Abstract
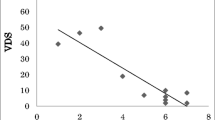
Dysphagia can be classified as oropharyngeal or esophageal, and functional or structural deficits of the esophagus can cause esophageal dysphagia. Dysphagia aortica (DA) is defined as dysphagia caused by extrinsic compression of the esophagus by the aorta. The aim of this study was to investigate the characteristics of DA by comparing the findings of videofluoroscopic swallowing studies (VFSS) with those of other dysphagia. Sixty-seven patients with postoperative dysphagia aortica (PDA), dysphagia after brainstem infarction (DBI), dysphagia after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (DACDF), and subjective swallowing difficulty (SSD) without penetration and/or aspiration, who had undergone VFSS incorporating tests using 5 ml of thin and thick liquids, were included. The clinical data were collected retrospectively. The penetration-aspiration scale, functional dysphagia scale (FDS), esophageal transit time (ETT), and aortic lesion parameters (maximal diameter and distance between the lesion and the apex of the aortic arch) were assessed. The patients with PDA had higher FDS scores than the patients with SSD and lower scores than the patients with DBI did on thin liquids, while the FDS scores on thick liquids were lower in the patients with PDA than in those with DBI or DACDF. The patients with PDA had longer ETT than the other three groups. No correlation was found between the aortic lesion parameters and the VFSS findings. Although PDA has some oropharyngeal symptoms, the esophageal phase was affected mainly by PDA. After an operation on the aorta, VFSS should be considered before resuming oral feeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lohe VK, Kadu RP. Dysphagia: a symptom not a disease. Oral Health Case Rep. 2016;2:1000117.
Tsukamoto M, Manabe N, Kamada T, Hirai T, Hata J, Haruma K, et al. Number of gastrointestinal symptoms is a useful means of identifying patients with cancer for dysphagia. Dysphagia. 2016;31:547–54.
Kuhlemeier KV. Epidemiology and dysphagia. Dysphagia. 1994;9:209–17.
Aldridge KJ, Taylor NF. Dysphagia is a common and serious problem for adults with mental illness: a systematic review. Dysphagia. 2012;27:124–37.
Abdel Jalil AA, Katzka DA, Castell DO. Approach to the patient with dysphagia. Am J Med. 2015;128(1138):e17-23.
Matsuo K, Palmer JB. Anatomy and physiology of feeding and swallowing: normal and abnormal. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2008;19:691–707.
Matta A, Elenizi K, Carrie D, Roncalli J. Dysphagia as an early sign of cardiac decompensation in elderly: case report. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2020;4:1–5.
Ferraris VA, Ferraris SP, Moritz DM, Welch S. Oropharyngeal dysphagia after cardiac operations. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;71:1792–6.
Min Y, Kim W-S, Kang SS, Choi JM, Yeom JS, Paik N-J. Incidence of dysphagia and serial videofluoroscopic swallow study findings after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: a prospective study. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29:E177–81.
Tsai SJ, Lin CC, Chang CW, Hung CY, Shieh TY, Wang HY, et al. Benign esophageal lesions: endoscopic and pathologic features. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:1091–8.
Badila E, Bartos D, Balahura C, Daraban AM. A rare cause of dysphagia—dysphagia aortica—complicated with intravascular disseminated coagulopathy. Maedica. 2014;9:83–7.
Choi SH, Yang GK, Gagnon J. Dysphagia aortica secondary to thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm resolved after endograft placement. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 2019;5:501–5.
Chan Y-H, Hung C-Y, Shieh T-Y, Wang H-Y, Chang C-W, Shih S-C, et al. Nonaneurysmatic dysphagia aortica in the elderly: three case reports and literature review. Int J Gerontol. 2016;10:52–5.
Bours GJ, Speyer R, Lemmens J, Limburg M, De Wit R. Bedside screening tests vs. videofluoroscopy or fibreoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing to detect dysphagia in patients with neurological disorders: systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2009;65:477–93.
Palmer JB, Kuhlemeier KV, Tippett DC, Lynch C. A protocol for the videofluorographic swallowing study. Dysphagia. 1993;8:209–14.
