Abstract
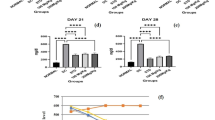
Nanotechnology is currently gaining immense attention to combat food borne bacteria, and biofilm. Diabetes is a common metabolic disease affecting majority of people. A better therapy relies on phytomediated nanoparticle synthesis. In this study, W. somnifera leaf extract-assisted ZnO NPs (Ws-ZnO NPs) was synthesized and characterized. From HR-TEM analysis, it has been found that the hexagonal wurtzite particle is 15.6 nm in size and − 12.14 mV of zeta potential. A greater antibacterial effect of Ws-ZnO NPs was noticed against E. faecalis and S. aureus at 100 µg mL−1. Also, the biofilm of E. faecalis and S. aureus was greatly inhibited at 100 µg mL−1 compared to E. coli and P. aeruginosa. The activity of α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzyme was inhibited at 100 µg mL−1 demonstrating its antidiabetic potential. The larval and pupal development was delayed at 25 µg mL−1 of Ws-ZnO NPs. A complete mortality (100%) was recorded at 25 µg mL−1. Ws-ZnO NPs showed least LC50 value (9.65 µg mL−1) compared to the uncoated ZnO NPs (38.8 µg mL−1) and leaf extract (13.06 µg mL−1). Therefore, it is concluded that Ws-ZnO NPs are promising to be used as effective antimicrobials, antidiabetic and insecticides to combat storage pests.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vijayakumar S, Vaseeharan B, Sudhakaran R, Jeyakandan J, Ramasamy P, Sonawane A, Padhi A, Velusamy P, Anbu P, Faggio C (2019) Bioinspired zinc oxide nanoparticles using Lycopersicon esculentum for antimicrobial and anticancer applications. J Clust Sci 30(6):1465–1479
Schwartz VB, Thétiot F, Ritz S, Pütz S, Choritz L, Lappas A, Förch R, Landfester K, Jonas U (2012) Antibacterial surface coatings from zinc oxide nanoparticles embedded in poly(n-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel surface layers. Adv Funct Mater 22(11):2376–2386
Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A, Kaus NHM, Ann LC, Bakhori SKM, Hasan H, Mohamad D (2015) Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nanomicro Lett 7(3):219–242
Yu L, Shang F, Chen X, Ni J, Yu L, Zhang M, Sun D, Xue T (2018) The anti-biofilm effect of silver-nanoparticle-decorated quercetin nanoparticles on a multi-drug resistant Escherichia coli strain isolated from a dairy cow with mastitis. PeerJ 6:e5711
Maikozhundan B, Vinodhini J (2018) Nanopesticidal effects of Pongamia pinnata leaf extract coated zinc oxide nanoparticle against the Pulse beetle Callosobruchus maculatus. Mater Today Commun 14:106–115
Parsons DMH, Credland PF (2003) Determination of oviposition in Acanthoscelides obtectus, a nonconformist bruchids. Physiol Entomol 28:221–231
Li L-S, Hu J, Yang W, Alivisatos AP (2001) Band gap variation of size- and shape-controlled colloidal CdSe quantum rods. Nano Lett 1:349–351
Vajargah MF, Imanpoor MR, Shabani A, Hedayati A, Faggio C (2019) Effect of long-term exposure of silver nanoparticles on growth indices, hematological and biochemical parameters and gonad histology of male Gold fish (Carassius auratus gibelio). Microsc Res Tech 82(7):1224–1230
Mazzaglia A, Zagami R, Romeo A, Ceraolo F, Vazzana M, Castriciano MA, Faggio C, Scolaro M (2018) Supramolecular adducts of anionic porphyrins and a biocompatible polyamine: effect of photodamage—on human red blood cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18(10):7269–7274
Vajargah MF, Valsuyi AM, Hedayati A, Faggio C (2018) Histopathological lesions and toxicity in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L. 1758) induced by copper nanoparticles. Microsc Res Tech 81(7):724–729
Kumar R, Sharon M, Choudhary AK (2010) Nanotechnology in agricultural diseases and food safety. J Phytol 2:83–92
Meruvu H, Vangalapati M, Chippada SC, Bammidi SR (2011) Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles and its antimicrobial activity against Bacillus Subtilis and Escherichia Coli. Rasayan J Chem 4:217–222
Malaikozhundan B, Vaseeharan B, Vijayakumar S, Merlin PT (2017) Bacillus thuringiensis coated zinc oxide nanoparticle and its biopesticidal effects on the Pulse beetle, Callosobruchus maculatus. J Photochem Photobiol 174:306–314
Pattipati S, Amanpreet S, Shrinivas K (2003) Effect of Withania somnifera root extract on haloperidol induced orofacial dyskinesia: possible mechanism of action. J Med Food 6(2):107–114
Malaikozhundan B, Vaseeharan B, Vijayakumar S, Sudhakaranb R, Gobi N, Shanthini G (2016) Antibacterial and antibiofilm assessment of Momordica charantia fruit extract coated silver nanoparticle. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 8:189–196
Ankamwar B, Chaudhary M, Sastry M (2005) Gold nanoparticles biologically synthesized using tamarind leaf extract and potential application in vapour sensing. Synth React Inorg Met-Org Nano-Met Chem 35:19–26
