Abstract
Background
A prerequisite for endoscopic treatment (ET) of not only mucosal, but also submucosal early adenocarcinoma of the esophagus (EAC) would be a rate of lymph node (LN) metastasis below the mortality rate of esophagectomy (2–5 %). The aim of the present study was to evaluate the rate of LN metastasis in patients with pT1b sm1 EAC.
Methods
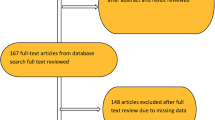
1996–2010, 1,718 patients with suspicion of EAC were referred to the Department of Internal Medicine II at HSK Wiesbaden. In 123/1718 patients, the suspicion (endoscopic ultrasound, EUS) or definitive diagnosis of sm1 EAC (ER/surgery) was made. Rate of LN metastasis was analyzed separately for low-risk (LR; G1–2, L0, V0) and high-risk lesions (HR; G3, L1, V1; ≥ 1 risk factor). LN metastasis was only evaluated in patients who had a proven maximum invasion depth of sm1 (ER and/or surgery), and who in case of ET had a follow-up (FU) by EUS of at least 24 months.
Results
Of the 72/123 patients included into the study, 49 patients had LR (68 %) and 23 HR lesions (32 %). In endoscopically treated LR patients (37/49), mean EUS-FU was 60 ± 30 mo (range 25–146); in HR patients undergoing ET (6/23), it was 63 ± 17 mo (46–86; p = 0.4). Mean number of resected LN was 27 ± 16 (12–62) in operated LR patients and 27 ± 10 (12–47) in HR-patients. The rate of LN metastasis was 2 % in the LR (1 patient) and 9 % in the HR group (2 patients; p = 0.24). Mortality of esophagectomy was 3 %.
Conclusions
The rate of LN metastasis in pT1b sm1 early adenocarcinoma with histological LR pattern was lower than the mortality rate of esophagectomy. ER may therefore be used alternatively to surgery in this group of patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ell C, May A, Gossner L et al (2000) Endoscopic mucosal resection of early cancer and high-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology 118(4):670–677
Ell C, May A, Pech O, Gossner L, Guenter E, Behrens A et al (2007) Curative endoscopic resection of early esophageal adenocarcinomas (Barrett’s cancer). Gastrointest Endosc 65(1):3–10
Pech O, Behrens A, May A, Nachbar L, Gossner L, Rabenstein T et al (2008) Long-term results and risk factor analysis for recurrence after curative endoscopic therapy in 349 patients with high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia and mucosal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut 57(9):1200–1206
Pech O, May A, Manner H et al (2014) Long-term efficacy and safety of endoscopic resection for patients with mucosal adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Gastroenterology 146(3):652–660
Nijhawan PK, Wang KK (2000) Endoscopic mucosal resection for lesions with endoscopic features suggestive of malignancy and high-grade dysplasia within Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 52(3):328–332
May A, Gossner L, Pech O, Müller H, Vieth M, Stolte M et al (2002) Intraepithelial high-grade neoplasia and early adenocarcinoma in short-segment Barrett’s esophagus (SSBE): curative treatment using local endoscopic treatment techniques. Endosc 34(8):604–610
Seewald S, Akaraviputh T, Seitz U, Brand B, Groth S, Mendoza G et al (2003) Circumferential EMR and complete removal of Barrett’s epithelium: a new approach to management of Barrett’s esophagus containing high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia and intramucosal carcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc 57(7):854–859
Giovannini M, Bories E, Pesenti C, Moutardier V, Monges G, Danisi C et al (2004) Circumferential endoscopic mucosal resection in Barrett’s esophagus with high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia or mucosal cancer. Preliminary results in 21 patients. Endoscopy 36(9):782–787
Peters FP, Kara MA, Rosmolen WD, Aalders MCG, ten Kate FJW, Bultje BC et al (2005) Endoscopic treatment of high-grade dysplasia and early stage cancer in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 61(4):506–514
Behrens A, May A, Gossner L, Günter E, Pech O, Vieth M et al (2005) Curative treatment for high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Endosc 37(10):999–1005
Conio M, Cameron A, Chak A, Blanchi S, Filiberti R (2005) Endoscopic treatment of high-grade dysplasia and early cancer in Barrett’s oesophagus. Lancet Oncol 6:311–321
