Abstract
Background
The efficacy of transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) performed with the EsophyX device (Redmond, Washington, USA) and its long-term outcomes in gastresophageal reflux disease (GERD) are debated. We, therefore, performed a systematic review with meta-analysis of studies evaluating the role of TIF in GERD.
Methods
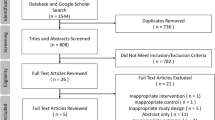
A systematic search of EMBASE, SCOPUS, PubMed, and the Cochrane Library Central was performed. All original studies reporting outcomes in GERD patients who underwent TIF were identified. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating the efficacy of TIF, and prospective observational studies reporting outcomes after TIF were included.
Results
A total of 18 studies (963 patients) published between 2007 and 2015 were identified, including five RCTs and 13 prospective observational studies. The pooled relative risk of response rate to TIF versus PPIs/sham was 2.44 (95 % CI 1.25–4.79, p = 0.0009) in RCTs in the intention-to-treat analysis. The total number of refluxes was reduced after TIF compared with the PPIs/sham group. The esophageal acid exposure time and acid reflux episodes after TIF were not significantly improved. Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) usage increased with time and most of the patients resumed PPIs treatment at reduced dosage during the long-term follow-up. The total satisfaction rate after TIF was about 69.15 % in 6 months. The incidence of severe adverse events consisting of gastrointestinal perforation and bleeding was 2.4 %.
Conclusions
TIF is an alternative intervention in controlling GERD-related symptoms with comparable short-term patient satisfaction. Long-term results showed decreased efficacy with time. Patients often resume PPIs at reduced doses in the near future.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonavina L, Attwood S (2015) Laparoscopic alternatives to fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux: the role of magnetic augmentation and electrical stimulation of the lower esophageal sphincter. Dis Esophagus Off J Int Soc Dis Esophagus ISDE. doi:10.1111/dote.12425
Bonatti H, Achem SR, Hinder RA (2008) Impact of changing epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease on its diagnosis and treatment. J Gastrointest Surg Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract 12:373–381. doi:10.1007/s11605-007-0294-9
Parekh PJ, Johnson DA (2015) Medical treatment versus surgery for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Tech Gastrointest Endosc 17:53–61. doi:10.1016/j.tgie.2015.02.003
Gerson LB, Boparai V, Ullah N, Triadafilopoulos G (2004) Oesophageal and gastric pH profiles in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and Barrett’s oesophagus treated with proton pump inhibitors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 20:637–643. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.02127.x
Moraes-Filho JPP (2012) Refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease. Arq Gastroenterol 49:296–301. doi:10.1590/S0004-28032012000400012
Niebisch S, Peters JH (2012) Update on fundoplication for the treatment of GERD. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 14:189–196. doi:10.1007/s11894-012-0256-6
Herron DM, Swanström LL, Ramzi N, Hansen PD (1999) Factors predictive of dysphagia after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc 13:1180–1183. doi:10.1007/PL00009616
Spechler SJ (1992) Comparison of medical and surgical therapy for complicated gastroesophageal reflux disease in veterans. The Department of Veterans Affairs Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Study Group. N Engl J Med 326:786–792. doi:10.1056/NEJM199203193261202
Catarci M, Gentileschi P, Papi C, Carrara A, Marrese R, Gaspari AL, Grassi GB (2004) Evidence-based appraisal of antireflux fundoplication. Ann Surg 239:325–337
Bell RCW, Cadière G-B (2011) Transoral rotational esophagogastric fundoplication: technical, anatomical, and safety considerations. Surg Endosc 25:2387–2399. doi:10.1007/s00464-010-1528-6
Wendling MR, Melvin WS, Perry KA (2013) Impact of transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) on subjective and objective GERD indices: a systematic review of the published literature. Surg Endosc 27:3754–3761. doi:10.1007/s00464-013-2961-0
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol 62:1006–1012. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L (1998) Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med 17:2815–2834
