Abstract
Background
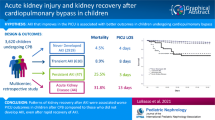
Acute renal injury increases risk of death after cardiac surgery. The objective of the study was to evaluate the ability of the pediatric Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss, End-Stage Renal Disease (pRIFLE) criteria to characterize the development of postoperative renal damage in children after cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) and to evaluate the relationship between the severity of kidney injury and mortality, pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) length of stay, and the duration of mechanical ventilation (MV).
Methods
In this retrospective study including children undergoing CPB surgery during a 3-year period in the PICU of a tertiary hospital, demographic, clinical, surgery-related, and postoperative clinical data were collected. Kidney damage was assessed with pRIFLE criteria.
Results
Four hundred and nine patients were included. Early acute kidney injury (AKI) was found in 82 patients (achieving categories Risk 44; Injury 16; Failure 22). Early AKI was associated with younger age (P = 0.010), longer CPB, deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (DHCA) use, ICU stay >12 days, MV >4 days, and death (P < 0.001). Controlling the effect of age, CPB, DHCA use, previous cardiac surgeries, and Risk Adjustment in Congenital Heart Surgery Surgical Severity Score (RACHS-1), early AKI development proved to predict ICU stay >12 days [odds ratio (OR) 3.5; 95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.9–6.5, P < 0.001)] and need of MV >4 days (OR 5.1; 95 % CI 2.6–10.2, P < 0.001).
Conclusions
Early AKI when evaluated with the pRIFLE criteria can predict prolonged ICU stay, need of prolonged MV, and mortality.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schneider J, Khemani R, Grushkin C, Bart R (2010) Serum creatinine as stratified in the RIFLE score for acute kidney injury is associated with mortality and length of stay for children in the pediatric intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 38:933–939
Sirvinskas E, Andrejaitiene J, Raliene L, Nasvytis L, Karbonskiene A, Pilvinis V, Sakalauskas J (2008) Cardiopulmonary bypass management and acute renal failure: risk factors and prognosis. J Perfusion 23:323–327
Zappitelli M, Bernier PL, Saczkowski RS, Tchervenkov CI, Gottesman R, Dancea A, Hyder A, Alkandari O (2009) A small post-operative rise in serum creatinine predicts acute kidney injury in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 76:885–892
Alkandari O, Eddington KA, Hyder A, Gauvin F, Ducruet T, Gottesman R, Phan V, Zappitelli M (2011) Acute kidney injury is an independent risk factor for pediatric intensive care unit mortality, longer length of stay and prolonged mechanical ventilation in critically ill children: a two-center retrospective cohort study. Crit Care 15:R146
Bagshaw SM, George C, Bellomo R (2008) Early acute kidney injury and sepsis: a multicentre evaluation. Crit Care 12:R47
Englberger L, Suri RM, Li Z, Casey ET, Daly RC, Dearani JA, Schaff HV (2011) Clinical accuracy of RIFLE and Acute Kidney Injury Network (AKIN) criteria for acute kidney injury in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Crit Care 15:R16
Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P (2004) Acute renal failure – definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care 8:R204–R212
Hsu CW, Symons JM (2010) Acute kidney injury: can we improve prognosis? Pediatr Nephrol 25:2401–2412
Mak RH (2008) Acute kidney injury in children: the dawn of a new era. Pediatr Nephrol 23:2147–2149
Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C (2007) Defining and classifying acute renal failure: from advocacy to consensus and validation of RIFLE criteria. Intensive Care Med 33:409–413
Abosaif NY, Tolba YA, Heap M, Russell J, El Nahas AM (2005) The outcome of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit according to RIFLE: model application, sensitivity, and predictability. Am J Kidney Dis 46:1038–1048
Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, Washburn KK, Jefferson LS, Goldstein SL (2007) Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 71:1028–1035
Plötz FB, Bouma AB, van Wijk JA, Kneyber MC, Bökenkamp A (2008) Pediatric acute kidney injury in the ICU: an independent evaluation of pRIFLE criteria. Intensive Care Med 34:1713–1717
Jenkins KJ, Gauvreau K, Newburger JW, Spray TL, Moller JH, Iezzoni LI (2002) Consensus-based method for risk adjustment for surgery for congenital heart disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 123:110–118
Marcin JP, Slonim AD, Pollack, Ruttimann UE (2001) Long-stay patients in the pediatric intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 29:652–657
Brown KL, Ridout DA, Goldman AL, Hoskote A, Penny DJ (2003) Risk factors for long intensive care unit stay after cardiopulmonary bypass in children. Crit Care Med 31:28–33
