Abstract
Background
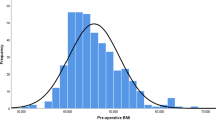
It has been hypothesized that patients who are super-supermorbidly obese, defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 60 kg/m2 or higher, have an increased rate of postoperative complications. As surgical techniques and operator experience with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass improved with time, the selection criteria have expanded to include the super-supermorbidly obese. We hypothesize that a higher BMI does not predict a higher postoperative complication rate.
Methods
The prospectively collected database for our Accredited Bariatric Program was queried for all laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass procedures performed between January 2004 and July 2006. All cases were performed by a single surgeon at a tertiary-care center. Average postoperative follow-up time was 1 year. Patients were stratified into two groups: BMI < 60 kg/m2 and BMI ≥ 60 kg/m2. The number of postoperative complications was compared between the two groups using a chi-square method with Yates correction.
Results
One hundred and sixty-nine patients with adequate follow-up data were identified during the study period. Of these, 148 patients had BMI < 60 kg/m2 (group 1) and 21 had BMI ≥ 60 kg/m2 (group 2). There were 28 (19%) total complications in group 1, and 4 (19%) total complications in group 2. There was no statistical difference between the two groups (p = 0.98). Stricture rate was 10% in group 1 and 5% in group 2.
Conclusion
Patients with BMI ≥ 60 kg/m2 do not have a higher postoperative morbidity compared with other patients undergoing laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. The stricture rate is less in patients with BMI ≥ 60 kg/m2 compared with other patients. Longer follow-up is required to detect complications that occur after 1 year. Our study shows that laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass can be safely performed on the super-supermorbidly obese.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Podnos YD, Jimenez JC, Wilson SE, Stevens CM, Nguyen NT (2003) Complications after laparoscopic gastric bypass. A review of 3464 cases. Arch Surg 138:957–961
Schauer PR, Ikramuddin S, Gourash W, Ramanathan R, Luketich J (2000) Outcomes after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Ann Surg 232:515–529
Artuso D, Wayne M, Kaul A, Bairamian M, Teixeira J, Cerabona T (2004) Extremely high body mass index is not a contraindication to laparoscopic gastric bypass. Obes Surg 6:750–754
Gould JC, Garren MJ, Boll V, Starling JR (2006) Laparoscopic gastric bypass: risks vs. benefits up to two years following surgery in super-super obese patients. Surgery 140:524–531
Oliak D, Ballantyne GH, Davies RJ, Wasielewski A, Schmidt HJ (2002) Short-term results of laparoscopic gastric bypass in patients with BMI more then 60. Obes Surg 12:643–647
Tichansky DS, DeMaria EJ, Fernandez AZ, Kellum JM, Wolfe LG, Meador JG et al (2005) Postoperative complications are not increased in super-super obese patients who undergo laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Endosc 19:939–941
Wittgrove AC, Clark GW, Tremblay LS (1994) Laparoscopic gastric bypass Roux-en-Y: preliminary report of five cases. Obes Surg 4:353–357
Parikh MS, Shen R, Weiner M, Siegel N, Ren CJ (2005) Laparoscopic bariatric surgery in super-obese patients (BMI > 50) is safe and effective: a review of 332 patients. Obes Surg 15:858–863
Kral JG (1985) Morbid obesity and related health risks. Ann Intern Med 103:1043–1047
Brolin RE, LaMarca LB, Kenler HA, Cody RP (2002) Malabsorptive gastric bypass in patients with superobesity. J Gastrointest Surg 6:195–205
Moose D, Lourie D, Powell W, Pehrsson B, Martin D, LaMar T et al (2003) Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: minimally invasive bariatric surgery for the superobese in the community hospital setting. Am Surg 69:930–932
Sánchez-Santos R, Vilarrasa N, Pujol J, Moreno P, Francos JM, Rafecas A et al (2006) Is Roux-en-Y gastric bypass adequate in the super-obese? Obes Surg 16:478–483
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kushnir, L., Dunnican, W.J., Benedetto, B. et al. Is BMI greater than 60 kg/m2 a predictor of higher morbidity after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass?. Surg Endosc 24, 94–97 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0552-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0552-x