Abstract
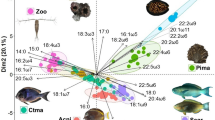
Coral reefs support spectacularly productive and diverse communities in tropical and sub-tropical waters throughout the world’s oceans. Debate continues, however, on the degree to which reef biomass is supported by new water column production, benthic primary production, and recycled detrital carbon (C). We coupled compound-specific stable C isotope ratio (δ13C) analyses with Bayesian mixing models to quantify C flow from primary producers to coral reef fishes across multiple feeding guilds and trophic positions in the Red Sea. Analyses of reef fishes with putative diets composed primarily of zooplankton (Amblyglyphidodon indicus), benthic macroalgae (Stegastes nigricans), reef-associated detritus (Ctenochaetus striatus), and coral tissue (Chaetodon trifascialis) confirmed that δ13C values of essential amino acids from all baseline C sources were both isotopically diagnostic and accurately recorded in consumer tissues. While all four source end-members contributed to the production of coral reef fishes in our study, a single-source end-member often dominated dietary C assimilation of a given species, even for highly mobile, generalist top predators. Microbially reworked detritus was an important secondary C source for most species. Seascape configuration played an important role in structuring resource utilization patterns. For instance, Lutjanus ehrenbergii showed a significant shift from a benthic macroalgal food web on shelf reefs (71 ± 13 % of dietary C) to a phytoplankton-based food web (72 ± 11 %) on oceanic reefs. Our work provides insights into the roles that diverse C sources play in the structure and function of coral reef ecosystems and illustrates a powerful fingerprinting method to develop and test nutritional frameworks for understanding resource utilization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alongi DDM (1988) Detritus in coral reef ecosystems: fluxes and fates. Proc 6th Int Coral Reef Symp 1:29–36
Arias-Gonzalez JE, Nunez-Lara E, Gonzalez-Salas C, Galzin R (2004) Trophic models for investigation of fishing effect on coral reef. Ecol Model 172:197–212. doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2003.09.007
Arthur KW, Kelez S, Larsen T, Choy CA, Popp BN (2014) Tracing the biosynthetic source of essential amino acids in marine turtles using δ13C fingerprints. Ecology 95:1285–1293. doi:10.1890/13-0263.1
Bearhop S, Adams CE, Waldron S, Fuller RA, Macleod H (2004) Determining trophic niche width: a novel approach using stable isotope analysis. J Anim Ecol 73:1007–1012. doi:10.1111/j.0021-8790.2004.00861.x
Berumen ML, Pratchett MS (2008) Trade-offs associated with dietary specialisation for corallivorous butterflyfishes. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 62:989–994. doi:10.1007/s00265-007-0526-8
Bond AL, Diamond AW (2011) Recent Bayesian stable-isotope mixing models are highly sensitive to variation in discrimination factors. Ecol App 21:1017–1023. doi:10.1890/09-2409
Borman A, Wood TR, Black HC, Anderson EG, Oesterling MJ, Womack M, Rose WC (1946) The role of arginine in growth with some observations on the effects of argininic acid. J Biol Chem 166:585–594
Brett MT (2014) Resource polygon geometry predicts Bayesian stable isotope mixing model bias. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 514:1–12. doi:10.3354/meps11017
Carassou L, Kulbicki M, Nicola TJR, Polunin NVC (2008) Assessment of fish trophic status and relationships by stable isotope data in the coral reef lagoon of New Caledonia, southwest Pacific. Aquat Living Resour 21:1–12. doi:10.1051/alr:2008017
Chen L-S (2002) Post-settlement diet shift of Chlorurus sordidus and Scarus schlegeli (Pisces: Scaridae). Zool Stud 41:47–58
Choat JH, Clements KD, Robbins WD (2002) The trophic status of herbivorous fishes on coral reefs. I. Dietary analyses. Mar Biol 140:613–623. doi:10.1007/s00227-001-0715-3
