Abstract
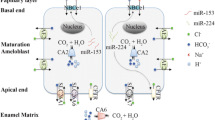
During the formation of dental enamel, maturation-stage ameloblasts express ion-transporting transmembrane proteins. The SLC4 family of ion-transporters regulates intra- and extracellular pH in eukaryotic cells by cotransporting HCO3 − with Na+. Mutation in SLC4A4 (coding for the sodium-bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1) induces developmental defects in human and murine enamel. We have hypothesized that NBCe1 in dental epithelium is engaged in neutralizing protons released during crystal formation in the enamel space. We immunolocalized NBCe1 protein in wild-type dental epithelium and examined the effect of the NBCe1-null mutation on enamel formation in mice. Ameloblasts expressed gene transcripts for NBCe1 isoforms B/D/C/E. In wild-type mice, weak to moderate immunostaining for NBCe1 with antibodies that recognized isoforms A/B/D/E and isoform C was seen in ameloblasts at the secretory stage, with no or low staining in the early maturation stage but moderate to high staining in the late maturation stage. The papillary layer showed the opposite pattern being immunostained prominently at the early maturation stage but with gradually less staining at the mid- and late maturation stages. In NBCe1 −/− mice, the ameloblasts were disorganized, the enamel being thin and severely hypomineralized. Enamel organs of CFTR −/− and AE2a,b −/− mice (CFTR and AE2 are believed to be pH regulators in ameloblasts) contained higher levels of NBCe1 protein than wild-type mice. Thus, the expression of NBCe1 in ameloblasts and the papillary layer cell depends on the developmental stage and possibly responds to pH changes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardo AA, Bernardo CM, Espiritu DJ, Arruda JA (2006) The sodium bicarbonate cotransporter: structure, function, and regulation. Semin Nephrol 26:352–360
Bevensee MO, Schmitt BM, Choi I, Romero MF, Boron WF (2000) An electrogenic Na(+)-HCO(3)(−) cotransporter (NBC) with a novel COOH-terminus, cloned from rat brain. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 278:C1200–C1211
Bronckers AL, Lyaruu DM, Jansen ID, Medina JF, Kellokumpu S, Hoeben KA, Gawenis LR, Oude-Elferink RP, Everts V (2009) Localization and function of the anion exchanger Ae2 in developing teeth and orofacial bone in rodents. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol 312B:375–387
Bronckers A, Kalogeraki L, Jorna HJ, Wilke M, Bervoets TJ, Lyaruu DM, Zandieh-Doulabi B, DenBesten P, de Jonge H (2010) The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is expressed in maturation stage ameloblasts, odontoblasts and bone cells. Bone 46:1188–1196
Bronckers AL, Guo J, Zandieh-Doulabi B, Bervoets TJ, Lyaruu DM, Li X, Wangemann P, DenBesten P (2011) Developmental expression of solute carrier family 26A member 4 (SLC26A4/pendrin) during amelogenesis in developing rodent teeth. Eur J Oral Sci 119 (Suppl 1):185–192
Garant PR, Sasaki S (1986) Ultracytochemistry of ouabain sensitive, K+ dependent para-nitrophenylphosphatase in rat enamel incisor organ. Anat Rec 216:1–9
Gawenis LR, Bradford EM, Prasad V, Lorenz JN, Simpson JE, Clarke LL, Woo AL, Grisham C, Sanford LP, Doetschman T, Miller ML, Shull GE (2007) Colonic anion secretory defects and metabolic acidosis in mice lacking the NBC1 Na+/HCO3- cotransporter. J Biol Chem 282:9042–9052
Josephsen K, Takano Y, Frische S, Praetorius J, Nielsen S, Aoba T, Fejerskov O (2010) Ion transporters in secretory and cyclically modulating ameloblasts: a new hypothesis for cellular control of preeruptive enamel maturation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299:C1299–C1307
Lacruz RS, Nanci A, Kurtz I, Wright JT, Paine ML (2010a) Regulation of pH during amelogenesis. Calcif Tissue Int 86:91–103
Lacruz RS, Nanci A, White SN, Wen X, Wang H, Zalzal SF, Luong VQ, Schuetter VL, Conti PS, Kurtz I, Paine ML (2010b) The sodium bicarbonate cotransporter (NBCe1) is essential for normal development of mouse dentition. J Biol Chem 285:24432–24438
