Abstract
Background
Subepithelial tumors (SETs) in the gastrointestinal tract are often incidentally found during endoscopic examinations. Although the utility and safety of endoscopic resection (ER) of SETs in the esophagus and stomach have been described, data about the ER of duodenal SETs remain scant. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the clinical outcomes associated with the ER of duodenal SETs and to assess possible predictive factors for incomplete resection.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective observational study of 62 patients (64 lesions) that underwent ER of duodenal SETs between June 2005 and December 2015 at the Pusan National University Hospital. The therapeutic outcomes from ER and procedure-related complications were analyzed.
Results
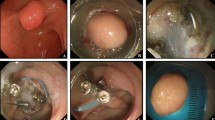
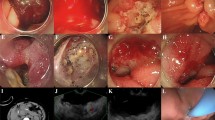
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) was performed in 38 tumors, EMR with a ligation device (EMR-L) in 18 and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) in 8. The overall en bloc resection and complete ER rates were 96.9 % (62/64) and 100 % (64/64), respectively. The complete pathologic resection rate was 76.6 % (49/64). Multivariate logistic regression analyses determined that the macroscopic type (Yamada type I or II; odds ratio [OR] 6.460, 95 % confidence interval [CI] 1.569–37.458, p = 0.027) and the treatment method (ESD; OR 7.178, 95 % CI 1.291–39.323, p = 0.024) were independently associated with incomplete pathologic resection. The procedure-related bleeding and perforation rates were 6.3 % and 4.7 %, respectively. No recurrences were observed in patients who had undergone complete ER at a median follow-up period of 20 months (range 6–112 months).
Conclusion
ER is an effective, safe, and feasible treatment for duodenal SETs, especially when the SET is located in the deep mucosal layer and/or the submucosal layer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Humphris JL, Jones DB (2008) Subepithelial mass lesions in the upper gastrointestinal tract. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23:556–566
Hwang JH, Rulyak SD, Kimmey MB, American Gastroenterological Association Institute (2006) American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on the management of gastric subepithelial masses. Gastroenterology 130:2217–2228
Bialek A, Wiechowska-Kozlowska A, Pertkiewicz J, Polkowski M, Milkiewicz P, Karpinska K, Lawniczak M, Starzynska T (2012) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for treatment of gastric subepithelial tumors (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 75:276–286
Lee JS, Kim GH, Park do Y, Yoon JM, Kim TW, Seo JH, Lee BE, Song GA (2015) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric subepithelial tumors: a single-center experience. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2015:425–469
Polkowski M (2005) Endoscopic ultrasound and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy for the diagnosis of malignant submucosal tumors. Endoscopy 37:635–645
Palazzo L, Landi B, Cellier C, Cuillerier E, Roseau G, Barbier JP (2000) Endosonographic features predictive of benign and malignant gastrointestinal stromal cell tumours. Gut 46:88–92
Karaca C, Turner BG, Cizginer S, Forcione D, Brugge W (2010) Accuracy of EUS in the evaluation of small gastric subepithelial lesions. Gastrointest Endosc 71:722–727
Cantor MJ, Davila RE, Faigel DO (2006) Yield of tissue sampling for subepithelial lesions evaluated by EUS: a comparison between forceps biopsies and endoscopic submucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc 64:29–34
Ji JS, Lee BI, Choi KY, Kim BW, Choi H, Huh M, Chung WC, Chae HS, Chung IS (2009) Diagnostic yield of tissue sampling using a bite-on-bite technique for incidental subepithelial lesions. Korean J Intern Med 24:101–105
Hunt GC, Smith PP, Faigel DO (2003) Yield of tissue sampling for submucosal lesions evaluated by EUS. Gastrointest Endosc 57:68–72
Fernandez-Esparrach G, Sendino O, Sole M, Pellise M, Colomo L, Pardo A, Martinez-Palli G, Arguello L, Bordas JM, Llach J, Gines A (2010) Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and trucut biopsy in the diagnosis of gastric stromal tumors: a randomized crossover study. Endoscopy 42:292–299