Larghi A, Lightdale CJ, Ross AS, Fedi P, Hart J, Rotterdam H et al (2007) Long-term follow-up of complete Barrett’s eradication endoscopic mucosal resection (CBE-EMR) for the treatment of high grade dysplasia and intramucosal carcinoma. Endosc 39(12):1086–1091
Hölscher AH, Bollschweiler E, Schneider PM, Siewert JR (1997) Early adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s oesophagus. Br J Surg 84(10):1470–1473
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ (2003) Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 349(23):2241–2252
Birkmeyer JD, Siewers AE, Finlayson EVA, Stukel TA, Lucas FL, Batista I et al (2002) Hospital volume and surgical mortality in the United States. N Engl J Med 346(15):1128–1137
Birkmeyer JD, Stukel TA, Siewers AE, Goodney PP, Wennberg DE, Lucas FL (2003) Surgeon volume and operative mortality in the United States. N Engl J Med 349(22):2117–2127
Thomas P, Doddoli C, Neville P, Pons J, Lienne P, Giudicelli R et al (1996) Esophageal cancer resection in the elderly. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 10(11):941–946
Braghetto I, Csendes A, Cardemil G, Burdiles P, Korn O, Valladares H (2006) Open transthoracic or transhiatal esophagectomy versus minimally invasive esophagectomy in terms of morbidity, mortality and survival. Surg Endosc 20(11):1681–1686
Hölscher AH, Vallböhmer D, Bollschweiler E (2008) Early Barrett’s carcinoma of the esophagus. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 14(6):347–354
Rice TW (2006) Pro: esophagectomy is the treatment of choice for high-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 101(10):2177–2179
Buskens CJ, Westerterp M, Lagarde SM, Bergman JJGHM, ten Kate FJW, van Lanschot JJB (2004) Prediction of appropriateness of local endoscopic treatment for high-grade dysplasia and early adenocarcinoma by EUS and histopathologic features. Gastrointest Endosc 60(5):703–710
Westerterp M, Koppert LB, Buskens CJ, Tilanus HW, ten Kate FJW, Bergman JJHGM et al (2005) Outcome of surgical treatment for early adenocarcinoma of the esophagus or gastro-esophageal junction. Virchows Arch 446(5):497–504
Nigro JJ, Hagen JA, DeMeester TR, DeMeester SR, Peters JH, Oberg S et al (1999) Prevalence and location of nodal metastases in distal esophageal adenocarcinoma confined to the wall: implications for therapy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 117(1):16–23; discussion 23–5
Stein HJ, Feith M, Bruecher BLDM, Naehrig J, Sarbia M, Siewert JR (2005) Early esophageal cancer: pattern of lymphatic spread and prognostic factors for long-term survival after surgical resection. Ann Surg 242(4):566–573; discussion 573–575
Stein HJ, Feith M, Mueller J, Werner M, Siewert JR (2000) Limited resection for early adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus. Ann Surg 232(6):733–742
Bollschweiler E, Baldus SE, Schröder W, Prenzel K, Gutschow C, Schneider PM et al (2006) High rate of lymph-node metastasis in submucosal esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. Endosc 38(2):149–156
Ancona E, Rampado S, Cassaro M, Battaglia G, Ruol A, Castoro C et al (2008) Prediction of Lymph Node Status in Superficial Esophageal Carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 15(11):3278–3288
Badreddine R, Prasad G, Lewis J et al (2010) Depth of submucosal invasion does not predict lymph node metastasis and survival of patients with esophageal carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol H 8:248–253
Sepesi B, Watson TJ, Zhou D, Polomsky M, Litle VR, Jones CE et al (2010) Are Endoscopic Therapies Appropriate for Superficial Submucosal Esophageal Adenocarcinoma? An Analysis of Esophagectomy Specimens. J Am Coll Surg 210(4):418–427
Hoelscher A, Bollschweiler E, Schroeder W et al (2011) Prognostic impact of upper, middle, and lower third mucosal or submucosal infiltration in early esophageal cancer. Ann Surg 254:802–808
Griffin SM, Burt AD, Jennings NA (2011) Lymph node metastasis in early esophageal adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg 254:731–737
Manner H, May A, Pech O, Gossner L, Rabenstein T, Günter E et al (2008) Early Barrett’s Carcinoma With “Low-Risk” Submucosal Invasion: Long-Term Results of Endoscopic Resection With a Curative Intent. Am J Gastroenterol 103(10):2589–2597
