Abstract
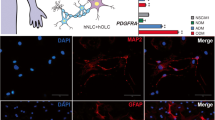
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are used extensively in cell therapy for repair and regeneration of several organs and tissues. Cell therapy is a valuable option to treat neurodegenerative diseases and MSCs have been shown to improve neuronal function through direct differentiation or secretion of neurotrophic factors. In the present study, we isolated and characterized stem cells from medial and central orbital adipose tissue and found that they could be grown in a monolayer culture. The orbital adipose tissue-derived cells were identical to bone marrow-derived MSCs in their cell surface marker expression, gene expression and multilineage differentiation abilities. The orbital adipose-derived MSCs (OAMSCs) express several neurotrophic factors, possess neuroectodermal differentiation ability and secreted factors from OAMSCs abrogated neuronal cell damage induced by oxidative stress. Thus, OAMSCs might be a valuable cell source for treatment of neurological diseases and to reverse oxidative damage in the neuronal cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beane OS, Fonseca VC, Cooper LL, Koren G, Darling EM (2014) Impact of aging on the regenerative properties of bone marrow-, muscle-, and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. PLoS One 9:e115963. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115963
Billon N et al (2007) The generation of adipocytes by the neural crest. Development 134:2283–2292. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.002642
Branch MJ, Hashmani K, Dhillon P, DRE J, Dua HS, Hopkinson A (2012) Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Human Corneal Limbal Stroma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:5109–5116. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.11-8673
Chen SY, Mahabole M, Horesh E, Wester S, Goldberg JL, Tseng SCG (2014) Isolation and Characterization of Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells From Human Orbital Adipose Tissue. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 55:4842–4852. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.14-14441
Cova L et al (2010) Multiple neurogenic and neurorescue effects of human mesenchymal stem cell after transplantation in an experimental model of Parkinson's disease. Brain Res 1311:12–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.11.041
Deng J, Petersen BE, Steindler DA, Jorgensen ML, Laywell ED (2006) Mesenchymal stem cells spontaneously express neural proteins in culture and are neurogenic after transplantation. Stem Cells 24:1054–1064. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2005-0370
Drago D, Cossetti C, IraciN GE, Musco G, Bachi A, Pluchino S (2013) The stem cell secretome and its role in brain repair. Biochimie 95:2271–2285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2013.06.020
Drobny M, Kurca E (2000) Possible extrapyramidal system degradation in Parkinson's disease. Brain Res Bull 53:425–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-9230(00)00367-1
Frese L, Dijkman PE, Hoerstrup SP (2016) Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine. Transfus Med Hemother 43:268–274. https://doi.org/10.1159/000448180
Gilgun-Sherki Y, Melamed E, Offen D (2004) The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: The need for effective antioxidant therapy. J Neurol 251:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-004-0348-9
Hermann A et al (2010) Age-dependent neuroectodermal differentiation capacity of human mesenchymal stromal cells: limitations for autologous cell replacement strategies. Cytotherapy 12:17–30. https://doi.org/10.3109/14653240903313941
Hu BY, Weick JP, Yu JY, Ma LX, Zhang XQ, Thomson JA, Zhang SC (2010) Neural differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells follows developmental principles but with variable potency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:4335–4340. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0910012107
Irion S, Zabierowski SE, Tomishima MJ (2017) Bringing Neural Cell Therapies to the Clinic: Past and Future Strategies. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 4:72–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2016.11.005
Johnston MC, Noden DM, Hazelton RD, Coulombre JL, Coulombre AJ (1979) Origins of avian ocular and periocular tissues. Exp Eye Res 29:27–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4835(79)90164-7
Jung JE, Kim GS, Chan PH (2011) Neuroprotection by Interleukin-6 is mediated by signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and Antioxidative signaling in ischemic stroke. Stroke 42:3574–U3371. https://doi.org/10.1161/Strokeaha.111.626648
Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, Kluter H, Bieback K (2006) Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells 24:1294–1301. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2005-0342
Korn BS, Kikkawa DO, Hicok KC (2009) Identification and Characterization of Adult Stem Cells From Human Orbital Adipose Tissue. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 25:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0b013e3181912292
Lanza C et al (2009) Neuroprotective mesenchymal stem cells are endowed with a potent antioxidant effect in vivo. J Neurochem 110:1674–1684. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06268.x
