Abstract
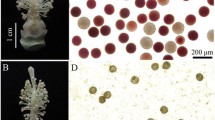
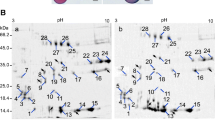
gaMS-2 is a gametophytic male-sterile mutant of maize, with sterile pollen grains developmentally blocked at the binucleate stage. To characterise differentially expressed proteins in gaMS-2 pollen, we compared protein profiles of anthers and mature pollen from heterozygous GaMS-2/gaMS-2 plants and wild type (wt) plants by two-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE). A basic protein present at a greatly reduced level in GaMS-2/gaMS-2 anthers was subsequently identified by tandem mass spectrometry as Zea m 1 (a glycoprotein of 31 kDa), the major group-1 allergen of maize pollen and a member of the β-expansin 1 family. Moreover, we show that Zea m 1 can be deglycosylated by peptide N-glycosidase F. After deglycosylation, four major isoforms—Zea m 1a (more acetic), Zea m 1b, Zea m1c and Zea m 1d (more basic)—can be discriminated in wt anther in 2-DE immunoblots probed with a monoclonal antibody against the group-1 pollen allergen, whereas all the isoforms, especially Zea m 1a, exist at reduced levels in GaMS-2/gaMS-2 anthers. Furthermore, the reduced Zea m 1 accumulation in the mutant appears to occur in immature pollen but not in anther sporophytic tissues. Finally, we separated sterile pollen grains (at the mononucleate stage) from fertile ones using 42% Percoll solution, and found that Zea m 1 is barely detectable in sterile pollen grains. Together, our results indicate that a reduced Zea m 1 level is associated with the sterile phenotype of gaMS-2.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broadwater AH, Rubinstein AL, Chay CH, Klapper DG, Bedinger PA (1993) Zea m 1, the maize homolog of the allergen-encoding Lol p 1 gene of rye grass. Gene 131:227–230
Coleman AW, Goff LJ (1985). Applications of fluorochromes to pollen biology. I. Mithramycin and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) as vital stains and for quantification of nuclear DNA. Stain Technol 60:145-154
Cosgrove DJ (2000) Loosening of plant cell walls by expansins. Nature 407:321–326
Cosgrove DJ, Bedinger P, Durachko DM (1997) Group I allergens of grass pollen as cell wall-loosening agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6559–6564
Cosgrove DJ, Li L-C, Cho H-T, Hoffmann-Benning S, Moore RC, Blecker D (2002) The growing world of expansins. Plant Cell Physiol 43:1436–1444
Görg A, Obermaier C, Boguth G, Harder A, Scheibe B, Wildgruber R, Weiss W (2000) The current state of two-dimensional electrophoresis with immobilized pH gradients. Electrophoresis 21:1037–1053
Griffith IJ, Smith PM, Pollock J, Theerakulpisut P, Avjioglu A, Davies S, Hough T, Singh MB, Simpson RJ, Ward LD, Knox RB (1991) Cloning and sequencing of Lol p I, the major allergenic protein of rye-grass pollen. FEBS Lett 279:210–215
Grobe K, Pöppelmann M, Becker WM, Petersen A (2002) Properties of group I allergens from grass pollen and their relation to cathepsin B, a member of the C1 family of cysteine proteinases. Eur J Biochem 269:2083–2092
Hamilton DA, Mascarenhas JP (1997) Gene expression during pollen development. In: Shivanna KR, Sawhney VK (eds) Pollen biotechnology for crop production and improvement. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 40–58
Howllett BJ, Vithanage HIMV, Knox RB (1979) Pollen antigens, allergens and enzymes. Curr Adv Plant Sci 35:1–17
Kapoor S, Kobayashi A, Takatsuji H (2002) Silencing of the tapetum-specific zinc finger TAZ1 causes premature degeneration of tapetum and pollen abortion in petunia. Plant Cell 14:2353–2367