Choat JH, Robbins WD, Clements KD (2004) The trophic status of herbivorous fishes on coral reefs. II. Food processing modes and trophodynamics. Mar Biol 145:445–454. doi:10.1007/s00227-004-1341-7
Cocheret de la Moriniere E, Pollux BJA, Nagelkerken I, Hemminga MA, Huiskes AHL, van der Velde G (2003) Ontogenetic dietary changes of coral reef fishes in the mangrove-seagrass-reef continuum: stable isotopes and gut-content analysis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 246:279–289. doi:10.3354/meps246279
Connell JH (1978) Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs. Science 199:1302–1310
Cote IM, Gill JA, Gardner GA, Watkinson AR (2005) Measuring coral reef decline through meta-analysis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 360:385–395. doi:10.1098/rstb.2004.1591
Cowen R (1988) The role of algal symbiosis in reefs through time. Palaios 3:221–227. doi:10.2307/3514532
Crossman DJ, Choat JH, Clements KD, Hardy T, McConochie J (2001) Detritus as food for grazing fishes on coral reefs. Limnol Oceanogr 46:1596–1605
Cruz-Rivera E, Hay ME (2000) The effects of diet mixing on consumer fitness: macroalgae, epiphytes, and animal matter as food for marine amphipods. Oecologia 123:252–264. doi:10.1007/s004420051012
Darwin C (1842) The structure and distribution of coral reefs. Appleton, New York
de Goeij JM, van Oevelen D, Vermeij MJ, Osinga R, Middelburg JJ, de Goeij AF, Admiraal W (2013) Surviving in a marine desert: the sponge loop retains resources within coral reefs. Science 342:108–110. doi:10.1126/science.1241981
Deb D (1997) Trophic uncertainty vs. parsimony in food web research. Oikos 78:191–194
Emery A (1973) Comparative ecology and functional osteology of fourteen species of damselfish (Pices: Pomacentridae) at Alligator Reef, Florida Keys. Bull Mar Sci 23:649–770
Ferrier-Pages C, Gattuso JP (1998) Biomass, production and grazing rates of pico- and nanoplankton in coral reef waters (Miyako Island, Japan). Microb Ecol 35:46–57
Fry B (2013) Alternative approaches for solving underdetermined isotope mixing problems. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 472:1–13. doi:10.3354/meps10168
Gast GJ, Wiegman S, Wieringa E, Van Duyl FC, Bak RPM (1998) Bacteria in coral reef water types: removal of cells, stimulation of growth and mineralization. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 167:37–45
Genin A, Monismith SG, Reidenbach MA, Yahel G, Koseff JR (2009) Intense benthic grazing of phytoplankton in a coral reef. Limnol Oceanogr 54:938–951. doi:10.4319/lo.2009.54.3.0938
Greenwood NDW, Sweeting CJ, Polunin NVC (2010) Elucidating the trophodynamics of four coral reef fishes of the Solomon Islands using δ15N and δ13C. Coral Reefs 29:785–792. doi:10.1007/s00338-010-0626-1
Hallock P, Schlager W (1986) Nutrient excess and demise of coral reefs and carbonate platforms. Palaios 1:389–398
Hamner WM, Jones MS, Carleton JH, Hauri IR, Williams DM (1988) Zooplankton, planktivorous fishes, and water currents on a windward reef face: Great Barrier reef, Australia. Bull Mar Sci 42:459–479
Hare PE, Fogel ML, Stafford TW, Mitchell AD, Hoering TC (1991) The isotopic composition of carbon and nitrogen in individual amino acids isolated from modern and fossil proteins. J Archaeol Sci 18:277–292. doi:10.1016/0305-4403(91)90066-X
Hata H, Kato M (2002) Weeding by the herbivorous damselfish Stegastes nigricans in nearly monocultural algae farms. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 237:227–231. doi:10.3354/meps237227
Hayes JM (2001) Fractionation of the isotopes of carbon and hydrogen in biosynthetic processes. In: Cole DR, Valley JW (eds) Reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry 43, stable isotope geochemistry. The Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, pp 225–277