Shankar S, Absar A, Murali S (2003) Geranium leaf assisted biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles. Biotech Prog 19:1627–1631
Vijayakumar S, Vaseeharan B, Malaikozhundan B, Shobiya M (2016) Laurus nobilis leaf extract mediated green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: characterization and biomedical applications. Biomed Pharmacother 84:1213–1222
Elia P, Zach R, Hazan S, Kolusheva S, Porat Z, Zeiri Y (2014) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using plant extract as reducing agents. Int J Nanomed 9:4007–4021
Malaikozhundan B, Vaseeharan B, Vijayakumar S, Sudhakaran R, Gobi N, Shanthini G (2016) Antibacterial and antibiofilm assessment of Momordica charantia fruit extract coated silver nanoparticle. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 8:189–196
Zhang LL, Jiang YH, Ding YL, Povey M, York D (2007) Investigation into the antibacterial behaviour of suspensions of ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO nanofluids). J Nanopart Res 9:479e489
Balan K, Qing W, Wang Y, Liu X, Palvannan T, Wang Y, Ma F, Zhang Y (2016) RSC Adv 6:40162–40168
ThiraviaRaj S, Malaikozhundan B (2011) Evaluation of varieties of Pulses against infestation by Cowpea bruchid, Callosobruchus maculatus (Fabricius). Indian J Entomol 73(4):346–348
Malaikozhundan B, Thiravia-Raj S (2012) A study on the developmental biology of Callosobruchus maculatus (fabricius) in different pulses. Legume Res 35(2):159–163
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entmol 18:265–267
Finney DJ (1964) Probit analysis, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, England, p 318
De Sa LFR, Wermelinger TT, Ribeiro ES, Gravina GA, Fernandes KVS, Xavier-Filho J, Venancio TM, Rezende GL, Oliveira AEA (2014) Effects of Phaseolus vulgaris (Fabaceae) seed coat on the embryonic and larval development of the cowpea weevil Callosobruchus maculatus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). J Insect Physiol 60:50–57
Khosravi R, Sendi JJ (2013) Effect of neem pesticide (achook) on midgut enzymatic activities and selected biochemical compounds in the hemolymph of lesser mulberry pyralid, Glyphodes pyloalis walker (lepidoptera: pyralidae). J Plant Prot Res 53(3):238–247
Nay B, Fournier D, Baudras A, Baudras B (1999) Mechanism of an insect glutathione S-transferase: kinetic analysis supporting a rapid equilibrium random sequential mechanism with housefly I1 isoform. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 29:71–79
Bradford MM (1976) Rapid, sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye-binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Wang ZL (2008) Splendid one-dimensional nanostructures of zinc oxide: a new nanomaterial family for nanotechnology. ACS Nano 2:1987–1992
Yang P, Yan R, Fardy M (2010) Semiconductor nanowire: what's next? Nano Lett 10:1529–1536
Santhoshkumar J, Venkat Kumar S, Rajeshkumar S (2017) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant leaf extract against urinary tract infection pathogen. Resourc Eff Technol 001:1–7
Malaikozhundan B, Vaseeharan B, Vijayakumar S, Pandiselvi K, Rajamohamed-Kalanjiam M, Murugan K, Benelli G (2017) Biological therapeutics of Pongamia pinnata coated zinc oxide nanoparticles against clinically important pathogenic bacteria, fungi and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Microb Pathog 104:268–277
Vijayakumar S, Vinoj G, Malaikozhundan B, Shanthi S, Vaseeharan B (2015) Plectranthus amboinicus leaf extract mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and its control of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm and blood sucking mosquito larvae. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 137(25):889–891
Sangeetha G, Rajeshwari S, Venckatesh R (2011) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract: Structure and optical properties. Mater Res Bull 46:2560–2566
Elumalai K, Velmurugan S, Ravi S, Kathiravan V, Ashokkumar S (2015) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera leaf extract and evaluation of its antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 143:158–164
Sundrarajan M, Ambika S, Bharathi K (2015) Plant-extract mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pongamia pinnata and their activity against pathogenic bacteria. Adv Powder Technol 26(5):1294–1299
Divya MJ, Sowmia C, Joona K, Dhanya KP (2013) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticle from Hibiscus rosa sinensis leaf extract and investigation of its antimicrobial activity. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 4(2):1137–1142
Selvarajan E, Mohanasrinivasan V (2013) Biosynthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles using Lactobacillus plantarum VITES07. Mater Lett 112:180–182
Stoimenov PK, Klinger RL, Marchin GL, Klabunde KJ (2002) Metal oxide nanoparticles as bactericidal agents. Langmuir 18:6679–6686
