Abstract
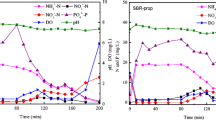
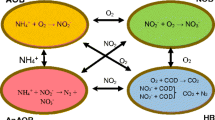
Advanced nitrogen removal without the addition of external carbon source is challenging in the conventional biological nitrogen removal processes. This study presented a novel anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic sequencing batch reactor (A/O/A SBR) based on endogenous nitrate (NO3−–N) respiration to enhance nitrogen removal. The mean effluent total nitrogen (TN) in the A/O/A SBR could be reduced to as low as 3.5 mg/L, when the average influent TN and chemical oxygen demand (COD) were 52.7 and 235.4 mg/L, respectively. This advanced nitrogen removal was attributed to the post-denitrification, since 82.7% of TN removal was achieved in the post-anoxic stage. The post-denitrification rate with nitrite (NO2−–N, 0.59 mg NO2−–N/gMLVSS/h) was higher than that with NO3−–N (0.35 mg NO3−–N/gMLVSS/h). Therefore, the post-anoxic time could be further optimized by achieving denitrification via NO2−–N. The A/O/A SBR has good potential in achieving advanced nitrogen removal, especially in nitrogen-sensitive rural areas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas M, Wright P, Blackall L, Urbain V, Keller J (2003) Optimisation of Noosa BNR plant to improve performance and reduce operating costs. Water Sci Technol 47:141–148
Tchobanoglous G, Burton FL, Stensel HD (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse. McGraw-Hill Ser in Water Res Environ Eng 73:50–51
Ge SJ, Peng YZ, Wang SY, Guo JH, Ma B, Zhang LA, Cao X (2010) Enhanced nutrient removal in a modified step feed process treating municipal wastewater with different inflow distribution ratios and nutrient ratios. Bioresour Technol 101:9012–9019
Winkler M, Coats ER, Brinkman CK (2011) Advancing post-anoxic denitrification for biological nutrient removal. Water Res 45:6119–6130
Baeza JA, Gabriel D, Lafuente J (2004) Effect of internal recycle on the nitrogen removal efficiency of an anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A 2/O) wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). Process Biochem 39:1615–1624
Zhu G, Peng Y, Wang S, Wu S, Ma B (2007) Effect of influent flow rate distribution on the performance of step-feed biological nitrogen removal process. Chem Eng J 131:319–328
Zhu GB, Peng YZ, Zhai LM, Yu W, Wang SY (2009) Performance and optimization of biological nitrogen removal process enhanced by anoxic/oxic step feeding. Biochem Eng J 43:280–287
Chang HY, Ouyang CF (2000) Improvement of nitrogen and phosphorus removal in the anaerobic-oxic-anoxic-OXIC (AOAO) process by stepwise feeding. Water Sci Technol 42:89–94
Laera G, Jin B, Lopez A (2011) Application of sequencing batch membrane bioreactors (SB-MBR) for the treatment of municipal wastewater. Water Sci Technol 64:391–396
Artan N, Orhon D, Tusli R (2002) Design of SBR systems for nutrient removal from wastewaters subject to seasonal fluctuations. Water Sci Technol 46:91–98
Artan N, Wilderer P, Orhon D, Tasli R, Morgenroth E (2002) Model evaluation and optimisation of nutrient removal potential for sequencing batch reactors. Water S A 28:423–432
Artan N, Tasli R, Orhon D (2006) Rational basis for optimal design of sequencing batch reactors with multiple anoxic filling for nitrogen removal. Process Biochem 41:901–908
Irvine RL (1989) Sequencing batch reactor for biological wastewater treatment. CRC Crit Rev Environ Control 18:255–294
Gao YQ, Peng YZ, Zhang JY, Wang SY, Guo JH, Ye L (2011) Biological sludge reduction and enhanced nutrient removal in a pilot-scale system with 2-step sludge alkaline fermentation and A(2)O process. Bioresour Technol 102:4091–4097
Henze M, Dupont R, Grau P, Delasota A (1993) Rising sludge in secondary settlers due to denitrification. Water Res 27:231–236
Comas J, Rodríguez-Roda I, Gernaey KV, Rosen C, Jeppsson U, Poch M (2008) Risk assessment modelling of microbiology-related solids separation problems in activated sludge systems. Environ Model Softw 23:1250–1261
Kim MH, Alghusain IA, Hao OJ, Lim BS (1994) Modeling of nitrate disappearance and sludge rising in a settling column system. Water Res 28:1861–1872
Smolders GJF, Meij JVD, Loosdrecht MCMV, Heijnen JJ (1994) Stoichiometric model of the aerobic metabolism of the biological phosphorus removal process. Biotechnol Bioeng 44:837–848
Yang Q, Peng YZ, Liu XH, Zeng W, Mino T, Satoh H (2007) Nitrogen removal via nitrite from municipal wastewater at low temperatures using real-time control to optimize nitrifying communities. Environ Sci Technol 41:8159–8164
Ma B, Wang SY, Zhang SJ, Li XY, Bao P, Peng YZ (2013) Achieving nitritation and phosphorus removal in a continuous-flow anaerobic/oxic reactor through bio-augmentation. Bioresour Technol 139:375–378