Hila A, Castell JA, Castell DO. Pharyngeal and upper esophageal sphincter manometry in the evaluation of dysphagia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001;33:355–61.
Kim YK, Cha JH, Lee KY. Comparison of dysphagia between infratentorial and supratentorial stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2019;43:149–55.
Haziz SRA, Bickle I, Chong VH. Dysphagia aortica: a rare cause of dysphagia. BMJ Case Rep. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2015-211726.
Levitt B, Richter J. Dysphagia lusoria: a comprehensive review. Dis Esophagus. 2007;20:455–60.
Shrestha N, Karki B, Shrestha PS. Dysphagia aortica-a rare cause of dysphagia. Oxf Med Case Rep. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1093/omcr/omaa004.
Lee S-I, Pyun S-B, Jang D-H. Dysphagia and hoarseness associated with painless aortic dissection: a rare case of cardiovocal syndrome. Dysphagia. 2006;21:129–32.
Moon HI, Yoon SY, Yi TI, Jeong YJ, Cho TH. Lesions responsible for delayed oral transit time in post-stroke dysphagia. Dysphagia. 2018;33:321–8.
Ko MJ, Kang MJ, Ko KJ, Ki YO, Chang HJ, Kwon JY. Clinical usefulness of schedule for oral-motor assessment (SOMA) in children with dysphagia. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011;35:477–84.
Steele CM, Namasivayam-MacDonald AM, Guida BT, Cichero JA, Duivestein J, Hanson B, et al. Creation and initial validation of the international dysphagia diet standardisation initiative functional diet scale. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;99:934–44.
Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1996;11:93–8.
Robbins J, Coyle J, Rosenbek J, Roecker E, Wood J. Differentiation of normal and abnormal airway protection during swallowing using the penetration–aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1999;14:228–32.
Han TR, Paik N-J, Park JW. Quantifying swallowing function after stroke: a functional dysphagia scale based on videofluoroscopic studies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001;82:677–82.
Garand KL, Culp L, Wang B, Davidson K, Martin-Harris B. Aging effects on esophageal transit time in the upright position during videofluoroscopy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2020;129:618–24.
Borazan H, Kececioglu A, Okesli S, Otelcioglu S. Oral magnesium lozenge reduces postoperative sore throat: a randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled study. Anesthesiology. 2012;117:512–8.
Philpott H, Garg M, Tomic D, Balasubramanian S, Sweis R. Dysphagia: thinking outside the box. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:6942–51.
Wang ID, Huang HK, Tsai PY, Chang WK. Dysphagia aortica. QJM. 2019;112:137–8.
Mehraban-Far S, Alrassi J, Patel R, Ahmad V, Browne N, Lam W, et al. Dysphagia in the elderly population: a videofluoroscopic study. Am J Otolaryngol. 2021;42:102854.
Paciaroni M, Mazzotta G, Corea F, Caso V, Venti M, Milia P, et al. Dysphagia following stroke. Eur Neurol. 2004;51:162–7.
Steinhagen V, Grossmann A, Benecke R, Walter U. Swallowing disturbance pattern relates to brain lesion location in acute stroke patients. Stroke. 2009;40:1903–6.
Kim SY, Kim TU, Hyun JK, Lee SJ. Differences in videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) findings according to the vascular territory involved in stroke. Dysphagia. 2014;29:444–9.
Panebianco M, Marchese-Ragona R, Masiero S, Restivo D. Dysphagia in neurological diseases: a literature review. Neurol Sci. 2020;41:3067–73.
Lapa S, Luger S, Pfeilschifter W, Henke C, Wagner M, Foerch C. Predictors of dysphagia in acute pontine infarction. Stroke. 2017;48:1397–9.
Takizawa C, Gemmell E, Kenworthy J, Speyer R. A systematic review of the prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, head injury, and pneumonia. Dysphagia. 2016;31:434–41.
Flowers HL, Skoretz SA, Streiner DL, Silver FL, Martino R. MRI-based neuroanatomical predictors of dysphagia after acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011;32:1–10.
Flowers HL, AlHarbi MA, Mikulis D, Silver FL, Rochon E, Streiner D, et al. MRI-based neuroanatomical predictors of dysphagia, dysarthria, and aphasia in patients with first acute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2017;7:21–34.