Lacruz RS, Smith CE, Moffatt P, Chang EH, Bromage TG, Bringas P Jr, Nanci A, Baniwal SK, Zabner J, Welsh MJ, Kurtz I, Paine ML (2012) Requirements for ion and solute transport, and pH regulation during enamel maturation. J Cell Physiol 227:1776–1785
Lee SK, Boron WF, Parker MD (2013) Substrate specificity of the electrogenic sodium/bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1-A (SLC4A4, variant A) from humans and rabbits. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 304:F883–F899
Lyaruu DM, Bronckers AL, Mulder L, Mardones P, Medina JF, Kellokumpu S, Oude Elferink RP, Everts V (2008) The anion exchanger Ae2 is required for enamel maturation in mouse teeth. Matrix Biol 27:119–127
Lyaruu DM, Medina JF, Sarvide S, Bervoets TJ, Everts V, DenBesten P, Smith CE, Bronckers AL (2014) Barrier formation: potential molecular mechanism of enamel fluorosis. J Dent Res 93:96–102
Lyman GE, Waddell WJ (1977) pH gradients in the developing teeth of young mice from autoradiography of [14C]DMO. Am J Physiol 232:F364–F367
Paine ML, Snead ML, Wang HJ, Abuladze N, Pushkin A, Liu W, Kao LY, Wall SM, Kim YH, Kurtz I (2008) Role of NBCe1 and AE2 in secretory ameloblasts. J Dent Res 87:391–395
Parker MD, Boron WF (2013) The divergence, actions, roles, and relatives of sodium-coupled bicarbonate transporters. Physiol Rev 93:803–959
Romero MF, Chen AP, Parker MD, Boron WF (2013) The SLC4 family of bicarbonate (HCO3 −) transporters. Mol Aspects Med 34:159–182
Sasaki S, Takagi T, Suzuki M (1991) Cyclical changes in pH in bovine developing enamel as sequential bands. Arch Oral Biol 36:227–231
Simmer JP, Fincham AG (1995) Molecular mechanisms of dental enamel formation. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 6:84–108
Smith CE (1998) Cellular and chemical events during enamel maturation. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 9:128–161
Snead CM, Smith SM, Sadeghein N, Lacruz RS, Hu P, Kurtz I, Paine ML (2011) Identification of a pH-responsive DNA region upstream of the transcription start site of human NBCe1-B. Eur J Oral Sci 119 (Suppl 1):136–141
Uriarte I, Banales JM, Saez E, Arenas F, Oude Elferink RP, Prieto J, Medina JF (2010) Bicarbonate secretion of mouse cholangiocytes involves Na(+)-HCO(3)(−) cotransport in addition to Na(+)-independent Cl(−)/HCO(3)(−) exchange. Hepatology 51:891–902
Wen X, Lacruz RS, Smith CE, Paine ML (2014) Gene-expression profile and localization of Na+/K+-ATPase in rat enamel organ cells. Eur J Oral Sci 122:21–26
Wright JT, Hall KI, Grubb BR (1996) Enamel mineral composition of normal and cystic fibrosis transgenic mice. Adv Dent Res 10:270–274
Zheng L, Zhang Y, He P, Kim J, Schneider R, Bronckers AL, Lyaruu DM, DenBesten PK (2011) NBCe1 in mouse and human ameloblasts may be indirectly regulated by fluoride. J Dent Res 90:782–787
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. H. de Jonge (Erasmus University, Rotterdam, The Netherlands) and Dr. J. Bolscher (Department of Oral Biochemistry, ACTA, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) for advice. The authors are also grateful to Dr. Gary E. Shull (Department of Molecular Genetics, Biochemistry and Microbiology, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, Ohio, USA) for providing breeding pairs of the NBCe1+/− animals. Currently, these mice are available from the Mutant Mice Regional Resource Center (MMRRC), stock no. 034263-JAX.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was in part supported by NIH DE13508 (P.DB., A.B.) and NIH DE019629 (M.L.P.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jalali, R., Guo, J., Zandieh-Doulabi, B. et al. NBCe1 (SLC4A4) a potential pH regulator in enamel organ cells during enamel development in the mouse. Cell Tissue Res 358, 433–442 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1935-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1935-4