Abstract
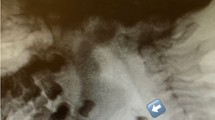
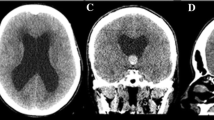
Vallecular cysts are formed when the duct of a mucous gland or lingual tonsillar crypt is dilated owing to obstruction from inflammation, irritation, or trauma. Small cysts are usually asymptomatic; however, cyst growth results in dysphagia, odynophagia, and acute airway complications. As complete transoral laser excision of a vallecular cyst often results in cyst resolution and improved symptoms, proper diagnosis and management of vallecular lesions are important. We describe the evaluation and treatment of a 53-year-old man with a history of intracerebral hemorrhage in the left basal ganglia who presented with dysphagia caused by a vallecular cyst.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Desanto LW, Devine KD, Weiland LH. Cysts of the larynx-classification. Laryngoscope. 1970;80(1):145–76.
Raftopulos M, Soma M, Lowinger D, Eisman P. Vallecular cysts: a differential diagnosis to consider for neonatal stridor and failure to thrive. JRSM Short Rep. 2013;4(4):29.
Gutiérrez JP, Berkowitz RG, Robertson CF. Vallecular cysts in newborns and young infants. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1999;27(4):282–5.
Leonardo GD, Federico M, Stefania N, Caterina F, Jurgeen S, Elisabetta Z. Endoscopic treatment of vallecular cyst in newborn. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol Extra. 2009;4(1):10–3.
Romak JJ, Olsen SM, Koch CA, Ekbom DC. Bilateral vallecular cysts as a cause of dysphagia: case report and literature review. Int J Otolaryngol. 2010;2010:697583.
Martino R, Foley N, Bhogal S, Diamant N, Speechley M, Teasell R. Dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke. 2005;36(12):2756–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Author Disclosure
This article was not supported by any grant or funding. All the authors, their immediate families, and any research foundation with which they are affiliated did not receive any financial payments or other benefits from any commercial entity related to the subject of this article. There was no previous presentation of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, SH., Seo, H.G. Unusual Cause of Dysphagia in a Post-Stroke Patient. Dysphagia 32, 721–723 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-017-9796-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-017-9796-0