Abstract
Background
Accurately aiming laser energy at a target from a two-dimensional endoscopic view is difficult during endoscopic laser surgery, particularly when the endoscope and the laser fiber are misaligned. We developed a composite optical fiberscope (COF) that can simultaneously visualize a target area and perform laser irradiation. The identical orientation of the endoscope and the laser fiber allows intuitive aiming at a target, even from a two-dimensional endoscopic view.
Methods
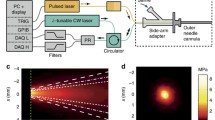
We developed an ultrasmall COF (1.1-mm diameter) with a central cauterizing laser fiber surrounded by imaging and illumination fibers as a tool for various surgical applications. Porcine mesenteric blood vessels were laser irradiated in vivo and the procedure was filmed using ultrahigh-speed (max 1,000,000 frames per second) and thermographic cameras. Blood flow and vessel diameters were measured before and after laser irradiation.
Results
The target vessels were highly visible and laser energy was delivered to the center of the view. Images from the ultrahigh-speed camera showed the blocking of the target vessel by the laser irradiation. The irradiated point initially became constricted, then discolored, and then decreased in size. Blood flow was decreased by 81.7% after laser irradiation and the diameter of the vessels at the irradiated point was approximately 46–48% smaller than that of the unirradiated vessels. Medical doctors also confirmed that the blood vessel was blocked after the experiments.
Conclusions
Our new laser surgery device may be useful for many surgical applications because it allows simultaneous diagnosis and treatment as well as intuitive aiming at a target despite its ultrasmall 1.1-mm diameter.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kohl T (2010) Minimally invasive fetoscopic interventions: an overview in 2010. Surg Endosc 24(8):2056–2067
Senat MV, Deprest J, Boulvain M, Paupe A, Winer N, Ville Y (2004) Endoscopic laser surgery versus serial amnioreduction for severe twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome. New Engl J Med 351(2):136–144
Noguchi M, Aoki E, Yoshida D, Kobayashi E, Omori S, Muragaki Y, Iseki H, Nakamura K, Sakuma I (2006) A novel robotic laser ablation system for precision neurosurgery with intraoperative 5-ALA-induced PpIX fluorescence detection. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 9(Pt 1):543–550
Shah RJ, Shen JH, Joos KM (2007) Endoscopic free electron laser technique development for minimally invasive optic nerve sheath fenestration. Laser Surg Med 39(7):569–589
Lee J, Gianduzzo TR (2009) Advances in laser technology in urology. Urol Clin North Am 36(2):189–198
Ansarin M, Santoro L, Cattaneo A, Massaro MA, Calabrese L, Giugliano G, Maffini F, Ostuni A, Chiesa F (2009) Laser surgery for early glottic cancer: impact of margin status on local control and organ preservation. Arch Otolaryngol 135(4):385–390
Pedreira DA, Acácio GL, Drummond CL, Oliveira RC, Deustch AD, Taborda WG (2005) Laser for the treatment of twin to twin transfusion syndrome. Acta Cir Bras 20(6):478–481
Oka K, Naganawa A, Yamashita H, Nakamura T, Chiba T (2008) Composite-type optical fiberscope for laser surgery for twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome. Lect Notes Comput Sci 5128:251–259
Oka K, Seki T, Naganawa A, Yamashita H, Kim K, Chiba T (2010) The development of composite-type optical fiberscope system for fetoscopic laser photocoagulation of chorionic plate anastomosing vessels (FLPC). Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 19(2):94–99
Seki T, Oka K, Naganawa A, Yamashita H, Kim K, Chiba T (2009) Blood flow measurement system for fetoscopic laser photocoagulation of chorionic plate anastomosing vessels. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 18(6):350–355
Seki T, Oka K, Naganawa A, Yamashita H, Kim K, Chiba T (2010) Laser distance measurement using a newly developed composite-type optical fiberscope for fetoscopic laser surgery. Opt Lasers Eng 48:974–977
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology (SCF) commissioned by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan.
Disclosures
Drs. Kiyoshi Oka, Takeshi Seki, Akihiro Naganawa, Keri Kim, and Toshio Chiba have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oka, K., Seki, T., Naganawa, A. et al. A novel ultrasmall composite optical fiberscope. Surg Endosc 25, 2368–2371 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1540-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1540-x