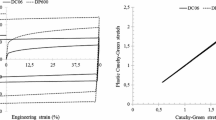
Abstract
An extended multiscale finite element method is developed for small-deformation elasto-plastic analysis of periodic truss materials. The base functions constructed numerically are employed to establish the relationship between the macroscopic displacement and the microscopic stress and strain. The unbalanced nodal forces in the micro-scale of unit cells are treated as the combined effects of macroscopic equivalent forces and microscopic perturbed forces, in which macroscopic equivalent forces are used to solve the macroscopic displacement field and microscopic perturbed forces are used to obtain the stress and strain in the micro-scale to make sure the correctness of the results obtained by the downscale computation in the elastic-plastic problems. Numerical examples are carried out and the results verify the validity and efficiency of the developed method by comparing it with the conventional finite element method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brittain ST, Sugimura Y, Schueller OJA, Evans AG, Whitesides GM (2001) Fabrication and mechanical performance of a mesoscale space-filling truss system. J Microelectromech Syst 10: 113–120
Huybrechts SM, Meink TE, Wegener PM, Ganley JM (2002) Manufacturing theory for advanced grid stiffened structures. Compos Appl Sci Manuf 33: 155–161
Hou A, Gramoll K (1998) Compressive strength of composite lattice structures. J Reinforce Plast Compos 17: 462–483
Deshpande VS, Ashby MF, Fleck NA (2001) Foam topology: bending versus stretching dominated architectures. Acta Materialia 49: 1035–1040
Wallach JC, Gibson LJ (2001) Mechanical behavior of a three-dimensional truss material. Int J Solids Struct 38: 7181–7196
Budiansky B (1965) On the elastic moduli of some heterogeneous materials. J Mech Phys Solids 13: 223–227
Chen HS, Acrivos A (1978) The effective elastic moduli of composite materials containing spherical inclusions at non-dilute concentrations. Int J Solids Struct 14: 349–364
Nemat-Nasser S, Hori M (1993) Micromechanics: overall properties of heterogeneous materials. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Kouznetsova V (2002) Computational homogenization for the multi-scale analysis of multi-phase materials. PhD-thesis, Technical University of Eindhoven, Eindhoven
Pecullan S, Gibiansky LV, Torquato S (1999) Scale effects on the elastic behavior of periodic and hierarchical two-dimensional composites. J Mech Phys Solids 47: 1509–1542
Noor AK (1988) Continuum modeling for repetitive lattice structures. Appl Mech Rev 41: 285–296
Gonella S, Ruzzene M (2008) Homogenization and equivalent in-plane properties of two-dimensional periodic lattices. Int J Solids Struct 45: 2897–2915
Suiker ASJ, Metrikine AV, de Borst R (2001) Comparison of wave propagation characteristics of the cosserat continuum model and corresponding discrete lattice models. Int J Solids Struct 38: 1563–1583
Benssousan A, Lions JL, Papanicoulau G (1978) Asymptotic analysis for periodic structures. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Paumelle P, Hassim F, Lene F (1991) Microstress analysis in woven composite structures. Rech Aerospatiale 6: 47–62
Lee K, Moorthy S, Ghosh S (1999) Multiple scale computational model for damage in composite materials. Comput Meth Appl Mech Eng 172: 175–201
Oskay C, Fish J (2008) On calibration and validation of eigendeformation-based multiscale models for failure analysis of heterogeneous systems. Comput Mech 42: 181–195
Terada K, Kikuchi N (1995) Nonlinear homogenization method for practical applications. In: Ghosh S, Ostoja-Starzewski M (eds) Computational Methods in Micromechanics, AMSE AMD, vol 212, pp 1–16
Fish J, Shek K, Pandheeradi M, Shephard M (1997) Computational plasticity for composite structures based on mathematical homogenization: theory and practice. Comput Meth Appl Mech Eng 148: 53–73
Terada K, Hori M, Kyoya T, Kikuchi N (2000) Simulation of the multi-scale convergence in computational homogenization approaches. Int J Solids Struct 37: 2285–2311
Matsui K, Terada K, Yuge K (2004) Two-scale finite element analysis of heterogeneous solids with periodic microstructures. Comput Struct 82: 593–606
Kouznetsova V, Brekelmans WAM, Baaijens FPT (2001) An approach to micro-macro modeling of heterogeneous materials. Comput Mech 27: 37–48
Babuska I, Osborn E (1983) Generalized finite element methods: Their performance and their relation to mixed methods. SIAM J Numer Anal 20: 510–536
Babuska I, Caloz G, Osborn E (1994) Special finite element methods for a class of second order elliptic problems with rough coefficients. SIAM J Numer Anal 31: 945–981
Hou TY, Wu XH (1997) A multiscale finite element method for elliptic problems in composite materials and porous media. J Comput Phys 134: 169–189
Hou TY (2005) Multiscale modelling and computation of fluid flow. Int J Numer Meth Fluid 47: 707–719
Efendiev Y, Ginting V, Hou TY, Ewing R (2006) Accurate multiscale finite element methods for two-phase flow simulations. J Comput Phys 220: 155–174
Aarnes JE (2004) On the use of a mixed multiscale finite element method for greater flexibility and increased speed or improved accuracy in reservoir simulation. Multiscale Model Sim 2: 421–439
Aarnes JE, Krogstad S, Lie KA (2006) A hierarchical multiscale method for two-phase flow based upon mixed finite elements and nonuniform coarse grids. Multiscale Model Sim 2: 421–439
Dostert P, Efendiev Y, Hou TY (2008) Multiscale finite element methods for stochastic porous media flow equations and application to uncertainty quantification. Comput Meth Appl Mech Eng 197: 3445–3455
Jenny P, Lee SH, Tchelepi HA (2003) Multi-scale finite volume method for elliptic problems in subsurface flow simulation. J Comput Phys 187: 47–67
Ginting V (2004) Computational upscaled modeling of heterogeneous porous media flows utilizing finite volume method. PHD thesis, Texas A & M University, College Station
Zhang HW, Fu ZD, Wu JK (2009) Coupling multiscale finite element method for consolidation analysis of heterogeneous saturated porous media. Adv Water Resour 32: 268–279
Zhang HW, Wu JK, Fu ZD (2010) Extended multiscale finite element method for mechanical analysis of periodic lattice truss materials. Int J Multiscale Com (accepted)
Ye HF, Wang JB, Zhang HW (2009) Numerical algorithms for prediction of mechanical properties of single-walled carbon nanotubes based on molecular mechanics model. Comp Mater Sci 44: 1089–1097
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H.W., Wu, J.K. & Fu, Z.D. Extended multiscale finite element method for elasto-plastic analysis of 2D periodic lattice truss materials. Comput Mech 45, 623–635 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-010-0475-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-010-0475-3