LiJYet a (2008) Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in subjects with Parkinson's disease suggest host-to-graft disease propagation. Nat Med 14:501–503. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1746
Lojewski X et al (2015) Perivascular Mesenchymal Stem Cells From the Adult Human Brain Harbor No Instrinsic Neuroectodermal but High Mesodermal Differentiation Potential. Stem Cells Transl Med 4:1223–1233. https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2015-0057
Maisel M et al (2010) Genome-wide expression profiling and functional network analysis upon neuroectodermal conversion of human mesenchymal stem cells suggest HIF-1 and miR-124a as important regulators. Exp Cell Res 316:2760–2778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.06.012
Maltman DJ, Hardy SA, Przyborski SA (2011) Role of mesenchymal stem cells in neurogenesis and nervous system repair. Neurochem Int 59:347–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2011.06.008
Mawrie D, Kumar A, Magdalene D, Bhattacharyya J, Jaganathan BG (2016) Mesenchymal stem cells from human extra ocular Muscle Harbor Neuroectodermal differentiation potential. PLoS One 11:e0156697. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0156697
Montzka K et al (2009) Neural differentiation potential of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells: misleading marker gene expression. BMC Neurosci 10:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-10-16
Paul G, Anisimov SV (2013) The secretome of mesenchymal stem cells: Potential implications for neuroregeneration. Biochimie 95:2246–2256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2013.07.013
Paul G et al (2012) The adult human brain harbors multipotent perivascular mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One 7:e35577. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035577
PolazziE, MengoniI, Pena-AltamiraE, MassenzioF, VirgiliM, PetrallaS, MontiB (2015) Neuronal regulation of neuroprotective microglial apolipoprotein E secretion in rat in vitro models of brain pathophysiology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 74:818–834. https://doi.org/10.1097/Nen.0000000000000222
Smith KJ, Kapoor R, Felts PA (1999) Demyelination: The role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Brain Pathol 9:69–92
Somaiah C et al (2015) Collagen promotes higher adhesion, survival and proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One 10:e0145068. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145068
Somaiah C et al (2018) Mesenchymal stem cells show functional defect and decreased anti-cancer effect after exposure to chemotherapeutic drugs. J Biomed Sci 25:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12929-018-0407-7
Sun YJ, Jin KL, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO, Logvinova A, Greenberg DA (2003) VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin Investig 111:1843–1851. https://doi.org/10.1172/Jci200317977
Teixeira FG, Carvalho MM, Sousa N, Salgado AJ (2013) Mesenchymal stem cells secretome: a new paradigm for central nervous system regeneration? Cell Mol Life Sci 70:3871–3882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1290-8
Togarrati PP et al (2017) Identification and characterization of a rich population of CD34(+) mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in human parotid, sublingual and submandibular glands. Sci Rep 7:3484z. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41598-017-03681-1
Uccelli A, Benvenuto F, Laroni A, Giunti D (2011) Neuroprotective features of mesenchymal stem cells. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 24:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beha.2011.01.004
Walker PA, Shah SK, Harting MT, Cox CS (2009) Progenitor cell therapies for traumatic brain injury: barriers and opportunities in translation. Dis Model Mech 2:23–38. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.001198
Wang XQ et al (2016) Neuroprotection effect of Y-27632 against H2O2-induced cell apoptosis of primary cultured cortical neuron. RSC Adv 6:49187–49197. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra03284b
Zuk PA et al (2001) Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng 7:211–228. https://doi.org/10.1089/107632701300062859
Acknowledgments
DM, AS, RS and AK were supported by MHRD, Govt. of India.
Funding
This work was supported by funds from the Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati (IITG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KB and BGJ conceived the study. DM, AK and BGJ designed the study. KB performed blepharoplasty surgery. DM, AS, RS and AK performed experiments. DM, KB, JB, HB, ND and BGJ analyzed the data. DM, KB and BGJ wrote the manuscript. All the authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical statement
All procedures involving human samples were in accordance with the Helsinki convention and approved by the ethics committee of the Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati and Sri Sankaradeva Nethralaya, Guwahati. The study was carried out in accordance with the human ethics committee guidelines and written informed consent was obtained from all the patients involved in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mawrie, D., Bhattacharjee, K., Sharma, A. et al. Human orbital adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells possess neuroectodermal differentiation and repair ability. Cell Tissue Res 378, 531–542 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-03072-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-03072-0