Abstract
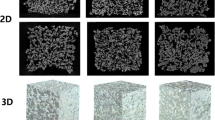
Hard, difficult-to-eat root crops (carrots and burdock roots) were homogeneously softened by an enzyme permeation method so that they could be mashed easily by the tongue while retaining appearance, flavor, and nutrients. The appearance, color, and nutritional value of these foods were equivalent to those of normally cooked root crops of the same type. The firmness of the softened root crops was at least 100 times as low as normally cooked root crops and lower than some care food products for patients with swallowing disorders. Compared with control root crops, which were treated with a freeze–thaw infusion method, the treated foods were 10 to 25 times as soft, with significantly lower rates of foodstuff syneresis and better preservation of color and nutritional value. Furthermore, the cell walls of the treated burdock roots resembled those of normally cooked ones, while the cells of freeze–thaw infusion burdock roots were destroyed and few cell walls remained. It was expected that these root crops softened by the enzymatic processing could be one of the best model foods for patients with masticatory disturbance or swallowing disorders or both.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Statistical Handbook of Japan (2012) Statistical Research and Training Institute, (Eds). Published by the Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications [Internet] (Cited 2013 Aug 19). Available from: http://www.stat.go.jp/data/nihon/back12/index.htm.
Hotaling DL. Nutritional considerations for the pureed diet texture in dysphagic elderly. Dysphagia. 1992;7:81–5.
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (2009) “Testing Method for Foods for People with Difficulty in Swallowing” specified in “Approval of Indication of Foods for Special Dietary Use.” (Notification No. 0212001, 20, Department of Food Safety, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, Feb. 12, 2009).
Fujisaki T. Universal Design Foods. J Jpn Soc Food Sci Technol. 2008;55(2):78–9 (in Japanese).
Sakai M, Egashira F, Kanaya S, Kayashita J. Comparison of food physical properties with reference to clinically effective stepwise swallowing foods. J Jpn Soc Dysphagia Rehabil. 2006;10(3):239–48 (in Japanese).
Sakamoto K, Shibata K, Ishihara M. Decreased hardness of dietary fiber-rich foods by the enzyme-infusion method. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2006;70(7):1564–70. doi:10.1271/bbb.50562.
Nakatsu S, Ishihara M, Maenishi M, Shibata K, Sakamoto K, Yokoyama K. Evaluation of acceptability by the elderly of root crops softened by freeze-thaw infusion. J Jpn Soc Dysphagia Rehabil. 2010;14(2):95–105 (in Japanese).
Nakatsu S, Kohyama K, Watanabe Y, Shibata K, Sakamoto K, Shimoda K. Mechanical properties of softened foodstuffs processed by freeze-thaw infusion of macerating enzyme. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol. 2012;16:267–76.
Kuwa M, Kuwa S, Yamano K, inventor; Placeram Co., Ltd., assignee. Method for food impregnation treatment. Japanese Unexamined Patent Application Publication No. 2003-174850, 24 Jun 2003.
Tashiro K, Higashiguchi T, Takeda Y, Tomitsuka T, Fujise N, Nakamura T, Masunaga H, Ito A. Study of solidified enteral and oral nutritional formula on transformation and transit in digestive tract—fundamental experiments in rats-. J Jpn Soc Parent Enter Nutr. 2006;21(2):115–25 (in Japanese).
Sato N, Masunaga H, inventor; EN Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., assignee. Excellently flavored amino acid/Peptide mixture, and method for producing the same. Japanese Unexamined Patent Application Publication No. 2006-75006, 23 Mar 2006.
Murakami M, Sato N, Sato N, Nakamura T, Masunaga H. Changes in lymphocyte and cytokine production by surgical stress in a rat small intestinal resection model. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2007;40(3):216–20.
Murakami M, Sato N, Tashiro K, Nakamura T, Masunaga H. Effects of caloric intake on intestinal mucosal morphology and immune cells in rats treated with 5-fluorouracil. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2009;45(1):74–81.
Abe S, Tanaka Y, Fujise N, Nakamura T, Masunaga H, Nagasawa T, Yagi M. An antioxidative nutrient-rich enteral diet attenuates lethal activity and oxidative stress induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. J Parent Enter Nutr. 2007;31(3):181–7.
Takahashi B, Sato N, Koyama Y, Hatakeyama K. Effects of nutrition with antioxidants in breast cancer rats. Jpn J Surg Metab Nutr. 2009;43(6):125–33 (in Japanese).
Hayashi M, Kuribayashi M, Sugiyama K. Softening method and softened cereal. Japan Patent Kokai. 2010-207128, 2010 (in Japanese).
Hayashi M, Kato K, Umene S, Masunaga H. Characterisation of a novel softened rice product. Food Chem. 2014;145:372–7.
Takei R. Enzymatic treatment solution, softening method and softened animal-based food product. PCT. (2012) Pub.No.:US2012/0308684 A1.
Takei R, Hayashi M, Umene S, Narita K, Kobayashi Y, Masunaga H. Novel beef as a protein source for patients with masticatory disturbance. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2014. doi:10.1007/s13539-014-0129-y. [Epub ahead of print].
Kawahira K, Taniguchi K, Sunada S, Kuribayashi M. Softening method and softened vegetable food. Japan Patent Kokai. 2010-115164 (in Japanese), 2010.
Umene S. Method for producing softened plant material. Japan Patent Kokai. WO2012/033051A1 (in Japanese), 2013.