Zhang LL, Jiang YH, Ding YL, Daskalakis N, Jeuken L, Povey M, Neill AJO, York DW (2010) Mechanistic investigation into antibacterial behaviour of suspensions of ZnO nanoparticles against E. coli. J Nanopart Res. 12:1625–1636
Malapermal V, Botha I, Krishna SBN, Mbatha JN (2017) Saudi J Biol Sci 24:1294–1305
Bakur A, Elshaarani T, Niua Y, Chen Q (2019) Comparative study of antidiabetic, bactericidal, and antitumor activities of MEL@AgNPs, MEL@ZnONPs, and Ag–ZnO/MEL/GA nanocomposites prepared by using MEL and gum Arabic. RSC Adv. 9:9745
Saratale GD, Saratale RG, Benelli G, Kumar G, Pugazhendhi A, Kim D-S, Shin H-S (2017) J Clust Sci 28:1709–1727
Rehana D, Mahendiran D, Kumar RS, Rahiman AK (2017) Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40:943–957
Bayrami A, Parvinroo S, Habibi-Yangjeh A, Rahim-Pouran S (2018) Artif Cells. Nanomed Biotechnol. 46:730–739
Elchiguerra JL, Burt JL, Morones JR, Camacho-Bragado A, Gao X, Lara HH, Yacaman MJ (2005) Interaction of silver nanoparticles with HIV-1. J Nanobiotechnol 3:6
ReddyK KM, Feris J, Bell DG, Wingett C, Hanley AP (2007) Selective toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to prokaryotic and eukaryotic system. Appl Phys Lett 90:2139021–2139023
Sahayaraj K, Madasamy M, Anbu-Radhika S (2016) Insecticidal activity of bio-silver and gold nanoparticles against Pericallia ricini Fab. (Lepidaptera: Archidae). J Biopestic 9(1):63–72
Wanna R, Xu ZH, Liu YH, Yu HX, Ren LJ et al (2010) Effects of the mixed biocide Bacillus thuringiensis–abamectin on the development of the parasitoid Microplitis mediator and its host Helicoverpa armigera. Entomol Exp Appl 137:111–119
Salama HS, Foda MS, El-Sharaby A, Salem S (1991) Potency of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner strains against major pests of oilseed crops. J Appl Entomol. 111:418–424
M. Rouhani, M.A. Samih, A. Aslani, Kh. Beiki. 2011. Side effect of nano-Zno-Tio2-Ag mix-oxide nanoparticles on Frankliniella occidentalis Pergande (Thys.: Thripidae). In: Proceedings Symposium: Third International Symposium on Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 2–5 July 2011. East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, p 51
Ishimoto M, Kitamura K (1989) Growth inhibitory effects of α-amylase inhibitor from kidney bean, Phaseolus vulgaris (L.) on three species of bruchids (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). Appl Entomol Zool 24:281–286
Shade RE, Schroeder HE, Pueyo JJ, Tabe LM, Murdock LL, Higgins TJV, Chrispeels MJ (1994) Transgenic pea seeds expressing the α-amylase inhibitor of the common bean are resist ant to bruchid beetles. Bio/Technology 12:793–796
Rawlings ND, Barrett AJ (1993) Evolutionary families of peptidases. Biochem J 290:205–218
Matsumoto I, Emori Y, Abe K, Arai S (1997) Characterization of a gene family encoding cysteine proteinases of Sitophilus zeamais (Maize weevil), and analysis of the protein distribution in various tissues including alimentary tract and germ cells. J Biochem 121:464–476
Zibaee I, Bandani AR, Sendi JJ, Talaei-Hassanlouei R, Kouchaki B (2010) Effects of Bacillus thurengiensisvarkurstaki, and medicinal plants (Artemisia annua L.) and (Lavandulastoechas L.) extracts on digestive enzymes and Lactate dehydrogenase of Hyphantria cunea Drury (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Invertebr Surv J 7(2):251–261
Terra WR, Ferriera C (2005) Biochemistry of digestion. In: Lawrence IG, Kostas I, Sarjeet SG (eds) Comprehensive molecular insect science, vol 3. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 171–224
Kimura K, Lee JH, Lee IS, Lee HS, Park KH, Chiba S, Kim D (2004) Two potent competitive inhibitors discriminating α-glucosidase family I, from family II. Carbohydr Res 339(6):1035–1040
Enayat A, Ranson H, Hemingway J (2005) Insect glutathione transferases and insecticide resistance. Insect Mol Biol 14(1):3–8
Santana CC, Barbosa LA, Basílio ID Jr, do-Nascimento TG, Dornelas CB, Grillo LAM (2017) Lipase activity in the larval midgut of Rhynchophorus palmarum: biochemical characterization and the effects of reducing agents. Insects 8(3):100
Senthil-Nathan S, Chunga PG, Murugan K (2006) Combined effect of biopesticides on the digestive enzymatic profiles of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guenee) (the rice leaf folder) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64(3):382–389
Acknowledgements
The research grant sanctioned under the Young Scientist Scheme (YSS/2015/000645) by the DST-SERB, New Delhi is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malaikozhundan, B., Vinodhini, J., Kalanjiam, M.A.R. et al. High synergistic antibacterial, antibiofilm, antidiabetic and antimetabolic activity of Withania somnifera leaf extract-assisted zinc oxide nanoparticle. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43, 1533–1547 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02346-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02346-0