Abstract
Background
This study aimed to report the need for an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist to evaluate the laryngeal findings and the voice quality of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) symptoms before and after surgery.
Methods
For this study, 38 GERD patients who had a Reflux Symptom Index (RSI) score higher than 14 underwent complete assessment in the ENT department. Standard 24-h pH monitoring, esophageal motility assessment, a detailed ENT examination including the RSI, the Reflux Finding Score (RFS), and objective voice analysis were performed for all the patients before reflux surgery, then 6 to 8 months afterward.
Results
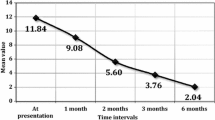
The subject’s mean RSI scores were 25.45 ± 7.5 before and 16.52 ± 5.06 after surgery (p < 0.05), and the mean RFS scores were, respectively, 10.37 ± 2.7 and 5.5 ± 1.45 (p < 0.05). The pre- and postoperative differences in the RSI and RFS scores and the voice parameters were statistically significant.
Conclusions
Objective voice analysis, RSI, and RFS can be used to evaluate the postoperative results for GERD patients with LPR symptoms. Examination of these patients by an ENT specialist is necessary before and after the operation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bor S, Mandiracıoglu A, Kitapcioglu G, Caymaz-Bor C, Gilbert RJ (2005) Gastroesophageal reflux disease in a low-income region in Turkey. Am J Gastroenterol 100: 759–765
Day JP, Richter JE (1990) Medical and surgical conditions predisposing to gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 19: 587–603
Noordzij PJ, Khidr A, Evans BA, Desper E, Mittal RK, Reibel JF, Levine PA (2001) Evaluation of omeprazole in the treatment of reflux laryngitis: a prospective, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study. Laryngoscope 111: 2147–2151
Eherer AJ, Habermann W, Hammer HF, Kiesler K, Friedrich G, Krejs GJ (2003) Effect of pantoprazole on the course of reflux-associated laryngitis: a placebo-controlled double-blind crossover study. Scand J Gastroenterol 38: 462–467
El-Serag HB, Lee P, Buchner A, Inadomi JM, Gavin M, McCarthy DM (2001) Lansoprazole treatment of patients with chronic idiopathic laryngitis: a placebo-controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol 96: 979–983
DeVault KR (1999) Overview of medical therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 28: 831–845
Watson DI, Jamieson GG (1998) Antireflux surgery in the laparoscopic era. Br J Surg 85: 1173–1184
Hinder RA, Filipi CJ, Wetscher G, Neary P, DeMeester TR, Perkidis G (1994) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is an effective treatment for gastoesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg 220: 472–483
Bammer T, Hinder RA, Klaus A, Klingler PJ (2001) Five- to eight-year outcome of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 5: 42–48
Cadiere GB, Houben JJ, Bruyns J, Himpens J, Panzer JM, Gelin M (1994) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: technique and preliminary results. Br J Surg 81: 400–403
Möbius C, Stein HJ, Feith M, Feussner H, Siewert JR (2001) Quality of life before and after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc 15: 353–356
Coster DD, Bower WH, Wilson VT, Butler DA, Locker SC, Brebrick RT (1995) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: a curative, safe, and cost-effective procedure for complicated gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Laparosc Endosc 5: 111–117
Peters JH, DeMeester TR, Crooked P, Oberg S, de Vos Shoop M, Hagen JA, Bremner CG (1998) The treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: prospective evaluation of 100 patients with “typical” symptoms. Ann Surg 228: 40–50
Velanovich V, Karmy-Jones R (2001) Psychiatric disorders affect outcomes of antireflux operations for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 15: 171–175
Westcott CJ, Hopkins MB, Bach K, Postma GN, Belafsky PC, Koufman JA (2004) Fundoplication for laryngopharyngeal reflux. J Am Coll Surg 199: 23–30
Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA (2002) The association between laryngeal pseudosulcus and laryngopharyngeal reflux. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126: 649–652
Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA (2001) The validity and reliability of the reflux finding score (RFS). Laryngoscope 111: 1313–1317
Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA (2002) Validity and reliability of the reflux symptom index (RSI). J Voice 16: 274–277
Westcott CJ, Hopkins MB, Bach K, Postma GN, Belafsky PC, Koufman JA (2004) Fundoplication for laryngopharyngeal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 199: 23–30
Johnson LF, DeMeester TR (1974) Twenty-four-hour pH monitoring of the distal esophagus: a quantitative measure of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol 62: 325–332
Hernandez-Espinosa C, Fernandez-Redondo M, Gomez-Vilda P, Godino-Llorente JI, Aguilera-Navarro S (2000) Diagnosis of vocal and voice disorders by the speech signal. Proceeding of the IEEE Internal Joint conference on Neural Networks 4: 253–258
Ogut F, Midilli R, Oder G, Engin EZ, Karci B, Kabasakal Y (2005) Laryngeal findings and voice quality in Sjogren’s syndrome. Auris Nasus Larynx 32: 375–380
Manfredi C, D’aniello M, Buscaglioni P, Ismaelli A (2000) A comparative analysis of fundamental frequency estimation methods with application to pathological voices. Med Eng Phys 22: 135–147
Koufman JA (1991) The otolaryngologic manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Laryngoscope 101: 1–78
Boyanov B, Hadjitodorov S (1997) Acoustic analysis of pathological voices. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 16: 74–82
Godino-Llorente JI, Aguilera-Navarro S, Gomez-Vilda P (2000) Nonsupervised neural net applied to the detection of voice impairment. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing 6: 3594–3597
Rosa MO, Pereira JC, Grellet M, Carvalho ACPLF (1999) Signal processing and statistical procedures to identify laryngeal pathologies. IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits, and Systems 1: 423–426
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogut, F., Ersin, S., Engin, E.Z. et al. The effect of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication on laryngeal findings and voice quality. Surg Endosc 21, 549–554 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-006-9077-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-006-9077-8