method. Appl Therm Eng 132:637–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.12.120
Chen M-Y (2013) A hybrid ANFIS model for business failure prediction utilizing particle swarm optimization and subtractive clustering. Inf Sci 220:180–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2011.09.013
Pousinho HMI, Mendes VMF, Catalão JPS (2011) A hybrid PSO–ANFIS approach for short-term wind power prediction in Portugal. Energy Convers Manag 52(1):397–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2010.07.015
Dadgarnia A, Heidari AA (2010) A Fast Systematic Approach for Microstrip Antenna Design and Optimization using ANFIS and GA. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications 24(16):2207–2221. https://doi.org/10.1163/156939310793699037
De Jesús Rubio J, Lughofer E, Meda-Campaña JA, Páramo LA, Novoa JF, Pacheco J (2018) Neural network updating via argument Kalman filter for modeling of Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy models. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 35(2):2585–2596. https://doi.org/10.3233/jifs-18425
Soares Alessandra M, Fernandes Bruno JT, Bastos-Filho Carmelo JA (2018) Pyramidal neural networks with evolved variable receptive fields. Neural Comput Appl 29(12):1443–1453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2656-2
De Jesús Rubio J (2018) Error convergence analysis of the SUFIN and CSUFIN. Appl Soft Comput 72:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.04.003
Liu Y, Wang Z, Yuan Y, Alsaadi FE (2018) Partial-nodes-based state estimation for complex networks with unbounded distributed delays. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems 29(8):3906–3912. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2017.2740400
De Jesús Rubio J (2009) SOFMLS: online self-organizing fuzzy modified least-squares network. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 17(6):1296–1309. https://doi.org/10.1109/tfuzz.2009.2029569
Li X, Li H, Sun B, Wang F (2018) Assessing information security risk for an evolving smart city based on fuzzy and grey FMEA. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 34(4):2491–2501. https://doi.org/10.3233/jifs-172097
Abdulshahed AM, Longstaff AP, Fletcher S (2015) The application of ANFIS prediction models for thermal error compensation on CNC machine tools. Appl Soft Comput 27:158–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.11.012
Abdulshahed AM, Longstaff AP, Fletcher S, Myers A (2015) Thermal error modelling of machine tools based on ANFIS with fuzzy c-means clustering using a thermal imaging camera. Appl Math Model 39(7):1837–1852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2014.10.016
Adio SA, Mehrabi M, Sharifpur M, Meyer JP (2016) Experimental investigation and model development for effective viscosity of MgO–ethylene glycol nanofluids by using dimensional analysis, FCM-ANFIS and GA-PNN techniques. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 72:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2016.01.005
Hosoz M, Ertunc HM, Karabektas M, Ergen G (2013) ANFIS modelling of the performance and emissions of a diesel engine using diesel fuel and biodiesel blends. Appl Therm Eng 60(1–2):24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2013.06.040
Huang C-N, Yu C-C (2016) Integration of Taguchi’s method and multiple-input, multiple-output ANFIS inverse model for the optimal design of a water-cooled condenser. Appl Therm Eng 98:605–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.11.112
Mohammadi K, Shamshirband S, Petković D, Yee PL, Mansor Z (2016) Using ANFIS for selection of more relevant parameters to predict dew point temperature. Appl Therm Eng 96:311–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.11.081
Shamshirband S, Malvandi A, Karimipour A, Goodarzi M, Afrand M, Petković D, Dahari M, Mahmoodian N (2015) Performance investigation of micro- and nano-sized particle erosion in a 90° elbow using an ANFIS model. Powder Technol 284:336–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2015.06.073
Sun W, Hu P, Lei F, Zhu N, Jiang Z (2015) Case study of performance evaluation of ground source heat pump system based on ANN and ANFIS models. Appl Therm Eng 87:586–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.04.082
Yaïci W, Entchev E (2016) Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System modelling for performance prediction of solar thermal energy system. Renewable Energy 86:302–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.08.028
Aouf A, Boussaid L, Sakly A (2018) TLBO-Based Adaptive Neurofuzzy Controller for Mobile Robot Navigation in a Strange Environment. Comput Intell Neurosci 2018:3145436. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3145436
Aydilek İB (2018) A hybrid firefly and particle swarm optimization algorithm for computationally expensive numerical problems. Appl Soft Comput 66:232–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.02.025
Rahbari O, Omar N, Firouz Y, Rosen MA, Goutam S, Van Den Bossche P, Van Mierlo J (2018) A novel state of charge and capacity estimation technique for electric vehicles connected to a smart grid based on inverse theory and a metaheuristic algorithm. Energy 155:1047–1058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.05.079
Yilmaz B, Aras E, Nacar S, Kankal M (2018) Estimating suspended sediment load with multivariate adaptive regression spline, teaching-learning based optimization, and artificial bee colony models. The Science of the total environment 639:826–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.153
García S, Herrera F (2008) An extension on statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets for all pairwise comparisons. Journal of Machine Learning Research 9:2677–2694
Demšar J (2006) Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. Journal of Machine learning research 7:1–30
García S, Molina D, Lozano M, Herrera F (2009) A study on the use of non-parametric tests for analyzing the evolutionary algorithms’ behaviour: a case study on the CEC’2005 special session on real parameter optimization. J Heuristics 15(6):617–644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10732-008-9080-4
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under Grant Number 107.01-2016.20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Chau, N., Dao, TP. & Dang, V.A. An efficient hybrid approach of improved adaptive neural fuzzy inference system and teaching learning-based optimization for design optimization of a jet pump-based thermoacoustic-Stirling heat engine. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 7259–7273 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04249-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04249-y