Abstract
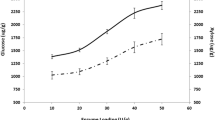
Oil palm fronds are the most abundant lignocellulosic biomass in Malaysia. In this study, fronds were tested as the potential renewable biomass for ethanol production. The soaking in aqueous ammonia pretreatment was applied, and the fermentability of pretreated fronds was evaluated using simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. The optimal pretreatment conditions were 7 % (w/w) ammonia, 80 °C, 20 h of pretreatment, and 1:12 S/L ratio, where the enzymatic digestibility was 41.4 % with cellulase of 60 FPU/g-glucan. When increasing the cellulase loading in the hydrolysis of pretreated fronds, the enzymatic digestibility increased until the enzyme loading reached 60 FPU/g-glucan. With 3 % glucan loading in the SSF of pretreated fronds, the ethanol concentration and yield based on the theoretical maximum after 12 and 48 h of the SSF were 7.5 and 9.7 g/L and 43.8 and 56.8 %, respectively. The ethanol productivities found at 12 and 24 h from pretreated fronds were 0.62 and 0.36 g/L/h, respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun RC, Fang JM, Mott L, Bolton J (1999) Fractional isolation and characterization of polysaccharides from oil palm trunk and empty fruit bunch fibres. Holzforschung 53:253–260
MPOC (2010) Palm oil: a success story in green technology innovations. http://www.akademisains.gov.my/download/asmic/asmic2010/Plenary12.pdf. Accessed 10 July 2011
Jung YH, Kim IJ, Kim JJ, Oh KK, Han J-I, Choi I-G, Kim KH (2011) Ethanol production from oil palm trunks treated with aqueous ammonia and cellulase. Bioresour Technol 102:7307–7312
Ko JK, Bak JS, Jung MW, Lee HJ, Choi I-G, Kim TH, Kim KH (2009) Ethanol production from rice straw using optimized aqueous-ammonia soaking pretreatment and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation processes. Bioresour Technol 100:4374–4380
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Crocker D (2008) Laboratory analytical procedure: determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden
Selig M, Weiss N, Ji Y (2008) Laboratory analytical procedure: enzymatic saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden
Kim TH, Lee YY (2007) Pretreatment of corn stover by soaking in aqueous ammonia at moderate temperatures. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 136–140:81–92
Jung YH, Kim IJ, Han J-I, Choi I-G, Kim KH (2011) Aqueous ammonia pretreatment of oil palm empty fruit bunches for ethanol production. Bioresour Technol 102:9806–9809
Lipinsky ES (1979) Perspectives on preparation of cellulose for hydrolysis. In: Brown RD Jr, Jurasek L (eds) Hydrolysis of cellulose: mechanisms of enzymatic and acid catalysis. American Chemical Society, Washington DC
Tu M, Pan X, Saddler JN (2009) Adsorption of cellulase on cellulolytic enzyme lignin from lodgepole pine. J Agric Food Chem 57:7771–7778
Yang B, Wyman CE (2006) BSA treatment to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose in lignin containing substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:611–617
Tomas-Pejo E, Oliva JM, Ballesteros M, Olsson L (2008) Comparison of SHF and SSF processes from steam-exploded wheat straw for ethanol production by xylose-fermenting and robust glucose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Biotechnol Bioeng 100:1122–1131
Kádár Z, Szengyel Z, Réczey K (2004) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) of industrial wastes for the production of ethanol. Ind Crop Prod 20:103–110
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Advanced Biomass R&D Center of Korea (2011-0031353) funded by MEST and also financially supported by the Ministry for Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Korea. Facility support at Korea University Food Safety Hall for the Institute of Biomedical Science and Food Safety is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, Y.H., Kim, S., Yang, T.H. et al. Aqueous ammonia pretreatment, saccharification, and fermentation evaluation of oil palm fronds for ethanol production. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35, 1497–1503 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0739-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0739-8