Higashiguchi T. Novel diet for patients with impaired mastication evaluated by consumption rate, nutrition intake, and questionnaire. Nutrition. 2013;29:858–64.
Gonzalez-Fernandez M, Huckabee ML, Doeltgen SH, Inamoto Y, Kagaya H, Saitoh E. Dysphagia rehabilitation: similarities and differences in three areas of the world. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. 2013;1:296–306.
Fujishima I, Nagao N, Otsuka J, Shigematsu T, Hojyo K, Kanazawa H. Study of the possibility of using ‘iEat®’ produced according to the enzyme homogeneous permeation method for sensory evaluation. Deglutition. 2014;3:110–7 (in Japanese).
AI-Muhtaseb AH, McMinn W, Megahey E, Neill G, Magee R, Rashid U. Textural characteristics of microwave-baked and convective-baked Madeira cake. J Food Process Technol. 2013;4:209. doi:10.4172/2157-7110.1000209.
Siefarth C, Tran TBT, Mittermaier P, Pfeiffer T, Buettner A. Effect of radio frequency heating on yoghurt, II: microstructure and texture. Foods. 2014;3:369–93. doi:10.3390/foods3020369.
A. O. A. C. Official methods of analysis of AOAC. 17th ed. Washington, D. C: Association of Official Analytical Chemists; 2002.
Kjeldahl J. A new method for the estimation of nitrogen in organic compounds. Z fuer Anal Chem. 1883;33:366.
A. O. A. C. Official methods of analysis of AOAC. 13th ed. Washington, D. C: Association of Official Analytical Chemists; 1980.
Britton G, Liaaen-Jensen S, Pfander H, (Ed). Carotenoids, vol. 1A. (1995) Isolation and Analysis. Birkuhauser. Basel.
Takagi S. Behaviors of tissues and pectic substances of foods of plant origins at heating and freezing states. J Cook Sci Jpn. 1991;24(2):150–6 (in Japanese).
Phothiset S, Charoenrein S. Effects of freezing and thawing on texture, microstructure and cell wall composition changes in papaya tissues. J Sci Food Agric. 2013;. doi:10.1002/jsfa.6226 [Equb ahead of print].
Stanga Z, Zurfluh Y, Roselli M, Sterchi AB, Tanner B, Knecht G. Hospital food: a survey of patients’ perceptions. Clin Nutr. 2003;23(3):241–6.
Nishinari K. Rheology, food texture and mastication. J Texture Stud. 2004;35:113–24.
Nieuwenhuizen WF, Weenen H, Rigby P, Hetherington MM. Older adults and patients in need of nutritional support: review of current treatment options and factors influencing nutritional intake. Clin Nutr. 2010;29:160–9.
Shibata S, Saitoh E. Dysphagia. Med Pract. 2010;27(10):1683–7 (in Japanese).
Kaneko N, Nohara K, Asano M, Sakai T, Mitsuyama M. Risk criteria tag of help with eating for elderly residents in nursing home. Jpn J Gerodontol. 2012;27(1):18–24 (in Japanese).
McCullough G, Pelletier C, Steele C. National Dysphagia Diet: What to swallow? ASHA Lead. 2003.
Cichero JAY, Steele C, Duivestein J, Clave P, Chen J, Kayashita J, Dantas R, Lecko C, Speyer R, Lam P, Murray J. The need for international terminology and definitions for texture-modified foods and thickened liquids used in dysphagia management: foundations of a global initiative. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. 2013;1:280–91.
Momosaki R, Abo M, Kobayashi K. Swallowing analysis for semisolid food texture in poststroke dyphagic patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;22(3):267–70.
Koc H, Vinyard CJ, Essick GK, Foegeding EA. Food Oral Processing: conversion of food structure to textural perception. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2013;4:237–66.
Tokifuji A, Matsushima Y, Hachisuka K, Yoshioka K. Texture, sensory and swallowing characteristics of high-pressure-heat-treated pork meat gel as a dysphagia diet. Meat Sci. 2013;93:843–8.
Clave P, de Kraa M, Arreola V, Girvent M, Farre R, Palomera E, Serra-Prat M. The effect of bolus viscosity on swallowing function in neurogenic dysphagia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24:1385–94.
Ozaki K, Kagaya H, Yokoyama M, Saitoh E, Okada S, González-Fernández M, Palmer JB, Uematsu H. The risk of penetration or aspiration during videofluoroscopic examination of swallowing varies depending on food types. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010;220(1):41–6.
Nayebzadeh K, Chen J, Dickinson E, Moschakis T. Surface structure smoothing effect of polysaccharide on a heat-set protein particle gel. Langmuir. 2006;22(21):8873–80.
Naito H. Estimation of soaking conditions for edible burdock in preparing low potassium diets. Jpn J Nutr. 1991;49(5):273–9 (in Japanese).
Shabala S, Pottosin I. Regulation of potassium transport in plants under hostile conditions: implications for abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. Physiol Plant. 2014;. doi:10.1111/ppl.12165.
Cherel I, Lefoulon C, Boeglin M, Sentenac H. Molecular mechanisms involved in plant adaptation to low K+ availability. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(3):833–48.
Conflict of interest
We have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umene, S., Hayashi, M., Kato, K. et al. Physical Properties of Root Crops Treated with Novel Softening Technology Capable of Retaining the Shape, Color, and Nutritional Value of Foods. Dysphagia 30, 105–113 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-014-9581-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-014-9581-2