Abstract
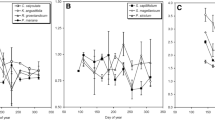
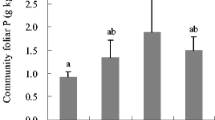
Nitrogen relations of natural and disturbed tropical plant communities in northern Australia (Kakadu National Park) were studied. Plant and soil N characteristics suggested that differences in N source utilisation occur at community and species level. Leaf and xylem sap N concentrations of plants in different communities were correlated with the availability of inorganic soil N (NH+ 4 and NO− 3). In general, rates of leaf NO− 3 assimilation were low. Even in communities with a higher N status, including deciduous monsoon forest, disturbed wetland, and a revegetated mine waste rock dump, levels of leaf nitrate reductase, xylem and leaf NO− 3 levels were considerably lower than those that have been reported for eutrophic communities. Although NO− 3 assimilation in escarpment and eucalypt woodlands, and wetland, was generally low, within these communities there was a suite of species that exhibited a greater capacity for NO− 3 assimilation. These “high- NO− 3 species” were mainly annuals, resprouting herbs or deciduous trees that had leaves with high N contents. Ficus, a high-NO− 3 species, was associated with soil exhibiting higher rates of net mineralisation and net nitrification. “Low-NO− 3 species” were evergreen perennials with low leaf N concentrations. A third group of plants, which assimilated NO− 3 (albeit at lower rates than the high-NO− 3 species), and had high-N leaves, were leguminous species. Acacia species, common in woodlands, had the highest leaf N contents of all woody species. Acacia species appeared to have the greatest potential to utilise the entire spectrum of available N sources. This versatility in N source utilisation may be important in relation to their high tissue N status and comparatively short life cycle. Differences in N utilisation are discussed in the context of species life strategies and mycorrhizal associations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 July 1997 / Accepted: 13 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, S., Stewart, G., Turnbull, M. et al. Nitrogen relations of natural and disturbed plant communities in tropical Australia. Oecologia 117, 95–104 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050636
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050636