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR (2007) Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials 8:16. doi:10.1186/1745-6215-8-16
Higgins J, Green S, Collaboration C (2008) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley, London
Moga C, Guo B, Schopflocher D, Harstall C (2012) Development of a quality appraisal tool for case series studies using a modified Delphi technique. Inst. Health Econ, Edmont
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:1–10. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
Trad KS, Barnes WE, Simoni G, Shughoury AB, Mavrelis PG, Raza M, Heise JA, Turgeon DG, Fox MA (2015) Transoral incisionless fundoplication effective in eliminating GERD symptoms in partial responders to proton pump inhibitor therapy at 6 months: the TEMPO randomized clinical trial. Surg Innov 22:26–40. doi:10.1177/1553350614526788
Trad KS, Simoni G, Barnes WE, Shughoury AB, Raza M, Heise JA, Turgeon DG, Fox MA, Mavrelis PG (2014) Efficacy of transoral fundoplication for treatment of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease incompletely controlled with high-dose proton-pump inhibitors therapy: a randomized, multicenter, open label, crossover study. BMC Gastroenterol 14:174. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-14-174
Cadière GB, Rajan A, Germay O, Himpens J (2008) Endoluminal fundoplication by a transoral device for the treatment of GERD: a feasibility study. Surg Endosc 22:333–342. doi:10.1007/s00464-007-9618-9
Cadière G-B, Van Sante N, Graves JE, Gawlicka AK, Rajan A (2009) Two-year results of a feasibility study on antireflux transoral incisionless fundoplication using EsophyX. Surg Endosc 23:957–964. doi:10.1007/s00464-009-0384-8
Håkansson B, Montgomery M, Cadiere GB, Rajan A, Bruley des Varannes S, Lerhun M, Coron E, Tack J, Bischops R, Thorell A, Arnelo U, Lundell L (2015) Randomised clinical trial: transoral incisionless fundoplication vs. sham intervention to control chronic GERD. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 42:1261–1270. doi:10.1111/apt.13427
Hunter JG, Kahrilas PJ, Bell RCW, Wilson EB, Trad KS, Dolan JP, Perry KA, Oelschlager BK, Soper NJ, Snyder BE, Burch MA, Melvin WS, Reavis KM, Turgeon DG, Hungness ES, Diggs BS (2015) Efficacy of transoral fundoplication vs omeprazole for treatment of regurgitation in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology 148(324–333):e5. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2014.10.009
Witteman BPL, Conchillo JM, Rinsma NF, Betzel B, Peeters A, Koek GH, Stassen LPS, Bouvy ND (2015) Randomized controlled trial of transoral incisionless fundoplication vs. proton pump inhibitors for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 110:531–542. doi:10.1038/ajg.2015.28
Rinsma NF, Farré R, Bouvy ND, Masclee AM, Conchillo JM (2015) The effect of endoscopic fundoplication and proton pump inhibitors on baseline impedance and heartburn severity in GERD patients. Neurogastroenterol Motil Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc 27:220–228. doi:10.1111/nmo.12468
Yew KC, Chuah S-K, Yew KC, Chuah S-K (2013) Antireflux endoluminal therapies: past and Present. Gastroenterol Res Pract Gastroenterol Res Pract 2013:e481417. doi:10.1155/2013/481417
Testoni PA, Vailati C (2012) Transoral incisionless fundoplication with EsophyX® for treatment of gastro-oesphageal reflux disease. Dig Liver Dis Off J Ital Soc Gastroenterol Ital Assoc Study Liver 44:631–635. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2012.03.019
Cadière G-B, Buset M, Muls V, Rajan A, Rösch T, Eckardt AJ, Weerts J, Bastens B, Costamagna G, Marchese M, Louis H, Mana F, Sermon F, Gawlicka AK, Daniel MA, Devière J (2008) Antireflux transoral incisionless fundoplication using EsophyX: 12-month results of a prospective multicenter study. World J Surg 32:1676–1688. doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9594-9
Repici A, Fumagalli U, Malesci A, Barbera R, Gambaro C, Rosati R (2010) Endoluminal fundoplication (ELF) for GERD using EsophyX: a 12-month follow-up in a single-center experience. J Gastrointest Surg 14:1–6. doi:10.1007/s11605-009-1077-2
Demyttenaere SV, Bergman S, Pham T, Anderson J, Dettorre R, Melvin WS, Mikami DJ (2010) Transoral incisionless fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease in an unselected patient population. Surg Endosc 24:854–858. doi:10.1007/s00464-009-0676-z
Testoni PA, Corsetti M, Di Pietro S, Castellaneta AG, Vailati C, Masci E, Passaretti S (2010) Effect of transoral incisionless fundoplication on symptoms, PPI use, and pH-impedance refluxes of GERD patients. World J Surg 34:750–757. doi:10.1007/s00268-010-0394-7
