Abstract
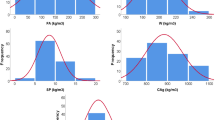
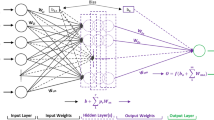
There are species of carbon steel in the industry suffering from corrosion phenomena under seawater environment. In this paper, for purposes of the prediction of 3C steel corrosion rate, the proposed methodology here adopts a hybrid model based on neural network (NN) and imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA). Additionally, to validate the suggested method, we have managed to apply a procedure, namely leaving-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV). Thus, the model in this paper is abbreviated as NN–ICA_LOOCV. In the case study, the model is implemented on 46 experimental samples. This dataset is included within five parameters, namely temperature, dissolved oxygen, salinity, PH value and oxidation–reduction potential as inputs and corrosion rate(s) as an output parameter. The dataset was divided into two parts: one for training and the other for testing with 42 and 4 data number, respectively. For an evaluation purpose, the performance of NN–ICA_LOOCV is compared with other models on the basis of indicators such as the coefficient of determination (R 2), root-mean-square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE). The model was successfully tested, yielding a prediction of corrosion rate with a RMSE of around 0.01, MAE of 0.011 and a correlation factor of 0.99 to the test data. The results demonstrate that the carefully designed hybrid model further succeeded to denote lower modeling error and higher accuracy. Hence, this model is an applicable and reliable offer to engineers in order to online and safe prediction of corrosion rate in 3C steel under seawater environment.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen Y, Cai C, Liu X, Pei J, Zhu X, Xiao T (2009) Corrosion rate prediction of 3C steel under different seawater environment by using support vector regression. Corros Sci 51(2):349–355
Fontana MG (2005) Corrosion engineering. Tata McGraw-Hill Education, New Delhi, Noida
Kim Y, Jeong G, Sohn H (1999) Mathematical modeling on the corrosion of unprotected structure due to stray current resulting from cathodic protection system. Met Mater 5(1):93–99
Jones DA (1992) Principles and prevention of corrosion. Macmillan, New York
Mazario E, Venegas R, Herrasti P, Alonso M, Recio F (2015) Pitting corrosion and stress corrosion cracking study in high strength steels in alkaline media. J Solid State Electrochem 19:1–5. doi:10.1007/s10008-015-2956-y
Chiu C-K, Lin Y-F (2014) Multi-objective decision-making supporting system of maintenance strategies for deteriorating reinforced concrete buildings. Autom Constr 39:15–31
Zhang Z, Tian N, Zhang L, Wu L (2015) Inhibition of the corrosion of carbon steel in HCl solution by methionine and its derivatives. Corros Sci 98:438–449
Paik JK, Thayamballi AK, Park YI, Hwang JS (2004) A time-dependent corrosion wastage model for seawater ballast tank structures of ships. Corros Sci 46(2):471–486
Melchers R (2006) Modelling immersion corrosion of structural steels in natural fresh and brackish waters. Corros Sci 48(12):4174–4201
Jingjun L, Yuzhen L, Xiaoyu L (2008) Numerical simulation for carbon steel flow-induced corrosion in high-velocity flow seawater. Anti-Corros Method Mater 55(2):66–72
Y-x Liu, X-c Gao, G-y Zhang, H-h Guo (2008) BP neural networks used in prediction and analyses of 3C steel corrosion function. Mater Sci Eng Hangzhou 26(1):94
Liu X, Tang X, Wang J (2009) Correlation between seawater environmental factors and marine corrosion rate using artificial neural network analysis. J Chin Soc Corros Prot 25(1):11–14
Kong D-Y, Song S-Z (1998) Analysis of corrosion data for carbon steel and low-alloy steels in seawater by artificial neural network. J Chin Soc Corro Prot 18:289–296
Paul S (2011) Model to study the effect of composition of seawater on the corrosion rate of mild steel and stainless steel. J Mater Eng Perform 20(3):325–334
Kharchenko U, Beleneva I, Kovalchuk YL, Karpov V (2011) Estimation of aggressiveness of seawater corrosion using indicators of microbiological activity of fouling communities formed on metals. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 47(7):907–910
Jaśniok T, Jaśniok M (2015) Influence of rapid changes of moisture content in concrete and temperature on corrosion rate of reinforcing steel. Procedia Eng 108:316–323
Ling W, Dong-Mei F (2009) A novel approach using SVR ensembles for minor prototypes prediction of seawater corrosion rate. In: Computer science and engineering, 2009. WCSE’09. Second international workshop on, 2009. IEEE, pp 39–43
You W, Liu Y (2008) Predicting the corrosion rates of steels in sea water using artificial neural network. In: Natural computation, 2008. ICNC’08. Fourth international conference on, 2008. IEEE, pp 101–105
Kamrunnahar M, Urquidi-Macdonald M (2010) Prediction of corrosion behavior using neural network as a data mining tool. Corros Sci 52(3):669–677
Hodhod O, Ahmed H (2014) Modeling the corrosion initiation time of slag concrete using the artificial neural network. HBRC J 10(3):231–234
Atashpaz-Gargari E, Lucas C (2007) Imperialist competitive algorithm: an algorithm for optimization inspired by imperialistic competition. In: Evolutionary computation, 2007. CEC 2007. IEEE Congress on, 2007. IEEE, pp 4661–4667
Ahmadi MA, Ebadi M, Shokrollahi A, Majidi SMJ (2013) Evolving artificial neural network and imperialist competitive algorithm for prediction oil flow rate of the reservoir. Appl Soft Comput 13(2):1085–1098
Rodger JA (2014) A fuzzy nearest neighbor neural network statistical model for predicting demand for natural gas and energy cost savings in public buildings. Expert Syst Appl 41(4):1813–1829
Ahmadi MA, Shadizadeh SR, Goudarzi A (2012) Combining artificial neural network and unified particle swarm optimization for oil flow rate prediction: case study. Neural Comput Appl 23:1–8. doi:10.1007/s00521-012-0955-9
Ahmadi MA, Shadizadeh SR, Ebadi M, Khalighi Sheshdeh R (2012) Prediction of condensate-to-gas ratio by using stochastic particle swarm optimization and neural network. Neural Comput Appl 23:1–9. doi:10.1007/s00521-012-0986-2
Ong BT, Sugiura K, Zettsu K (2015) Dynamically pre-trained deep recurrent neural networks using environmental monitoring data for predicting PM2. 5. Neural Comput Appl 26:1–14. doi:10.1007/s00521-015-1955-3
Sadowski L, Nikoo M (2014) Corrosion current density prediction in reinforced concrete by imperialist competitive algorithm. Neural Comput Appl 25(7–8):1627–1638
Mohebi J, Zadeh Shirazi A, Tabatabaeec H (2015) Adaptive-neuro fuzzy inference system (Anfis) model for prediction of blast-induced ground vibration. Sci Int 27(3):2079–2091
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
See Table 4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zadeh Shirazi, A., Mohammadi, Z. A hybrid intelligent model combining ANN and imperialist competitive algorithm for prediction of corrosion rate in 3C steel under seawater environment. Neural Comput & Applic 28, 3455–3464 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2251-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2251-6