Summary
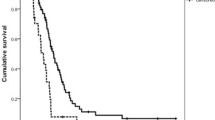
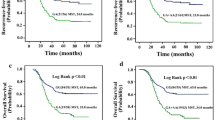
To investigate the impacts of gene variations on survival outcomes of advanced gastric cancer (AGC) patients treated with 5‑fluorouracil (5-FU)-based chemotherapy, we analyzed the associations of 2 indels of the TS gene rs34743033 (double or triple tandem repeats of a 28 bp sequence in 5′-UTR, denoted as 2R or 3R allele) and rs16430 (a 6 bp variation at 1494 bp in 3′-UTR, denoted as ins6 or del6 allele) and 2 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of ABCB1gene rs2032582 in exon 21 and rs1045642 in exon 26, with clinical outcomes after 5‑FU treatment. Generally, indels rs34743033 and rs16430 were genotyped by PCR and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis assay and SNPs rs2032582 and rs1045642 were genotyped by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) assay in 110 Chinese AGC patients post-chemotherapy. Cox regression analysis was used to analyze the risk factors affecting patient survival. As a result, rs34743033, rs1045642 and rs2032582 were shown to be significantly associated with overall survival (P < 0.05), and associations between the four polymorphisms with disease-free survival were also observed (P < 0.05). Moreover, we found that genotypes rs34743033 3R/2R, rs16430 ins6/del6, rs1045642 CC or CT, and rs2032582 GG were beneficial predictors of clinical treatment outcome in AGC patients, suggesting some clinical implications in chemotherapy of a Chinese population.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roder DM. The epidemiology of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2005;5:5–11.
Roukos DH. Extended (D2) lymph node dissection for gastric cancer: Do patients benefit? Ann Surg Oncol. 2000;7:7253–5.
Dickson JL, Cunningham D. Systemic treatment of gastric cancer. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;16:255–63.
Sadighi S, Mohagheghi MA, Montazeri A, Sadighi Z. Quality of life in patients with advanced gastric cancer: a randomized trial comparing docetaxel, cisplatin, 5‑FU (TCF) with epirubicin, cisplatin, 5‑FU (ECF). BMC Cancer. 2006;6:6274.
Li QF, Yao RY, Liu KW, et al. Genetic polymorphism of GSTP1: prediction of clinical outcome to oxaliplatin/5-FU-based chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25:846–52.
Carreras CW, Santi DV. The catalytic mechanism and structure of thymidylate synthase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:64721–62.
Graziani S, Bernauer J, Skouloubris S, et al. Catalytic mechanism and structure of viral flavin-dependent thymidylate synthase ThyX. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:24048–57.
Toriumi F, Kubota T, Saikawa Y, et al. Thymidylate synthetase (TS) genotype and TS/dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase mRNA level as an indicator in determining chemosensitivity to 5‑fluorouracil in advanced gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2004;24:2455–63.
Lin D, Li H, Tan W, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in folate-metabolizing enzymes and risk of gastroesophageal cancers: a potential nutrient-gene interaction in cancer development. Forum Nutr. 2007;60:140–5.
Ishibashi K, Sobajima J, Ishiguro T, et al. Expression of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in primary colorectal cancer and liver metastasis – a relationship between mRNA levels in cancer cells and protein levels in cancerous tissue and effect of 5‑fluorouracil. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2009;36:2232–5.
Orina JN, Calcagno AM, Wu CP, et al. Evaluation of current methods used to analyze the expression profiles of ATP-binding cassette transporters yields an improved drug-discovery database. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:2057–66.
Leschziner GD, Andrew T, Pirmohamed M, Johnson MR. ABCB1 genotype and PGP expression, function and therapeutic drug response: a critical review and recommendations for future research. Pharmacogenomics J. 2007;7:154–79.
Hung CC, Chen CC, Lin CJ, Liou HH. Functional evaluation of polymorphisms in the human ABCB1 gene and the impact on clinical responses of antiepileptic drugs. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008;18:390–402.
Peethambaram P, Fridley BL, Vierkant RA, et al. Polymorphisms in ABCB1 and ERCC2 associated with ovarian cancer outcome. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet. 2011;2:185–95.
Tian C, Ambrosone CB, Darcy KM, et al. Common variants in ABCB1, ABCC2 and ABCG2 genes and clinical outcomes among women with advanced stage ovarian cancer treated with platinum and taxane-based chemotherapy: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol. 2012;124:575–81.
Johnatty SE, Beesley J, Gao B, et al. ABCB1 (MDR1) polymorphisms and ovarian cancer progression and survival: a comprehensive analysis from the Ovarian Cancer Association Consortium and the Cancer Genome Atlas. Gynecol Oncol. 2013;131:8–14.