Kim GH, Cho YK, Kim EY, Kim HK, Cho JW, Lee TH, Moon JS, Korean EUSSG (2014) Comparison of 22-gauge aspiration needle with 22-gauge biopsy needle in endoscopic ultrasonography-guided subepithelial tumor sampling. Scand J Gastroenterol 49:347–354
Tae HJ, Lee HL, Lee KN, Jun DW, Lee OY, Han DS, Yoon BC, Choi HS, Hahm JS (2014) Deep biopsy via endoscopic submucosal dissection in upper gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors: a prospective study. Endoscopy 46:845–850
Inoue H, Ikeda H, Hosoya T, Onimaru M, Yoshida A, Eleftheriadis N, Maselli R, Kudo S (2012) Submucosal endoscopic tumor resection for subepithelial tumors in the esophagus and cardia. Endoscopy 44:225–230
Lee CK, Lee SH, Chung IK, Lee TH, Park SH, Kim EO, Chung MS, Cho HD, Kim SJ (2012) Endoscopic full-thickness resection of a gastric subepithelial tumor by using the submucosal tunnel technique with the patient under conscious sedation (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 75:457–459
Schmidt A, Bauder M, Riecken B, Caca K (2014) Endoscopic resection of subepithelial tumors. World J Gastrointest Endosc 6:592–599
Ye LP, Zhang Y, Luo DH, Mao XL, Zheng HH, Zhou XB, Zhu LH (2016) Safety of endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer: an analysis of 733 tumors. Am J Gastroenterol 111:788–796
Honda T, Yamamoto H, Osawa H, Yoshizawa M, Nakano H, Sunada K, Hanatsuka K, Sugano K (2009) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial duodenal neoplasms. Dig Endosc 21:270–274
Seo JY, Hong SJ, Han JP, Jang HY, Myung YS, Kim C, Lee YN, Ko BM (2014) Usefulness and safety of endoscopic treatment for nonampullary duodenal adenoma and adenocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:1692–1698
Gaspar JP, Stelow EB, Wang AY (2016) Approach to the endoscopic resection of duodenal lesions. World J Gastroenterol 22:600–617
Yamada T, Ichikawa H (1974) X-ray diagnosis of elevated lesions of the stomach. Radiology 110:79–83
Kim GH, Kim JI, Jeon SW, Moon JS, Chung IK, Jee SR, Kim HU, Seo GS, Baik GH, Lee YC, Korean College of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research (2014) Endoscopic resection for duodenal carcinoid tumors: a multicenter, retrospective study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:318–324
Matsumoto S, Yoshida Y (2014) Selection of appropriate endoscopic therapies for duodenal tumors: an open-label study, single-center experience. World J Gastroenterol 20:8624–8630
Nonaka S, Oda I, Tada K, Mori G, Sato Y, Abe S, Suzuki H, Yoshinaga S, Nakajima T, Matsuda T, Taniguchi H, Saito Y, Maetani I (2015) Clinical outcome of endoscopic resection for nonampullary duodenal tumors. Endoscopy 47:129–135
Alexander S, Bourke MJ, Williams SJ, Bailey A, Co J (2009) EMR of large, sessile, sporadic nonampullary duodenal adenomas: technical aspects and long-term outcome (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 69:66–73
Abbass R, Rigaux J, Al-Kawas FH (2010) Nonampullary duodenal polyps: characteristics and endoscopic management. Gastrointest Endosc 71:754–759
Lepilliez V, Chemaly M, Ponchon T, Napoleon B, Saurin JC (2008) Endoscopic resection of sporadic duodenal adenomas: an efficient technique with a substantial risk of delayed bleeding. Endoscopy 40:806–810
Park SM, Ham JH, Kim BW, Kim JS, Kim CW, Kim JI, Lim CH, Oh JH (2015) Feasibility of endoscopic resection for sessile nonampullary duodenal tumors: a multicenter retrospective study. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2015:692492
Miettinen M, Lasota J (2006) Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: pathology and prognosis at different sites. Semin Diagn Pathol 23:70–83
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (0920050) and by the Medical Research Center Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korea government (NRF-2015R1A5A2009656).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Tae Wook Kim, Gwang Ha Kim, Do Youn Park, Sangjeong Ahn, Won Lim, Bon Eun Lee, and Geun Am Song have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, T.W., Kim, G.H., Park, D.Y. et al. Endoscopic resection for duodenal subepithelial tumors: a single-center experience. Surg Endosc 31, 1936–1946 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5200-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5200-7