Zhang M, Yang Q, Zhang JH, Wang C, Wang SY, Peng YZ (2016) Enhancement of denitrifying phosphorus removal and microbial community of long-term operation in an anaerobic anoxic oxic-biological contact oxidation system. J Biosci Bioeng 122:456–466
Saunders AM, Oehmen A, Blackall LL, Yuan Z, Keller J (2003) The effect of GAOs (glycogen accumulating organisms) on anaerobic carbon requirements in full-scale Australian EBPR (enhanced biological phosphorus removal) plants. Water Sci Technol 47:37–43
Mino Takashi, Liu WenTso, Kurisu Futoshi, Matsuo Tomonori (1995) Modelling glycogen storage and denitrification capability of microorganisms in enhanced biological phosphate removal processes. Water Sci Technol 31:25–34
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Am Public Health Assoc Washington DC USA 24:481–486
Zeng RJ, van Loosdrecht MCM, Yuan ZG, Keller J (2003) Metabolic model for glycogen-accumulating organisms in anaerobic/aerobic activated sludge systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:92–105
Oehmen A, Zeng RJ, Yuan Z, Keller J (2005) Anaerobic metabolism of propionate by polyphosphate-accumulating organisms in enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 91:43–53
Wang XX, Wang SY, Xue TL, Li BK, Dai X, Peng YZ (2015) Treating low carbon/nitrogen (C/N) wastewater in simultaneous nitrification-endogenous denitrification and phosphorous removal (SNDPR) systems by strengthening anaerobic intracellular carbon storage. Water Res 77:191–200
Jenni S, Vlaeminck SE, Morgenroth E, Kai MU (2014) Successful application of nitritation/anammox to wastewater with elevated organic carbon to ammonia ratios. Water Res 49:316–326
Li ZM, Wang SY, Zhang WT, Miao L, Cao TH, Peng YZ (2014) Nitrogen removal from medium-age landfill leachate via post-denitrification driven by PHAs and glycogen in a single sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour Technol 169:773–777
Tan TW, Ng HY (2008) Influence of mixed liquor recycle ratio and dissolved oxygen on performance of pre-denitrification submerged membrane bioreactors. Water Res 42:1122–1132
Yan X, Han YP, Li QL, Sun JH, Su XF (2016) Impact of internal recycle ratio on nitrous oxide generation from anaerobic/anoxic/oxic biological nitrogen removal process. Biochem Eng J 106:11–18
Ouyang CF, Chou YJ, Pai TY, Chang HY, Liu WT (2001) Optimization of enhanced biological wastewater treatment processes using a step-feed approach. In: Matsuo T, Hanaki K, Takizawa S, Satoh H (eds) Advances in water and wastewater treatment technology in 2000–Molecular technology, nutrient removal, sludge reduction and environmental health. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 295–304
Rahimi Y, Torabian A, Mehrdadi N, Shahmoradi B (2011) Simultaneous nitrification-denitrification and phosphorus removal in a fixed bed sequencing batch reactor (FBSBR). J Hazard Mater 185:852–857
Miao L, Wang SY, Li BK, Cao TH, Xue TL, Peng YZ (2015) Advanced nitrogen removal via nitrite using stored polymers in a modified sequencing batch reactor treating landfill leachate. Bioresour Technol 192:354–360
Guo YY, Peng YZ, Wang B, Li BK, Zhao MY (2016) Achieving simultaneous nitrogen removal of low C/N wastewater and external sludge reutilization in a sequencing batch reactor. Chem Eng J 306:925–932
Zeng RJ, Lemaire R, Yuan Z, Keller J (2003) Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal in a lab-scale sequencing batch reactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 84:170–178
Chung J, Bae W (2002) Nitrite reduction by a mixed culture under conditions relevant to shortcut biological nitrogen removal. Biodegradation 13:163–170
Turk O, Mavinic DS (1987) Benefits of using selective inhibition to remove nitrogen from highly nitrogenous wastes. Environ Technol Lett 8:419–426
Beccari M, Passino R, Ramadori R, Tandoi V (1983) Kinetics of dissimilatory nitrate and nitrite reduction in suspended growth culture. J Water Pollut Control Fed 55:58–64
Abufayed AA, Schroeder ED (1986) Kinetics and stoichiometry of SBR/denitrification with a primary sludge carbon source. Journal 58:398–405
Kujawa K, Klapwijk B (1999) A method to estimate denitrification potential for predenitrification systems using NUR batch test. Water Res 33:2291–2300
Li S, Li H, Liang XQ, Chen YX, Cao ZH, Xu ZH (2009) Rural wastewater irrigation and nitrogen removal by the paddy wetland system in the Tai Lake region of China. J Soils Sed 9:433–442
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21677005), 111 Project (D16003) and the Funding Projects of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, L., Ma, B., Li, X. et al. Advanced nitrogen removal without addition of external carbon source in an anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic sequencing batch reactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42, 1507–1515 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02148-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02148-z