Abstract
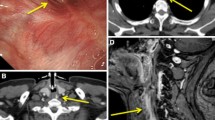
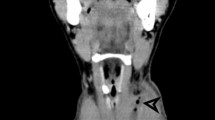
Pharyngocele is infrequently reported in the literature and is rarely considered in the differential diagnosis of upper dysphagia. We describe the case of a healthy young man, without any history of activities that would result in elevated intrapharyngeal pressure, with difficulty swallowing since childhood. Bilateral pharyngoceles were diagnosed after barium swallow and carbonated-beverage ingestion. We discuss the possibility that our patient’s pharyngoceles may be congenital in origin from an internal branchial sinus anomaly.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wheeler WJ: Pharyngocele and dilation of pharynx. Dublin J Med Sci 82:349–357, 1886
Norris CW: Pharyngoceles of the hypopharynx. Laryngoscope 89:1788–1807, 1979
Van de Ven PM, Schutte HK: The pharyngocele: infrequently encountered and easily misdiagnosed. J Laryngol Otol 109:247–249, 1995
Ward PH: Bilateral laryngoceles in a young trumpet player: case report [letter]. Ear Nose Throat J 80:132, 2001
Hubbard C: Laryngocele: a study of five cases with reference to radiological features. Clin Radiol 38:639–644, 1987
Chevallier P, Motamedi JP, Marcy PY, Foa C, Padovani B, Bruneton JN: Sonographic discovery of a pharyngocele. J Clin Ultrasound 28:101–103, 2000
Choi SS, Zalzar GH: Branchial anomalies: a review of cases. Laryngoscope 105:909–113, 1995
Godin MS, Kearns DB, Pransky SM, Seid AB, Wilson DB: Fourth branchial pouch sinus: principles of diagnosis and management. Laryngoscope 100:174–178, 1990
Chang CY, Furdyna JA: Bilateral pharyngoceles (branchial cleft anomalies?) and endoscopic surgical considerations. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 114:529–532, 2005
Restrepo S, Villamil MA, Rojas IC, Palacios E: Pharyngocele: CT and MRI findings. Ear Nose Throat J 82:492–494, 2003
Komisar A: Pharyngoceles (lateral pharyngeal diverticula) of the hypopharynx. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 91:450–452, 1983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katsinelos, P., Chatzimavroudis, G., Pilpilidis, I. et al. Congenital Bilateral Pharyngoceles: An Unusual Case of Upper Dysphagia. Dysphagia 23, 98–100 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9091-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9091-6