Abstract
Background
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) is a promising treatment option for motor disorders of the esophagus. The purpose of this study was to assess quality of life (QOL) postoperatively.
Methods
All patients who presented to our institution for surgical treatment of achalasia after 2011 were asked to complete QOL (SF-36), dysphagia, reflux severity index, and GERD questionnaires in clinic preoperatively and postoperatively at approximately 3 weeks, 6 months, and 1 year.
Results
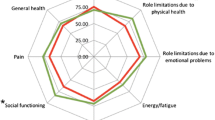
Those patients who underwent a POEM procedure (n = 37) demonstrated a significant improvement in dysphagia scores, reflux severity scores, and GERD scores (p < 0.05) at each time point. SF-36 questionnaires specifically demonstrated a significant improvement in several concepts. At 3 weeks, emotional well-being scores were significantly higher (p = 0.006). At 6 months, the following concepts were significantly higher: emotional well-being (p = 0.039), social functioning (p = 0.038), and general health (p = 0.029). At 1 year, the following concepts were significantly higher: role limitations due to physical health (p = 0.001) and social functioning (p = 0.002).
Conclusion
There is a significant improvement in several measures of QOL after POEM, which is comparable to that seen after laparoscopic Heller myotomy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Francis DL, Katzka DA (2010) Achalasia: update on the disease and its treatment. Gastroenterology 139:369–374
Annese V, Basciani M, Perri F, Lombardi G, Frusciante V, Simone P, Andriulli A, Vantrappen G (1996) Controlled trial of botulinum toxin injection versus placebo and pneumatic dilation in achalasia. Gastroenterology 111:1418–1424
Allescher HD, Storr M, Seige M, Gonzales-Donoso R, Ott R, Born P, Frimberger E, Weigert N, Stier A, Kurjak M, Rösch T, Classen M (2001) Treatment of achalasia: botulinum toxin injection vs. pneumatic balloon dilation. A prospective study with long-term follow-up. Endoscopy 33:1007–1017
Leyden JE, Moss AC, MacMathuna P (2006) Endoscopic pneumatic dilation versus botulinum toxin injection in the management of primary achalasia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD005046
Kroupa R, Hep A, Dolina J, Valek V, Matyasova Z, Prokesova J, Mrazova J, Sedmik J, Novotny I (2010) Combined treatment of achalasia–botulinum toxin injection followed by pneumatic dilatation: long-term results. Dis Esophagus 23:100–105
Parise P, Santi S, Solito B, Pallabazzer G, Rossi M (2011) Laparoscopic Heller myotomy plus Dor fundoplication in 137 achalasic patients: results on symptoms relief and successful outcome predictors. Updates Surg 63:11–15
Kilic A, Schuchert MJ, Pennathur A, Gilbert S, Landreneau RJ, Luketich JD (2009) Long-term outcomes of laparoscopic Heller myotomy for achalasia. Surgery 146:826–831 (discussion 831–833)
Zaninotto G, Costantini M, Rizzetto C, Zanatta L, Guirroli E, Portale G, Nicoletti L, Cavallin F, Battaglia G, Ruol A, Ancona E (2008) Four hundred laparoscopic myotomies for esophageal achalasia: a single centre experience. Ann Surg 248:986–993
Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, Sato Y, Kaga M, Suzuki M, Satodate H, Odaka N, Itoh H, Kudo S (2010) Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy 42:265–271
Hungness ES, Teitelbaum EN, Santos BF, Arafat FO, Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ, Soper NJ (2013) Comparison of perioperative outcomes between peroral esophageal myotomy (POEM) and laparoscopic Heller myotomy. J Gastrointest Surg 17:228–235
Eleftheriadis N, Inoue H, Ikeda H, Onimaru M, Yoshida A, Hosoya T, Maselli R, Kudo SE (2012) Training in peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Ther Clin Risk Manag 8:329–342
Swanström LL, Rieder E, Dunst CM (2011) A stepwise approach and early clinical experience in peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia and esophageal motility disorders. J Am Coll Surg 213:751–756
Costamagna G, Marchese M, Familiari P, Tringali A, Inoue H, Perri V (2012) Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for oesophageal achalasia: preliminary results in humans. Dig Liver Dis 44:827–832
von Rahden BH, Filser J, Reimer S, Inoue H, Germer CT (2014) Peroral endoscopic myotomy for treatment of achalasia: literature review and own initial experience. Chirurg 85(5):420–432
Ujiki MB, Yetasook AK, Zapf M, Linn JG, Carbray JM, Denham W (2013) Peroral endoscopic myotomy: a short-term comparison with the standard laparoscopic approach. Surgery 154:893–897 (discussion 897–900)
Velanovich V (2007) Behavior and analysis of 36-item Short-Form Health Survey data for surgical quality-of-life research. Arch Surg 142(5):473-477 (discussion 478)
Eckardt AJ, Eckardt VF (2009) Current clinical approach to achalasia. World J Gastroenterol 15:3969–3975
Vaezi MF, Richter JE (1999) Diagnosis and management of achalasia. American College of Gastroenterology Practice Parameter Committee. Am J Gastroenterol 94:3406–3412
Campos GM, Vittinghoff E, Rabl C, Takata M, Gadenstätter M, Lin F, Ciovica R (2009) Endoscopic and surgical treatments for achalasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg 249:45–57
Swanstrom LL, Kurian A, Dunst CM, Sharata A, Bhayani N, Rieder E (2012) Long-term outcomes of an endoscopic myotomy for achalasia: the POEM procedure. Ann Surg 256:659–667
Youssef Y, Richards WO, Sharp K, Holzman M, Sekhar N, Kaiser J, Torquati A (2007) Relief of dysphagia after laparoscopic Heller myotomy improves long-term quality of life. J Gastrointest Surg 11:309–313
Katilius M, Velanovich V (2001) Heller myotomy for achalasia: quality of life comparison of laparoscopic and open approaches. J Soc Laparoendosc Surg 5:227–231
Disclosures
Yalini Vigneswaran, Ryota Tanaka, Matthew Gitelis, Joann Carbray, and Michael B. Ujiki have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Poster presentation, Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons, April 2014 meeting, Salt Lake City, Utah.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vigneswaran, Y., Tanaka, R., Gitelis, M. et al. Quality of life assessment after peroral endoscopic myotomy. Surg Endosc 29, 1198–1202 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3793-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3793-2