Abstract
Background
The role of fundoplication in addition to hiatal hernia repair has been controversial. The aim of this study was to compare quality of life related to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in patients who underwent intra-thoracic stomach repair with and without fundoplication. We proposed that the group without a fundoplication would have poorer quality of life due to continued symptoms.
Methods
All patients undergoing foregut surgery at the Creighton University Esophageal Center are entered in a prospectively maintained database. The database was queried to identify patients who underwent surgery for a near complete (>75 % of stomach in chest) intra-thoracic stomach with gastric volvulus between 2004 and 2013. A questionnaire was derived from the Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia and Frequency Scale for Symptoms of GERD questionnaires to assess for symptoms related to reflux, and this questionnaire was administered by phone.
Results
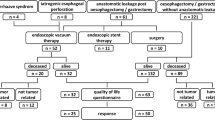
A total of 150 patients underwent repair of ITS during the study period. A total of 109 patients had ITS repair with fundoplication, while 41 had only ITS repair. Follow-up was available in 54 % of patients in the fundoplication group (median follow-up of 5.2 years) and in 49 % of patients in the non-fundoplication group (median follow-up of 4 years). Significantly, more patients woke up at night (p < 0.01) and found themselves coughing around mealtime (p < 0.01) in the fundoplication group. Patients in the non-fundoplication group had significantly more daytime reflux (p = 0.02). Despite these symptoms, only one patient in the fundoplication group and no patients in the non-fundoplication group admitted that these symptoms were severe enough to severely affect their quality of life. All other patients contacted felt satisfied, and >80 % rated their quality of life as either good or excellent.
Conclusions
We conclude that there is not a significant difference in quality-of-life parameters on long-term follow-up between patients undergoing ITS repair with or without fundoplication.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morris-Stiff G, Hassn A (2008) Laparoscopic paraoesophageal hernia repair: fundoplication is not usually indicated. Hernia. doi:10.1007/s10029-008-0332-x
Jobe BA, Hunter JG, Peters JH (2010) Esophagus and diaphragmatic hernia. In: Brunicardi FC, Andersen DK, Rilliar TR, Dunn DL, Hunter JG, Matthews JB, Pollock RE (eds) Schwartz’s principles of surgery, 9th edn. McGraw Hill Medical, New York. http://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com.cuhsl.creighton.edu/content.aspx?bookid=352&Sectionid=40039767. Accessed 26 Oct 2014
Polomsky M, Hu R, Sepesi B, O’Connor M, Qui X, Raymond DP, Litle VR, Jones CE, Watson TJ, Peters JH (2010) A population-based analysis of emergent vs. elective hospital admissions for an intrathroacic stomach. Surg Endosc. doi:10.1007/s00464-009-0755-1
Cuschieri A, Shimi S, Nathanson LK (1992) Laparoscopic reduction, crural repair, and fundoplication of large hiatal hernia. Am J Surg. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/000296109290046T. April 1992; Accessed 26 Oct 2014
Kohn GP, Price RR, DeMeester SR, Zehetner J, Muensterer OJ, Awad Z, Mittal SK, Richardson WS, Stefanidis D, Fanelli RD (2013) Guidelines for the management of hiatal hernia. Surg Endosc. doi:10.1007/s00464-013-3173-3
Marano L, Schettino M, Profidia R, Grassia M, Petrillo M, Esposito G, Braccio B, Gallo PL, Pezzella M, Cosenza A, Izzo G, Di Martino N (2014) The laparoscopic hiatoplasty with antireflux surgery is a safe and effective procedure to repair giant hiatal hernia. BMC Surg. doi:10.1186/1471-2482-14-1
Yano F, Stadlhuber RJ, Tsuboi K, Gerhardt J, Filipi CJ, Mittal SK (2009) Outcomes of surgical treatment of intrathoracic stomach. Dis Esophagus. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2050.2008.00919.x
Wikland IK, Junghard O, Grace E, Talley NJ, Kamm M, Veldhuyzen van Zanten S, Paré P, Chiba N, Leddin DS, Bigard MA, Colin R, Schoenfeld P (1998) Quality of life in reflux and dyspepsia patients. Psychometric documentation of a new disease specific questionnaire (QOLRAD). Eur J Surg Suppl. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/10027672. 1998. Accessed 13 Feb 2014
Kusano M, Shimoyama Y, Sugimoto S, Kawamura O, Maeda M, Minashi K, Kuribayashi S, Higuchi T, Zai H, Ino K, Horikoshi T, Sugiyama T, Toki M, Ohwada T, Mori M (2004) Development and evaluation of FSSG: frequency scale for the symptoms of GERD. J Gastroenterol. doi:10.1007/s00535-004-1417-7
Kulich KR, Madisch A, Pacini F, Piqué JM, Regula J, Van Rensburg CJ, Ujszászy L, Carlsson J, Halling K, Wiklund IK (2008) Reliability and validity of the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) questionnaire in dyspepsia: a six-country study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-6-12
Mittal SK, Bikhchandani J, Gurney O, Yano F, Lee T (2011) Outcomes after repair of the intrathroacic stomach: objective follow-up of up to 5 years. Surg Endosc. doi:10.1007/s00464-010-1219-3
Mittal SK (2014) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. In: Luketich JD, Landreneau RJ, Pennathur A (eds) Master techniques in surgery: esophageal surgery. Wolters Kluwer Health, Philadelphia, pp 1–13
Stylopoulos N, Gazelle GS, Rattner DW (2008) Paraesophageal hernias: Operation or observation? Ann Surg. doi:10.1097/01.SLA.0000029000.06861.17
Williamson WA, Ellis FH Jr, Streitz JM Jr, Shahian DM (1993) Para-esophageal hiatal hernia: is an antireflux procedure necessary? Ann Thorac Surg. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/000349759390878L. Sep 1993; Accessed 26 Oct 2014
Fuller CB, Hagen JA, DeMeester TR, Peters JH, Ritter M, Bremmer CG (1996) The role of fundoplication in the treatment of type II paraesophageal hernia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. doi:10.1016/S0022-5223(96)70319-7
Müller-Stich BP, Achtstätter V, Diener MK, Gondan M, Warschkow R, Marra F, Zerz A, Gutt CN, Bϋchler MW, Linke GR (2015) Repair of paraesophageal hiatal hernias—Is a fundoplication needed? A randomized controlled pilot trial. J Am Coll Surg. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.03.003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Drs. Wendy Jo Svetanoff, Sumeet K. Mittal, Pradeep Pallati, Kalyana Nandipati, and Tommy Lee have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Svetanoff, W.J., Pallati, P., Nandipati, K. et al. Does the addition of fundoplication to repair the intra-thoracic stomach improve quality of life?. Surg Endosc 30, 4590–4597 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4796-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4796-y