Hilting AK, Currin CA, Kosaki RK (2013) Evidence for benthic primary production support of a top predator-dominated coral reef food web. Mar Biol 160:1681–1695. doi:10.1007/s00227-013-2220-x
Howland MR, Corr LT, Young SMM, Jones V, Jim S, van der Merwe NJ, Mitchell AD, Evershed RP (2003) Expression of the dietary isotope signal in the compound-specific δ13C values of pig bone lipids and amino acids. Int J Osteoarchaeol 13:54–65. doi:10.1002/oa.658
Hughes TP, Bellwood DR, Connolly SR (2002) Biodiversity hotspots, centres of endemicity, and the conservation of coral reefs. Ecol Lett 5:775–784. doi:10.1046/j.1461-0248.2002.00383.x
Hughes TP, Rodrigues MJ, Bellwood DR, Ceccarelli D, Hoegh-Guldberg O, McCook L, Moltschaniwskyj N, Pratchett MS, Steneck RS, Willis B (2007) Phase shifts, herbivory, and the resilience of coral reefs to climate change. Curr Biol 17:360–365. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.12.049
Jim S, Jones V, Ambrose SH, Evershed RP (2006) Quantifying dietary macronutrient sources of carbon for bone collagen biosynthesis using natural abundance stable carbon isotope analysis. Br J Nutr 95:1055–1062. doi:10.1079/BJN20051685
JMP (2013) Graphic builder, version 11. SAS Institute, Cary, NC, URL http://www.jmp.com/software/jmp
Kleppel GS (1993) On the diets of calanoid copepods. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 99:183–195
Kramer MJ, Bellwood O, Bellwood DR (2013) The trophic importance of algal turfs: the crustacean link. Coral Reefs 32:575–583. doi:10.1007/s00338-013-1009-1
Lammens EHRR, de Nie HW, Vijverberg J, van Densen WLT (1985) Resource partitioning and niche shifts of bream (Abramis brama) and eel (Anguilla Anguilla) mediated by predation of smelt (Osmerus eperlanus) on Daphnia hyaline. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 42:1342–1351. doi:10.1139/f85-169
Larsen T, Taylor DL, Leigh MB, O’Brien DM (2009) Stable isotope fingerprinting: a novel method for identifying plant, fungal, or bacterial origins of amino acids. Ecology 90:3526–3535. doi:10.1890/08-1695.1
Larsen T, Ventura M, Andersen N, O’Brien DM, Piatowski U, McCarthy MD (2013) Tracing carbon sources through aquatic and terrestrial food webs using amino acid stable isotope fingerprinting. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0073441
Larsen T, Bach LT, Salvatteci R, Wang YV, Andersen N, Ventura M, McCarthy MD (2015) Assessing the potential of amino acid δ13C patterns as a carbon source tracer in marine sediments: effects of algal growth conditions and sedimentary diagenesis. Biogeosci Discuss 12:1613–1651. doi:10.5194/bgd-12-1613-2015
Lecchini D, Poignonec D (2009) Spatial variability of ontogenetic patterns in habitat associations by coral reef fishes (Moorea lagoon–French Polynesia). Est Coast Shelf Sci 82:553–556. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2009.01.023
Ledlie MH, Graham NAJ, Bythell JC, Wilson SK, Jennings S, Polunin NVC, Hardcastle J (2007) Phase shifts and the role of herbivory in the resilience of coral reefs. Coral Reefs 26:6411–6653. doi:10.1007/s00338-007-0230-1
Letourneur Y, Lison De Loma T, Richard P, Harmelin-Vivien ML, Cresson P, Banaru D, Fontaine MF, Gref T, Planes S (2013) Identifying carbon sources and trophic position of coral reef fishes using diet and stable isotope (δ15N and δ13C) analyses in two contrasted bays in Moorea, French Polynesia. Coral Reefs 32:1091–1102. doi:10.1007/s00338-013-1073-6
Lieske E, Myers RF (2004) Coral reef guide: Red Sea. Harper Collins, Oxford
Lindeman RL (1942) The trophic-dynamic aspect of ecology. Ecology 23:399–417. doi:10.2307/1930126
Marshell A, Mumby PJ (2012) Revisiting the functional roles of the surgeonfish Acanthurus nigrofuscus and Ctenochaetus striatus. Coral Reefs 31:1093–1101. doi:10.1007/s00338-012-0931-y
