Abstract
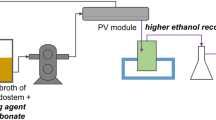
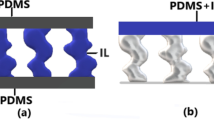
The effects of by-products from ethanol fermentation and hydrolysates of lignocelluloses on ethanol diffusion through polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) membranes with/without silicalite-1 were investigated. A pervaporation process was integrated with lignocellulosic fermentation to concentrate bioethanol using bare PDMS membranes. Results showed that yeasts, solid particles, and salts increased ethanol flux and selectivity through the membranes (PDMS with/without silicalite-1), whereas glucose exerted negative effects on the performance. On bare PDMS membrane, the performance was not obviously affected by the existence of aliphatic acids. However, on PDMS-silicalite-1 membrane, a remarkable decrease in ethanol selectivity and a rapid growth of total flux in the presence of aliphatic acids were observed. These phenomena were due to the interaction of acids with silanol (Si–OH) groups to break the dense membrane surface. On the PDMS membranes with/without silicalite-1, degradation products of lignocellulosic hydrolysates such as furfural and hydroxyacetone slightly influenced separation performance. These results revealed that an integrated process can effectively eliminate product inhibition, improve ethanol productivity, and enhance the glucose conversion rate.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farrell AE, Plevin RJ, Turner BT, Jones AD, O’Hare M, Kammen DM (2006) Ethanol can contribute to energy and environmental goals. Science 27:506–508
Wyman CE (1996) Ethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass: overview. In: Wyman CE (ed) Handbook on Bioethanol: Product I on and Utilization. Taylor & Francis, Washington, DC, pp 1–18
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83:1–11
Ezeji TC, Qureshi N, Blaschek HP (2004) Acetone butanol ethanol (ABE) production from concentrated substrate: reduction in substrate inhibition by fed-batch technique and product inhibition by gas stripping. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:653–658
Carton A, Benito GG, Rey JA, de la Fuente M (1998) Selection of adsorbents to be used in an ethanol fermentation process adsorption isotherms and kinetics. Bioresour Technol 66:75–78
Tanimura S, Yamaguchi K, Nakao S, Kimura S (1992) Separation of Alcohol aqueous-solutions by reverse-osmosis and pervaporation using a Poly-(1-Trimethylsilyl-1-Propyne) Membrane. J Chem Eng Jpn 25(5):580–585
Levario T. Characterization of Novel Adsorbents for the Recovery of Alcohol Biofuels from aqueous solutions via solid-phase extraction. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses (9781124781655) 2011-01-01
Banat FA, Al-Shannag M (2000) Recovery of dilute acetone-butanol-ethanol (ABE) solvents from aqueous solutions via membrane distillation. Bioprocess Biosystems Eng 23(6):643–649
Peng P, Shi B, Lan Y (2011) A review of membrane materials for ethanol recovery by pervaporation. Sep Sci Technol 46(2):234–246
Ikegami T, Kitamoto D, Negishi H, Haraya K, Matsuda H, Nitanai Y (2003) Drastic improvement of bioethanol recovery using a pervaporation separation technique employing a silicone rubber-coated silicalite membrane. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 78:1006–1010
Vane LM (2005) A review of pervaporation for product recovery from biomass fermentation process. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 80:603–629
Leeper SA (1986) Membrane separation I: the production of alcohol fuels by fermentation. In: Mc Gregor WC (ed) Membrane separation in biotechnology. Marcel Dekker Inc.1, New York, pp 161–200
Mohammadi T, Aroujalian A, Bakhshi A (2005) Pervaporation of dilute alcoholic mixtures using PDMS membrane. Chem Eng Sci 60:1875–1880
O’Brien DJ, Senske GE, Kurantz MJ, Craig JC Jr (2004) Ethanol recovery from corn fiber hydrolysate fermentations by pervaporation. Bioresour Technol 92(1):15–19
Grous WR, Converse AO, Grethlein HE (1986) Effect of steam explosion pretreatment on pore-size and enzymatic-hydrolysis of poplar. Enzyme Microb Technol 8(5):274–280
Aden A, Ruth M, Ibsen K, et al (2002) Lignocellulosic biomass to ethanol process design and economics utilizing co-current dilute acid prehydrolysis and enzymatic hydrolysis for corn stover, NREL report TP-510-32438
Chovau S, Gaykawad S, Straathof AJJ, Van der Bruggen B (2011) Influence of fermentation by-products on the purification of ethanol from water using pervaporation. Bioresour Technol 102(2):1669–1674
Fadeev AG, Kelley SS, McMillan JD, Selinskaya YaA, Khotimsky VS, Volkov VV (2003) Effect of yeast fermentation by-products on poly[1-(trimethylsilyl)-1-propyne] pervaporative performance. J Membr Sci 214:229–238
García M, Sanz MT, Beltran S (2009) Separation by pervaporation of ethanol from aqueous solutions and effect of other components present in fermentation broths. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:1873–1882
Lipnizki F, Hausmanns S, Field RW (2004) Influence of impermeable components on the permeation of aqueous 1-propanol mixtures in hydrophobic pervaporation. J Membr Sci 228(2):129
Qu X, Dong H, Zhou Z, Zhang L, Chen H (2010) Pervaporation separation of xylene isomers by hybrid membranes of PAAS filled with Si lane-modified zeolite. Ind Eng Chen Res 49(16):7504–7514
Yan L, Zhang H, Chen J, Lin Z, Jin Q, Jia H, Huang H (2009) Dilute sulfuric acid cycle spray flow-through pretreatment of corn stoverfor enhancement of sugar recovery. Bioresour Technol 100(5):1803–1808
Zheng R, Zhang H, Zhao J, Lei M, Huang H (2011) Direct and simultaneous determination of representative byproducts in a lignocellulosic hydrolysate of corn stover via gas chromatography–mass spectrometry with a Deans switch. J Chromatogr A 1218:5319–5327
Bowen TC, Meier RG, Vane LM (2007) Stability of MFI zeolite-filled PDMS membranes during pervaporation ethanol recovery from aqueous mixtures containing acetic acid. J Membr Sci 298:117–125
Barton AFM (1983) Handbook of solubility parameters and other cohesion parameters. CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton
Dong Y, Zhang L, Shen J, Song M, Chen H (2006) Preparation of poly(vinyl alcohol)-sodium alginate hollow-fiber composite membranes and pervaporation dehydration characterization of aqueous alcohol mixtures. Desalination 193:202–210
Abdolreza A, Kaled B, Stephen J, Ginette T, Yves P (2006) Effect of residual sugars in fermentation broth on pervaporation flux and selectivity for ethanol. Desalination 193:103–108
Hussain MAM, Anthony JL, Pfromm PH (2012) Reducing the energy demand of corn-based fuel ethanol through salt extractive distillation enabled by electrodialysis. AlChE J. 58(1):163–172
Wu Y, Xiao Z, Huang W, Zhong Y (2005) Mass transfer in pervaporation of active fermentation broth with a composite PDMS membrane. Sep Purif Technol 42:47–53
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21176124; 20876078), the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.20936002; 2009CB724700); the National Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (No. 2009AA02Z208), the National Key Technology Support Program of China (2011BAD23B03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Zhang, H., Wei, P. et al. Pervaporation behavior and integrated process for concentrating lignocellulosic ethanol through polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) membrane. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37, 183–191 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-0984-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-0984-5