Baroudi O, Baroudi T, Omrane I, et al. Thymidylate synthase polymorphism in sporadic colorectal and gastric cancer in Tunisian population: a predictive role in 5‑fluorouracil based chemotherapy treatment. Med Oncol. 2014;31:825.
Zhu X, Zhao X, Peng W, et al. Epirubicin combined with oxaliplatin and 5‑day continuous infusion of 5‑fluorouracil as a first-line treatment for metastatic gastric cancer: treatment outcomes and analysis of prognostic factors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015;141:109–18.
Blum M, Suzuki A, Ajani JA. A comprehensive review of S‑1 in the treatment of advanced gastric adenocarcinoma. Future Oncol. 2011;7:715–26.
Ma Y, Tang L, Wang HX, et al. Capecitabine for the treatment for advanced gastric cancer: efficacy, safety and ethnicity. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2012;37:266–75.
Jin Z, Jiang W, Wang L. Biomarkers for gastric cancer: progression in early diagnosis and prognosis (review). Oncol Lett. 2015;9(4):1502–8.
Durães C, Almeida GM, Seruca R, Oliveira C, Carneiro F. Biomarkers for gastric cancer: prognostic, predictive or targets of therapy? Virchows Arch. 2014;464(3):367–78.
Emoto S, Ishigami H, Yamashita H, Yamaguchi H, Kaisaki S, Kitayama J. Clinical significance of CA125 and CA72-4 in gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination. Gastric Cancer. 2012;15(2):154–61.
Smith MG, Hold GL, Tahara E, El-Omar EM. Cellular and molecular aspects of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:2979–90.
Fu DG. Epigenetic alterations in gastric cancer (review). Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(3):3223–30.
Wang S, Chen L, Zhao Q, et al. Effect of TP53 codon 72 and MDM2 SNP309 polymorphisms on survival of gastric cancer among patients who receiving 5‑fluorouracil-based postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013;71:1073–82.
Lu ZM, Luo TH, Nie MM, et al. Influence of ERCC1 and ERCC4 polymorphisms on response to prognosis in gastric cancer treated with FOLFOX-based chemotherapy. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:2941–8.
Kristensen MH, Weidinger M, Bzorek M, et al. Correlation between thymidylate synthase gene variants, RNA and protein levels in primary colorectal adenocarcinomas. J Int Med Res. 2010;38:484–97.
Mandola MV, Stoehlmacher J, Zhang W, et al. A 6 bp polymorphism in the thymidylate synthase gene causes message instability and is associated with decreased intratumoral TS mRNA levels. Pharmacogenetics. 2004;14:319–27.
Fujishima M, Inui H, Hashimoto Y, et al. Relationship between thymidylate synthase (TYMS) gene polymorphism and TYMS protein levels in patients with high-risk breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:4373–9.
Vignoli M, Nobili S, Napoli C, et al. Thymidylate synthase expression and genotype have no major impact on the clinical outcome of colorectal cancer patients treated with 5‑fluorouracil. Pharmacol Res. 2011;64:242–8.
Arevalo E, Castanon E, Lopez I, et al. Thymidylate synthase polymorphisms in genomic DNA as clinical outcome predictors in a European population of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving pemetrexed. J Transl Med. 2014;12:98.
Ishida Y, Kawakami K, Tanaka Y, et al. Association of thymidylate synthase gene polymorphism with its mRNA and protein expression and with prognosis in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2002;22:2805–9.
Omar M, Crowe A, Parsons R, et al. P‑glycoprotein expression in Helicobacter pylori-positive patients: the influence of MDR1 C3435T polymorphism. J Dig Dis. 2012;13:414–20.
Nakamura T. MDR1 genotypes related to pharmacokinetics and MDR1 expression. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003;123:773–9.
Bonyadi MJ, Gerami SM, Somi MH, Khoshbaten M. Effect of the C3435T polymorphism of the multidrug resistance 1 gene on the severity of inflammatory bowel disease in Iranian Azeri Turks. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:172–6.
Zhang D, Wang C, Zhou Z. Meta-analysis of ABCB1 3435C>T polymorphism and colorectal cancer. Pak J Med Sci. 2013;29:1269–74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
J. Chen, X. Ying, L. Zhang, X. Xiang and J. Xiong declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
J. Chen and X. Ying contributed equally to the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Ying, X., Zhang, L. et al. Influence of TS and ABCB1 gene polymorphisms on survival outcomes of 5‑FU-based chemotherapy in a Chinese population of advanced gastric cancer patients. Wien Klin Wochenschr 129, 420–426 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-016-1147-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-016-1147-x