Abstract
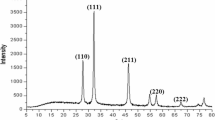
Emergence of antibiotic resistance by bacteria has become a serious threat for public health worldwide. In this study, Streptomyces isolated from fertile soil sample was tested for biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNps) using cell-free supernatant and synthesized AgNps were screened for anti-ESBL (extended spectrum β-lactamase) activity against multi-drug resistant (MDR) ESBL-producing strain Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC 700603) and other medically important pathogens. Synthesis of AgNps was confirmed by change in pale yellow color to dark brown color and characteristic absorption spectra at 420 nm. The XRD spectrum displayed typical peaks of crystalline silver and EDAX analysis showed a major signal for silver. FTIR spectra revealed prominent peaks at 3,294 cm−1 (NH stretching due to amide group), 2,952 cm−1 (aldehydic C–H stretching) 1,658 cm−1 indicating the presence of carbonyl group. AgNps were spherical in shape with size ranging from 20 to 70 nm. The synthesized AgNps showed significant antimicrobial activity against standard ESBL pathogen K. pneumoniae (22 mm), 21 mm against clinical ESBL isolate E. coli and 16 mm against clinical ESBL isolates K. pneumoniae and Citrobacter species, respectively. The results of this study suggest that AgNps synthesized by Streptomyces sp. VITSJK10 can be used as a potential alternative to control MDR ESBL pathogens. The present study aimed for green synthesis of AgNps using Streptomyces species and to explore its anti-ESBL activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stuart BL (2002) J Antimicrob Chemother 49:25–30
Szijarto V, Pal T, Nagy G, Nagy E, Ghazawi A, Al HM, El KS, Sonnevend A (2012) FEMS Microbiol Lett 332:131–136
Deepti R, Deepthi N (2010) J Glob Infect Dis 2:263–274
Grover SS, Sharma M, Chattopadhya D, Kapoor H, Pasha ST, Singh G (2006) J Infect 53:279–288
David LP, Robert AB (2005) Clin Microbiol Rev 18:657–686
Herindrainy P, Randrianirina F, Ratovoson R, Ratsima HE, Buisson Y, Genel N, Decré D, Arlet G, Talarmin A, Richard V (2011) PLoS One 6:22738
Johann DDP, Patrice N, Kevin BL, Laurent P (2005) J Antimicrob Chemother 56:52–59
Marin HK, Yoav G, Scott TM, Andrew FS, Marcos IR (2011) Clin Infect Dis 53:33–55
Lin RD, Chin YP, Lee MH (2005) Phytother Res 19:612–617
Mahajan GB, Balachandran L (2012) Front Biosci 4:240–253
Selvameenal, Radhakrishnan M, Balagurunathan R (2009) Indian J Pharm Sci 71:499–504
Xiangqian L, Huizhong X, Zhe SC, Guofang C (2011) Biosynthesis of nanoparticles by microorganisms and their applications. J Nanomaterials. doi:10.1155/2011/270974
Wei W, Quanguo H, Changzhong J (2008) Nanoscale Res Lett 3:397–415
Yan H, Zhiyun D, Huibin L, Qianfa J, Zhikai T, Xi Z, Kun Z, Fenghua Z (2013) Int J Nanomed 8:1809–1815
Thenmozhi M, Kannabiran K, Kumar R, Gopiesh VK (2013) J Mycol Med 5:145–149
Kumar S, Kannabiran K (2010) J Nat Env Sci 1:56–65
Nathan A, Magarvey, Jessica MK, Valerie B, Martin D, David HS (2004) Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7520–7529
Martin GC, Steven AM, Ronald NJ (1996) J Clin Microbiol 1996(34):1880–1884
Neha S, Vibhuti R (2012) Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4:0975–1491
Benita MR, Kannabiran K (2010) Pharmacologyonline 1:124–132
Mohamed A. Mahmoud, Saleh A. Al S, Monira R. Alothman, Abeer R, Abd el MA, Saleh AE (2013) Dig J Nanomater Bios 8:589–596
Sadhasivam S, Shanmugam P, Yun K (2010) Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 81:358–362
Prabu S, Poulose E (2012) Intl Nano Letters 2:32–42
Shetty PR, Kumar BS, Kumar YS, Shankar GG (2012) J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:614–621
Zonooz NF, Salouti M (2011) Scientia Eranica F 18:1631–1635
Sudhanshu SB, Jayanta KP, Krishna P, Niladri P, Hrudayanath T (2012) WJNSE 2:196–200
Jannu V, Thenmozhi M, Kannabiran K, Rajakumar G, Rahuman AA (2013) Mater Lett 93:360–362
Lara HH, Nilda VA, Turrent LCI, Padilla CR (2010) World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:615–621
Khabat V, Ali GM, Sedighe K (2007) Nanomedicine 3:95–101
Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim JH, Park SJ, Lee HJ, Kim SH, Park YK, Park YH, Hwang CY, Kim YK, Lee YS, Jeong DH, Cho MH (2007) Nanomedicine 3:95–101
Shahin G, Behrouz L, Mohammad M (2013) TJEAS 3:48–58
Fidel MG, Peggy LO, Adriana B, Erasmo O, Nereyda N, Elpidio MS, Facundo R, Horacio B, Yossef AG (2010) Nanomed Nanotechnol 6:681–688
Sivalingam P, Antony JJ, Siva D, Achiraman S, Anbarasu K (2012) Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 981:12–17
Shubhrasekhar C, Supriya M, Karthik L, Gaurav K, Bhaskara Rao KV (2013) Res J Biotech 8:1
Rai R, Bai J (2011) In: Mendez-Vilas A (ed) Formatex Research Centre 1:197–09
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the management of VIT University for providing facilities to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subashini, J., Gopiesh Khanna, V. & Kannabiran, K. Anti-ESBL activity of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized using soil Streptomyces species. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37, 999–1006 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-1070-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-1070-8