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9-CM). Los Angeles, Practice Management Information, 2003
Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelman CM, Spitzer A (1976) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 58:259–263
Osterman ME, Taube D, Morgan CJ, Evans TW (2000) Acute renal failure following cardiopulmonary bypass: a changing picture. Intensive Care Med 26:565–571
Li S, Krawczeski CD, Zappitelli M, Devarajan P, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Coca SG, Kim RG, Parikh CR (2011) Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery—a prospective multicenter study. Crit Care Med 39(6):1493–1499
El Halal DS, Carvalho PR (2013) Acute kidney injury according to pediatric RIFLE criteria is associated with negative outcomes after heart surgery in children. Pediatr Nephrol 28(8):1307–1314
Zappitelli M, Parikh CR, Akcan-Arikan A, Washburn KK, Moffett BS, Goldstein SL (2008) Ascertainment and epidemiology of acute kidney injury varies with definition interpretation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:948–954
Ostermann M, Chang R (2007) Acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit according to RIFLE. Crit Care Med 35:1837–1843
Hoste EA, Clermont G, Kersten A, Venkataraman R, Angus DC, De Bacquer D, Kellum JA (2006) RIFLE criteria for acute kidney injury are associated with hospital mortality in critically ill patients: a cohort analysis. Crit Care 10:R73
Slater MB, Anand V, Uleryk EM, Parshuram CS (2012) A systematic review of RIFLE criteria in children, and its application and association with measures of mortality and morbidity. Kidney Int 81:791–798
Kuitunen A, Vento A, Suojaranta-Ylinen R, Pettilä V (2006) Acute renal failure after cardiac surgery - evaluation of the RIFLE classification. Ann Thorac Surg 81:542–546
Washburn KK, Zappitelli M, Arikan AA, Loftis L, Yalavarthy R, Parikh CR, Edelstein CL, Goldstein SL (2008) Urinary interleukin-18 is an acute kidney injury biomarker in critically ill children. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:566–572.37
Zappitelli M, Washburn KK, Arikan AA, Loftis L, Ma Q, Devarajan P, Parikh CR, Goldstein SL (2007) Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care 11:R84
Zappitelli M, Moffett BS, Hyder A, Goldstein SL (2011) Acute kidney injury in non-critically ill children treated with aminoglycoside antibiotics in a tertiary healthcare centre: a retrospective cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:144–150
Ruth JL, Wassner SJ (2006) Body composition: salt and water. Pediatr Rev 27:181–187, quiz 188
Palmieri T, Lavrentieva A, Greenhalgh D (2009) An assessment of acute kidney injury with modified RIFLE criteria in pediatric patients with severe burns. Intensive Care Med 35:2125–2129
Manrique A, Jooste EH, Kuch BA, Lichtenstein SE, Morell V, Munoz R, Ellis D, Davis PJ (2009) The association of renal dysfunction and the use of aprotinin in patients undergoing congenital cardiac surgery requiring cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesth Analg 109:45–52
Uchino S, Bellomo R, Goldsmith D, Bates S, Ronco C (2006) An assessment of the RIFLE criteria for acute renal failure in hospitalized patients. Crit Care Med 34:1913–1917
Bagshaw SM, George C, Dinu I, Bellomo R (2008) A multi-centre evaluation of the RIFLE criteria for early acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:1203–1210
Van den Akker JPC, Egal M, Groeneveld ABJ (2013) Invasive mechanical ventilation as a risk factor for acute kidney injury in the critically ill: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care 17:R98
Ricci Z, Ronco C (2010) Pulmonary/renal interaction. Curr Opin Crit Care 16:13–18
Krawczeski CD, Vandevoorde RG, Kathman T, Bennett MR, Woo JG, Wang Y, Griffiths RE, Devarajan P (2010) Serum cystatin C is an early predictive biomarker of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5(9):1552–1557
Dennen P, Altmann C, Kaufman J, Klein CL, Andres-Hernando A, Ahuja NH, Edelstein CL, Cadnapaphornchai MA, Keniston A, Faubel S (2010) Urine interleukin-6 is an early biomarker of acute kidney injury in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Crit Care 14:R181
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the assistance of the medical and nursing staff of the PICU and the laboratory technicians of the Gregorio Marañón General University Hospital. We also thank Dr. J.M. Bellón for his help in statistical analysis.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gil-Ruiz Gil-Esparza, M.A., Alcaraz Romero, A.J., Romero Otero, A. et al. Prognostic relevance of early AKI according to pRIFLE criteria in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Pediatr Nephrol 29, 1265–1272 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2757-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2757-z