McCarthy DM, Benner R, Lee C, Hedges JL, Fogel ML (2004) Amino acid carbon isotopic fractionation patterns in oceanic dissolved organic matter: an unaltered photoautotrophic source for dissolved organic nitrogen in the ocean? Mar Chem 92:123–134. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2004.06.021
McMahon KW, Fogel ML, Elsdon T, Thorrold SR (2010) Carbon isotope fractionation of amino acids in fish muscle reflects biosynthesis and isotopic routing from dietary protein. J Anim Ecol 79:1132–1141. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2656.2010.01722.x
McMahon KW, Fogel ML, Johnson BJ, Houghton LA, Thorrold SR (2011) A new method to reconstruct fish diet and movement patterns from δ13C values in otolith amino acids. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 68:1330–1340. doi:10.1139/f2011-070
McMahon KW, Berumen ML, Thorrold SR (2012) Linking habitat mosaics and connectivity in a coral reef seascape. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 109:15372–15376. doi:10.1073/pnas.1206378109
McMahon KW, Hamady L-L, Thorrold SR (2013) Ocean ecogeochemistry: a review. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 51:327–374
McMahon KW, Polito M, Abel S, McCarthy MD, Thorrold SR (2015) Carbon and nitrogen isotope fractionation of amino acids in an avian marine predator, the gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua). Ecol Evol 5:1278–1290. doi:10.1002/ece3.1437
Moore JC, Berlow EL, Coleman DC, de Ruiter PC, Dong Q, Hastings A, Collins Johnson N, McCann KS, Melville K, Morin PJ, Nadelhoffer K, Rosemond AD, Post DM, Sabo JL, Scow KM, Vanni MJ, Wall DH (2004) Detritus, trophic dynamics and biodiversity. Ecol Lett 7:584–600. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00606.x
Moriarty DJW (1982) Feeding of Holothuria atra and Stichopus chloronotus on bacteria, organic carbon and nitrogen in sediments of the Great Barrier Reef. Austral J Mar Freshwater Res 33:255–263. doi:10.1071/MF9820255
Muscatine L (1973) Nutrition of corals. In: Jones OA, Endea R (eds) Biology and geology of coral reefs, vol II. Academic Press, New York, pp 77–115
Muscatine L, Porter JW (1977) Reef corals: mutualistic symbioses adapted to nutrient-poor conditions. Bioscience 27:454–460. doi:10.2307/1297526
Odum HT, Odum EP (1955) Trophic structure and productivity of a windward coral reef community on Eniwetok Atoll. Ecol Monogr 25:291–320
Pandolfi JM, Bradbury RH, Sala E, Hughes TP, Bjorndal KA, Cooke RG, McArdle D, McClenachan L, Newman MJH, Paredes G, Warner RR, Jackson JBC (2003) Global trajectories of the long-term decline of coral reef ecosystems. Science 301:955–958. doi:10.1126/science.1085706
Parnell AC, Inger R, Bearhop S, Jackson AL (2010) Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too much variation. PLoS One 5:e9672. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009672
Polovina JJ (1984) Model of a coral reef ecosystem. I. The ECOPATH model and its application to French frigate shoals. Coral Reefs 3:1–11. doi:10.1007/BF00306135
Post DM (2002) Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 83:703–718. doi:10.2307/3071875
R Development Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org
Raubenheimer D, Simpson SJ, Mayntz D (2009) Nutrition, ecology and nutritional ecology: toward an integrated framework. Funct Ecol 23:4–16. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2435.2009.01522.x
Reeds P (2000) Dispensable and indispensable amino acids for humans. J Nutr 130:1835S–1840S
Richter C, Wunsch M, Rasheed M, Koetter I, Badran MI (2001) Endoscopic exploration of Red Sea coral reefs reveals dense populations of cavity dwelling sponges. Nature 413:726–730. doi:10.1038/35099547
Ryther JH (1969) Relationship of photosynthesis to fish production in the sea. Science 166:72–76. doi:10.1126/science.166.3901.72
Schiff JT, Batista FC, Sherwood OA, Guilderson TP, Hill TM, Ravelo AC, McMahon KW, McCarthy MD (2014) Compound specific amino acid δ13C patterns in a deep-sea proteinaceous coral: implications for reconstructing detailed δ13C records of exported primary production. Mar Chem 166:82–91