Martino R, Foley N, Bhogal S, Diamant N, Speechley M, Teasell R. Dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke. 2005;36:2756–63.
Vansant MB, Kunduk M, McWhorter AJ. A review of postsurgical dysphagia in nonmalignant disease. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;24:477–82.
Yang Y, Ma L, Liu H, Xu M. A meta-analysis of the incidence of patient-reported dysphagia after anterior cervical decompression and fusion with the zero-profile implant system. Dysphagia. 2016;31:134–45.
González-Fernández M, Ottenstein L, Atanelov L, Christian AB. Dysphagia after stroke: an overview. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. 2013;1:187–96.
Mann G, Hankey GJ, Cameron D. Swallowing function after stroke: prognosis and prognostic factors at 6 months. Stroke. 1999;30:744–8.
Singh S, Hamdy S. Dysphagia in stroke patients. Postgrad Med J. 2006;82:383–91.
Broadley S, Croser D, Cottrell J, Creevy M, Teo E, Yiu D, et al. Predictors of prolonged dysphagia following acute stroke. J Clin Neurosci. 2003;10:300–5.
Anderson KK, Arnold PM. Oropharyngeal dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: a review. Global Spine J. 2013;3:273–86.
Kyaw WA, Lim CY, Khalil MAM, Lim KC, Chong VH, Tan J. A fatal case of Ortner’s syndrome and dysphagia aortica secondary to rapidly expanding mycotic thoracic aortic aneurysm in a chronic kidney disease patient. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050313X18799247.
Lodewyks CL, White CW, Bay G, Hiebert B, Wu B, Barker M, et al. Vocal cord paralysis after thoracic aortic surgery: incidence and impact on clinical outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;100:54–8.
Martin-Harris B, Brodsky MB, Michel Y, Castell DO, Schleicher M, Sandidge J, et al. MBS measurement tool for swallow impairment–MBSImp: establishing a standard. Dysphagia. 2008;23:392–405.
Cordova-Fraga T, Sosa M, Wiechers C, De la Roca-Chiapas JM, Maldonado Moreles A, Bernal-Alvarado J, et al. Effects of anatomical position on esophageal transit time: a biomagnetic diagnostic technique. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:5707–11.
Martino R, Terrault N, Ezerzer F, Mikulis D, Diamant NE. Dysphagia in a patient with lateral medullary syndrome: insight into the central control of swallowing. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:420–6.
Papakonstantinou NA, Patris V, Antonopoulos CN, Samiotis I, Argiriou M. Oesophageal necrosis after thoracic endovascular aortic repair: a minimally invasive endovascular approach-a dramatic complication. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2019;28:9–16.
Kim JH, Jang SW, Kim DB, Lee HJ, Kim JG, Kwon BJ, et al. A patient with dysphagia due to an aortic aneurysm. Korean Circ J. 2009;39:258–60.
Lawal A, Shaker R. Esophageal dysphagia. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2008;19:729–45.
Bae JS, Suh I, Kim JK, Lim JY. Comparison of straw and cup for liquid swallowing in poststroke patients. Int J Rehabil Res. 2021;44:181–4.
Reginelli A, D’Amora M, Del Vecchio L, Monaco L, Barillari MR, Di Martino N, et al. Videofluoroscopy and oropharyngeal manometry for evaluation of swallowing in elderly patients. Int J Surg. 2016;33:S154–8.
Riley RD, Ensor J, Snell KIE, Harrell FE Jr, Martin GP, Reitsma JB, et al. Calculating the sample size required for developing a clinical prediction model. BMJ. 2020;368:m441.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: JKK and JYL; Formal analysis and investigation: JKK, SS, IS and JSB; Writing—original draft preparation: JKK; Writing—review and editing: JYL.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical Approval
This study was conducted in accordance with the regulatory standards of Good Clinical Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki (1964) and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of our institution before study initiation. The requirement for informed consent was waived by the board because of the retrospective nature of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, ., Son, S., Suh, I. et al. Postoperative Dysphagia Aortica: Comparison with Other Dysphagia. Dysphagia 37, 1112–1119 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-021-10370-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-021-10370-9