Abstract
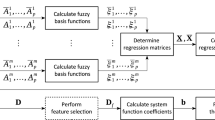
In this paper we will present a novel approach to data-driven fuzzy modeling which aims to create highly accurate but also easily comprehensible models. This is achieved by a three-stage approach which separates the definition of the underlying fuzzy sets, the learning of the initial fuzzy model, and finally a local or global optimization of the resulting model. The benefit of this approach is that it allows to use a language comprising of comprehensible fuzzy predicates and to incorporate expert knowledge by defining problem specific fuzzy predicates. Furthermore, we achieve highly accurate results by applying a regularized optimization technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamo JM (1980) Fuzzy decision trees. Fuzzy sets Sys 4:207–219
Baldwin JF, Lawry J, Martin TP (1997) A mass assignment based ID3 algorithm for decision tree induction. Int J Intell Syst 12:523–552
Baranyi P, Yam Y, Tikk D, Patton RJ (2003) Trade-off between approximation accuracy and complexity: TS controller design via HOSVD based complexity minimization. In: Casillas J, Cordón O, Herrera F, Magdalena L (eds), Interpretability Issues in Fuzzy Modeling, of Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing, Springer, Berlin Heidel berg New York Vol 128, pp, 249–277
Blake CL, Merz CJ (1998) UCI repository of machine learning databases. University. of California, Irvine, Dept of Information and Computer Sciences http://www.ics.uci.edu/~mlearn/MLRepository.html
Bodenhofer U (1999a) The construction of ordering-based modifiers In Brewka G, Der R, Gottwald S, Schierwagen A, (eds) Fuzzy-Neuro Systems ’99, Leipziger Universitätsverlag pp 55–62
Bodenhofer U (199b) A Similarity-Based Generalization of Fuzzy Orderings, vol C 26 of Schriftenreihe der Johannes-Kepler-Universität Linz. Universitätsverlag Rudolf Trauner
Bodenhofer U, Bauer P (2003). A formal model of interpretability of linguistic variables. In: Casillas J, Cordón O, Herrera F, Magdalena L (eds). Interpretability issues in fuzzy modeling. vol 128 of Studies in fuzziness and soft computing. Springer, Berlin Heidel berg New York, pp 524–545
Breiman L, Friedman J, Stone CJ, Olshen RA, (eds) (1984) Classification and regression trees. CRC Press Bow, Raton
Burger M, Haslinger J, Bodenhofer U, Engl HW (2002) Regularized data-driven construction of fuzzy controllers. J Inverse Ill-Posed Probl 10(4):319–344
Casillas J, Cordón O, Herrera F, Magdalena L ed. (2003) Interpretability issues in fuzzy modeling, vol 128 of Studies in fuzziness and soft computing. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg Newyork
Castellano G, Fanelli AM, Mencar C (2002) A double-clustering approach for interpretable granulation of data. In: Proceeding of 2002 IEEE International Conference on systems, man and cybernetics, Hammamet, Tunisia
de Boor C (1998) A practical guide to splines. Springer, Heidelberg New York
De Cock M, Bodenhofer U, Kerre EE (2006) Modelling linguistic expressions using fuzzy relations. In: Proceedings of 6th International. Conference. on Soft Computing, pp 353–360, Iizuka
Draper NR, Smith H, Applied Regression Analysis. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Drobics M (2004) Choosing the best predicates for data-driven fuzzy modeling. In: Proceedings of . 13th IEEE international conference. on fuzzy systems, Budapests pp 245–249
Guillaume S, Charnomordic B (2004) Generating an interpretable family of fuzzy partitions from data. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst, 12(3)
Höppner F, Klawonn F (2005) Improved fuzzy partitions for fuzzy regression models. Internat J Approx Reason 32:85–102
Janikow CZ, Fuzzy decision trees: issues and methods. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B 28(1): 1–14
Klawonn F, Kruse R (1997) Constructing a fuzzy controller from data. Fuzzy Sets Systems 85:177–193
Maher PE, Clair DS, (1993) Uncertain reasoning in an ID3 machine learning framework. In: Proceeding of 2nd IEEE international Conference on fuzzy systems, San Francisco, CA
Marsala C (2000) Fuzzy decision trees to help flexible querying. Kybernetika 36(6):689–705
McClelland JL, Rumelhart DE ed. (1996) Parallel distributed processing—exploration in the Microstructures of Cognition, Vol II: Psychological and Biological Models. MIT Press, Cambridge
Mikut R, Jäkel J, Gröll L (2000) Automatic design of interpretable membership functions. In: Proceeding of 8th zittau fuzzy colloquium, Hochschule Zittau/Görlitz
Mikut R, Jäkel J, Gröll L, Interpretability issues in data-based learning of fuzzy systems. Fuzzy Sets and Syst 150: 179–197
Nelles O, Fink A, Isermann R (2000) Local linear model trees (LOLIMOT) toolbox for nonlinear system identification. In: Proceeding of 12th IFAC symposium on system Identification, Santa Barbara
Olaru C, Wehenkel L (2003) A complete fuzzy decision tree technique. Fuzzy Sets Syst 138(2):221–254
Peng Y, Flach PA (2001) Soft discretization to enhance the continuous decision tree induction. In: Proceeding of ECML/PKDD01 workshop integrating aspects of data mining, decision support and meta-learning, PP 109–118
Quinlan JR (1992) Learning with continuous classes. In: Proceeding of 5th Australin Joint Conference on artificial intelligence, pp 343–348
Quinlan JR, C4.5: Programs for machine learning. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo
Regattieri Delgado JR, Von Zuben F, Gomide F (2001) Local and global estimation of Takagi-Sugeno consequent parameters in genetic fuzzy systems. In: Proceeding of Joint 9th IFSA world congress and 20th NAFIPS International Confference,
Rumelhart DE, McClelland JL, Parallel distributed processing—exploration in the microstructures of cognition, Vol I: Foundations. MIT Press, Cambridge
Takagi T, Sugeno M (1985) Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 15(1):116–132
Wang X, Chen B, Qian G, Ye F (2006) On the optimization of fuzzy decision trees. Fuzzy Sets Syst 112:117–125
Witten IH, Frank E Data mining: practical machine learning tools with Java implementations. Morgan Kaufmann
Yager RR, Filev E, Sanmateo (1994) Approximate clustering via the mountain method. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 24(8):1279–1284
Yuan Y, Shaw MJ (1999) Induction of fuzzy decision trees. Fuzzy Sets and Syst 69:125–139
Zadeh LA, Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8:338–353
Zeidler J, Schlosser M (1996) Continuous valued attributes in fuzzy decision trees. In: Proc 8th Int conf. on information processing and management of uncertainty in knowledge-based systems, pp 395–400
Zurada JM, Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks. West Publishing, St. Paul
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drobics, M., Himmelbauer, J. Creating comprehensible regression models. Soft Comput 11, 421–438 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-006-0107-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-006-0107-1