Knox RB, Taylor P, Smith P, Hough T, Ong EK, Suphioglu C, Lavithis M, Davies S, Avjioglu A, Singh M (1993) Pollen allergens: botanical aspects. In: Kraft D, Sehon A (eds) Molecular biology and immunology of allergens. CRC, Boca Raton, Fla., pp 31–38
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 222:680–685
Laffer S, Duchene M, Reimitzer I, Susani M, Mannhalter C, Kraft D, Valenta R (1996) Common IgE-epitopes of recombinant Phl p 1, the major timothy grass pollen allergen and natural group I grass isoallergens. Mol Immunol 33:417–426
Li L-C, Bedinger PA, Volk C, Jones D, Cosgrove DJ (2003) Purification and characterization of four β-expansins (Zea m 1 isoforms) from maize pollen. Plant Physiol 132:2073–2085
Liu F, Cui X, Horner HT, Weiner H, Schnable PS (2001) Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase activity is required for male fertility in maize. Plant Cell 13:1063–1078
Petersen A, Becker WM, Moll H, Blümke M, Schlaak M (1995) Determination of the carbohydrate structure of the timothy grass pollen allergen Phl p 1. Electrophoresis 16:869–875
Petersen A, Vieths S, Aulepp H, Schlaak M, Becker MW (1996) Ubiquitous structures responsible for IgE cross-reactivity between tomato fruit and grass pollen allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol 98:805–815
Rozwadowski K, Zhao R, Jackman L, Huebert T, Burkhart WE, Hemmingsen SM, Greewood J, Rothstein SJ (1999) Characterization and immunolocaliztion of a cytosolic calcium-binding protein from Brassica napus and Arabidopsis pollen. Plant Physiol 120:787–798
Sari-Gorla M, Ferrario S, Villa M, Pè ME (1996) gaMS-1, a gametophytic male sterile mutant in maize. Sex Plant Reprod 9:216–220
Sari-Gorla M, Gatti E, Villa M, Pè ME (1997) A multi-nucleate male-sterile mutant of maize with gametophytic expression. Sex Plant Reprod 10:22–26
Shivanna KR, Cresti M, Ciampolini F (1997) Pollen development and pollen-pistil interaction. In: Shivanna KR, Sawhney VK (eds) Pollen biotechnology for crop production and improvement. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 15–58
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Tretter V, Altmann F, März L (1991) Peptide-N4-(N-acetyl-β-glucosaminyl)asparagine amidase F cannot release glycans with fucose attached α1→3 to the asparagine-linked N-acetyl-glucosamine residue. Eur J Biochem 199:647–652
Wang W, Scali M, Vignani R, Spadafora A, Sensi E, Mazzuca S, Cresti M (2003) Protein extraction for two-dimensional electrophoresis from olive leaf, a plant tissue containing high levels of interfering compounds. Electrophoresis 24:2369–2375
Willing RP, Bashe D, Mascarenhas JP (1988) An analysis of the quantity and diversity of messenger RNAs from pollen and shoots of Zea mays. Theor Appl Genet 75:751–753
Wu J, Meeley RB, Cosgrove DJ (2001) Analysis and expression of the α-expansin and β-expansin gene families in maize. Plant Physiol 126:222–232
Zhao D-Z, Wang G-F, Speal B, Ma H (2002) The EXCESS MICROSPOROCYTES1 gene encodes a putative leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase that controls somatic and reproductive cell fates in the Arabidopsis anther. Gen Dev 16:2021–2031
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Alessandra Moscatelli (Università di Milano) and Dr. Elisabetta Sensi (Università di Siena) for help during this study, which was supported by COFIN 2000 (MURST, Italy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
W. Wang and M. Scali contributed equally to this study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Scali, M., Vignani, R. et al. Male-sterile mutation alters Zea m 1 (β-expansin 1) accumulation in a maize mutant. Sex Plant Reprod 17, 41–47 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-004-0207-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-004-0207-y