Frazzoni M, Conigliaro R, Manta R, Melotti G (2011) Reflux parameters as modified by EsophyX or laparoscopic fundoplication in refractory GERD: EsophyX fundoplication in refractory GERD. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 34:67–75. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04677.x
Petersen RP, Filippa L, Wassenaar EB, Martin AV, Tatum R, Oelschlager BK (2012) Comprehensive evaluation of endoscopic fundoplication using the EsophyXTM device. Surg Endosc 26:1021–1027. doi:10.1007/s00464-011-1989-2
Testoni PA, Vailati C, Testoni S, Corsetti M (2012) Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF 2.0) with EsophyX for gastroesophageal reflux disease: long-term results and findings affecting outcome. Surg Endosc 26:1425–1435. doi:10.1007/s00464-011-2050-1
Witteman BPL, Strijkers R, de Vries E, Toemen L, Conchillo JM, Hameeteman W, Dagnelie PC, Koek GH, Bouvy ND (2012) Transoral incisionless fundoplication for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease in clinical practice. Surg Endosc 26:3307–3315. doi:10.1007/s00464-012-2324-2
Bell RCW, Mavrelis PG, Barnes WE, Dargis D, Carter BJ, Hoddinott KM, Sewell RW, Trad KS, Gill BD, Ihde GM (2012) A prospective multicenter registry of patients with chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease receiving transoral incisionless fundoplication. J Am Coll Surg 215:794–809. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.07.014
Muls V, Eckardt AJ, Marchese M, Bastens B, Buset M, Devière J, Louis H, Rajan A, Daniel MA, Costamagna G (2013) Three-year results of a multicenter prospective study of transoral incisionless fundoplication. Surg Innov 20:321–330
Wilson EB, Barnes WE, Mavrelis PG, Carter BJ, Bell RCW, Sewell RW, Ihde GM, Dargis D, Hoddinott KM, Shughoury AB, Gill BD, Fox MA, Turgeon DG, Freeman KD, Gunsberger T, Hausmann MG, Leblanc KA, Deljkich E, Trad KS (2014) The effects of transoral incisionless fundoplication on chronic GERD patients: 12-month prospective multicenter experience. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 24:36–46. doi:10.1097/SLE.0b013e3182a2b05c
Testoni PA, Testoni S, Mazzoleni G, Vailati C, Passaretti S (2015) Long-term efficacy of transoral incisionless fundoplication with Esophyx (Tif 2.0) and factors affecting outcomes in GERD patients followed for up to 6 years: a prospective single-center study. Surg Endosc 29:2770–2780. doi:10.1007/s00464-014-4008-6
Funk LM, Zhang JY, Drosdeck JM, Melvin WS, Walker JP, Perry KA (2015) Long-term cost-effectiveness of medical, endoscopic and surgical management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surgery 157:126–136. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2014.05.027
Acknowledgments
Guarantor of the article: HUANG Xiaoquan. The authors are grateful to Center of Evidence-Based Medicine, Fudan University, 200032, Shanghai, China.
Author contributions
HUANG Xiaoquan contributed to study conception and design; article retrieval; data extraction; analysis and interpretation of data; risk of bias rating; statistical analyses; manuscript writing. CHEN Shiyao helped with study conception and design; data extraction; analysis and interpretation of data; statistical analyses. ZHAO Hetong is acknowledged for article retrieval; data extraction; analysis and interpretation of data; risk of bias rating. ZENG Xiaoqing drafted the manuscript and provided supervision. LIAN Jingjing contributed to analysis and interpretation of data; risk of bias rating; TSENG YuJen: manuscript writing and modification. CHEN Jie critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript, including the authorship list.
Funding
This work was supported by the Foundation of Discipline Construction of Evidence-based Medicine Center, Zhongshan Hospital, China. And the study was partly supported by the Fund of National Science & Technology Pillar Program (No. 2013BAI09B14). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
CHEN Shiyao received grants from National Science and Technology Pillar Program. The funder had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. HUANG Xiaoquan, CHEN Shiyao, ZHAO Hetong, ZENG Xiaoqing, LIAN Jingjing, TSENG Yujen, CHEN Jie have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Chen, S., Zhao, H. et al. Efficacy of transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) for the treatment of GERD: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 31, 1032–1044 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5111-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5111-7