Manner H, Pech O, Heldmann Y et al (2013) Efficacy, safety, and Long-Term Results of Endoscopic Treatment for Early-Stage Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus with low-risk sm1 invasion. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(6):630–635
Alvarez Herrero L, Pouw RE, van Vilsteren FG, ten Kate FJW, Visser M, van Berge Henegouwen MI et al (2010) Risk of lymph node metastasis associated with deeper invasion by early adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and cardia: study based on endoscopic resection specimens. Endoscopy 42(12):1030–1036
Association Japanese Gastric Cancer (1998) Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma - 2nd English Edition -. Gastric Cancer 1(1):10–24
Koop H, Schepp W, Müller-Lissner S, Madisch A, Micklefield G, Messmann H et al (2005) Consensus Conference of the DGVS on Gastroesophageal Reflux. Z Gastroenterol 43(2):163–164
Hamilton S, Aalton L (eds) (2000) Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Digestive System: World Health Organization classification of tumours. International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) Press, Lyon
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind CH (eds) (2009) TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 7th edn. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, pp 66–72
World Medical Association declaration of Helsinki (1997) Recommendations guiding physicians in biomedical research involving human subjects. JAMA 277(11):925–926
Behrens A, Pech O, Graupe F, May A, Lorenz D, Ell C (2011) Barrett’s adenocarcinoma of the esophagus—better outcomes through new methods of diagnosis and treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int 108(18):313–319
Birkmeyer JD, Sievers AE, Finlayson EV et al (2002) Hospital volume and surgical mortality in the United States. N Engl J Med 346(15):1128–1137
van Sandick JW, van Lanschot JJ, ten Kate FJ, Offerhaus GJ, Fockens P, Tytgat GN et al (2000) Pathology of early invasive adenocarcinoma of the esophagus or esophagogastric junction: implications for therapeutic decision making. Cancer 88(11):2429–2437
Rice TW, Boyce GA, Sivak MV, Adelstein DJ, Kirby TJ (1992) Esophageal carcinoma: esophageal ultrasound assessment of preoperative chemotherapy. Ann Thorac Surg 53(6):972–977
Pech O, May A, Günter E et al (2006) The impact of endoscopic ultrasound and computed tomography on the TNM staging of early cancer in Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 101(10):2223–2229
Dresner SM, Griffin SM (2000) Pattern of recurrence following radical oesophagectomy with two-field lymphadenectomy. Br J Surg 87(10):1426–1433
Pech O, May A, Manner H, et al (2011) Endoscopic resection in 953 patients with mucosal Barrett’s cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 73(4); Supplement, Page AB1 46 (abstract)
Rice TW, Zuccaro G, Adelstein DJ, Rybicki LA, Blackstone EH, Goldblum JR (1998) Esophageal carcinoma: depth of tumor invasion is predictive of regional lymph node status. Ann Thorac Surg 65(3):787–792
Liu L, Hofstetter WL, Rashid A, Swisher SG, Correa AM, Ajani JA et al (2005) Significance of the depth of tumor invasion and lymph node metastasis in superficially invasive (T1) esophageal adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 29(8):1079–1085
Tian J, Ganapathy AP, Lutzke LS et al (2011) Outcomes of T1b esophageal carcinoma patients. Gastrointest Endosc 74:1201–1206
Disclosures
Authors Hendrik Manner, Oliver Pech, Yvonne Heldmann, Andrea May, Michael Pauthner, Dietmar Lorenz, Annette Fisseler-Eckhoff, Manfred Stolte, Michael Vieth, and Christian Ell have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study formed the basis for Yvonne Heldmann’s doctoral thesis at the University of Mainz, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manner, H., Pech, O., Heldmann, Y. et al. The frequency of lymph node metastasis in early-stage adenocarcinoma of the esophagus with incipient submucosal invasion (pT1b sm1) depending on histological risk patterns. Surg Endosc 29, 1888–1896 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3881-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3881-3