Scott JH, O’Brien DM, Emerson D, Sun H, McDonald GD, Salgado A, Fogel M (2006) An examination of the carbon isotope effects associated with amino acid biosynthesis. Astrobiology 6:867–880. doi:10.1089/ast.2006.6.867
Sheppard CRC, Sheppard ALS (1991) Corals and coral communities of Arabia. Fauna Saudi Arabia 12:7–192
Silfer JA, Engel MH, Macko SA, Jumeau EJ (1991) Stable carbon isotope analysis of amino-acid enantiomers by conventional isotope ratio mass spectrometry and combined gas-chromatography isotope ratio mass-spectrometry. Anal Chem 63:370–374. doi:10.1021/ac00004a014
Sommer C, Schneider W, Poutiers JM (1996) FAO species identification field guide for fishery purposes. The living marine resources of Somalia. Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Uthicke S (1999) Sediment bioturbation and impact of feeding activity of Holothuria (Halodeima) atra and Stichopus chloronotus, two sediment feeding holothurians, at Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef. Bull Mar Sci 64:129–141
Ward EJ, Semmens BX, Schindler DE (2010) Including source uncertainty and information in the analysis of stable isotope mixing models. Environ Sci Technol 44:4645–4650. doi:10.1021/es100053v
Wild C, Huettel M, Kleute A, Kremb SG, Rasheed MYM, Jorgensen BB (2004) Coral mucus functions as an energy carrier and particle trap in the reef ecosystem. Nature 428:66–70. doi:10.1038/nature02344
Wyatt AS, Lowe RJ, Humphries S, Waite AM (2010) Particulate nutrient fluxes over a fringing coral reef: relevant scales of phytoplankton production and mechanisms of supply. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 405:113–130. doi:10.3354/meps08508
Wyatt ASJ, Falter JL, Lowe RJ, Humphries S, Waite AM (2012a) Oceanographic forcing of nutrient uptake and release over a fringing coral reef. Limnol Oceanogr 57:401–419. doi:10.4319/lo.2012.57.2.0401
Wyatt ASJ, Waite AM, Humphries S (2012b) Stable isotope analysis reveals community-level variation in fish trophodynamics across a fringing coral reef. Coral Reefs 31:1029–1044. doi:10.1007/s00338-012-0923-y
Wyatt ASJ, Lowe RJ, Humphries S, Waite AM (2013) Particulate nutrient fluxes over a fringing coral reef: source-sink dynamics inferred from carbon to nitrogen ratios and stable isotopes. Limnol Oceanogr 58:409–427. doi:10.4319/lo.2013.58.1.0409
Acknowledgments
This research was based on work supported by Awards USA 00002 and KSA 00011 from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST); additional funding was provided by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), a KAUST-WHOI award (SPCF-7000000104), and KAUST baseline research funds. We thank E. Mason and the Dream Divers crew for boat and dive operation support, C. Braun for creating the site map, and the following people for field assistance: C. Braun, T. Sinclair-Taylor, M. Priest, G. Nanninga, N. desRosiers, P. de la Torre, J. Bouwmeester, L.-L. Hamady. We also thank two anonymous reviewers and the handling editor for valuable comments on this paper.
Author contribution statement
K. W. M., S. R. T., and M. L. B. conceived of and designed the study; K. W. M. and M. L. B. conducted the fieldwork; K. W. M. and L. A. H. conducted the laboratory analyses; K. W. M. and S. R. T. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; M. L. B. and L. A. H. revised and edited the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Deron E. Burkepile.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McMahon, K.W., Thorrold, S.R., Houghton, L.A. et al. Tracing carbon flow through coral reef food webs using a compound-specific stable isotope approach. Oecologia 180, 809–821 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-015-3475-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-015-3475-3