Abstract
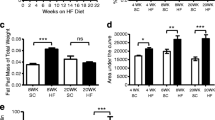
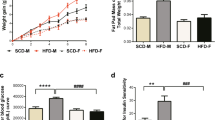
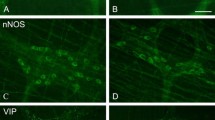
Obesity and type 2 diabetes are increasing in prevalence at an alarming rate in developed and developing nations and over 50 % of patients with prolonged stages of disease experience forms of autonomic neuropathy. These patients have symptoms indicating disrupted enteric nervous system function including gastric discomfort, gastroparesis and intestinal dysmotility. Previous assessments have examined enteric neuronal injury within either type 1 diabetic or transgenic type 2 diabetic context. This study aims to assess damage to myenteric neurons within the duodenum of high-fat diet ingesting mice experiencing symptoms of type 2 diabetes, as this disease context is most parallel to the human condition and disrupted duodenal motility underlies negative gastrointestinal symptoms. Mice fed a high-fat diet developed symptoms of obesity and diabetes by 4 weeks. After 8 weeks, the total number of duodenal myenteric neurons and the synaptophysin density index were reduced and transmission electron microscopy showed axonal swelling and loss of neurofilaments and microtubules, suggesting compromised neuronal health. High-fat diet ingestion correlated with a loss of neurons expressing VIP and nNOS but did not affect the expression of ChAT, substance P, calbindin and CGRP. These results correlate high-fat diet ingestion, obesity and type 2 diabetes symptoms with a loss of duodenal neurons, biasing towards those with inhibitory nature. This pathology may underlie dysmotility and other negative GI symptoms experienced by human type 2 diabetic and obese patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anitha M, Chandrasekharan B, Salgado JR, Grouzmann E, Mwangi S, Sitaraman SV, Srinivasan S (2006) Glial-derived neurotrophic factor modulates enteric neuronal survival and proliferation through neuropeptide Y. Gastroenterology 131:1164–1178
Aring AM, Jones DE, Falko JM (2005) Evaluation and prevention of diabetic neuropathy. Am Fam Physician 71:2123–2128
Ballmann M, Conlon JM (1985) Changes in the somatostatin, substance P and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide content of the gastrointestinal tract following streptozotocin-induced diabetes in the rat. Diabetologia 28:355–358
Baudry C, Reichardt F, Marchix J, Bado A, Schemann M, des Varannes SB, Neunlist M, Moriez R (2012) Diet-induced obesity has neuroprotective effects in murine gastric enteric nervous system: involvement of leptin and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Physiol 590:533–544
Belai A, Lincoln J, Milner P, Burnstock G (1991) Differential effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on the innervation of the ileum and distal colon. Gastroenterology 100:1024–1032
Bytzer P, Talley NJ, Leemon M, Young LJ, Jones MP, Horowitz M (2001) Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: a population-based survey of 15,000 adults. Arch Intern Med 161:1989–1996
Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, Poggi M, Knauf C, Bastelica D, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Tuohy KM, Chabo C, Waget A, Delmée E, Cousin B, Sulpice T, Chamontin B, Ferrières J, Tanti J-F, Gibson GR, Casteilla L, Delzenne NM, Alessi MC, Burcelin R (2007) Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 56:1761–1772
Cellek S, Qu W, Schmidt AM, Moncada S (2004) Synergistic action of advanced glycation end products and endogenous nitric oxide leads to neuronal apoptosis in vitro: a new insight into selective nitrergic neuropathy in diabetes. Diabetologia 47:331–339
Chaikomin R, Wu KL, Doran S, Jones KL, Smout AJPM, Renooij W, Holloway RH, Meyer JH, Horowitz M, Rayner CK (2007) Concurrent duodenal manometric and impedance recording to evaluate the effects of hyoscine on motility and flow events, glucose absorption, and incretin release. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292:G1099–G1104
Chandrasekharan B, Srinivasan S (2007) Diabetes and the enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol Motil 19:951–960
Chandrasekharan B, Anitha M, Blatt R, Shahnavaz N, Kooby D, Staley C, Mwangi S, Jones DP, Sitaraman SV, Srinivasan S (2011) Colonic motor dysfunction in human diabetes is associated with enteric neuronal loss and increased oxidative stress. Neurogastroenterol Motil 23:131–138
D’Cruz ST, Weibley NB, Kimball RS, Alistair J, Barber JA (2012) Post-translational processing of Synaptophysin in the rat retina is disrupted by diabetes. PLoS ONE 7(9):e44711
de La Serre CB, Ellis CL, Lee J, Hartman AL, Rutledge JC, Raybould HE (2010) Propensity to high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats is associated with changes in the gut microbiota and gut inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299:G440–G448
Ding S, Chi MM, Scull BP, Rigby R, Schwerbrock NMJ, Magness S, Jobin C, Lund PK (2010) High-fat diet: bacteria interactions promote intestinal inflammation which precedes and correlates with obesity and insulin resistance in mouse. PLoS ONE 5:e12191
Donnerer J, Barthó L, Holzer P, Lembeck F (1984) Intestinal peristalsis associated with release of immunoreactive substance P. Neuroscience 11:913–918
Du F, Wang L, Qian W, Liu S (2009) Loss of enteric neurons accompanied by decreased expression of GDNF and PI3K/Akt pathway in diabetic rats. Neurogastroenterol Motil 21:1229–e114
Duchman SM, Ryan AJ, Schedl HP, Summers RW, Bleiler TL, Gisolfi CV (1997) Upper limit for intestinal absorption of a dilute glucose solution in men at rest. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29:482–488
Dyck PJ, Kratz KM, Karnes JL, Litchy WJ, Klein R, Pach JM, Wilson DM, O’Brien PC, Melton LJ, Service FJ (1993) The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology 43:817–824
Ellis LM, Mawe GM (2003) Distribution and chemical coding of cocaine- and amphetamine- regulated transcript peptide (CART)-immunoreactive neurons in the guinea pig bowel. Cell Tissue Res 3:265–274
El-Salhy M, Spångéus A (1998) Neuropeptide contents in the duodenum of non-obese diabetic mice. Acta Diabetol 35:9–12
Enck P, Frieling T (1997) Pathophysiology of diabetic gastroparesis. Diabetes 46(Suppl 2):S77–S81
Fehér E, Batbayar B, Vér A, Zelles T (2006) Changes of the different neuropeptide-containing nerve fibers and immunocells in the diabetic rat’s alimentary tract. Ann NY Acad Sci 1084:280–295
Furlan MM, de Miranda Neto MH, D de Sant’ana M, Molinari SL (1999) Number and size of myenteric neurons of the duodenum of adult rats with acute diabetes. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 57:740–745
Furlan MMDP, Molinari SL, de Miranda Neto MH (2002) Morphoquantitative effects of acute diabetes on the myenteric neurons of the proximal colon of adult rats. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 60:576–581
Furness JB (2006) The enteric nervous system. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford
Furness JB, Young HM, Pompolo S, Bornstein JC, Kunze WA, McConalogue K (1995) Plurichemical transmission and chemical coding of neurons in the digestive tract. Gastroenterology 108:554–563
Gabella G, Trigg P (1984) Size of neurons and glial cells in the enteric ganglia of mice, guinea-pigs, rabbits and sheep. J Neurocytol 13:49–71
Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M, MacIntyre I, Hillyard CJ, Girgis S (1985) Co-localization of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity with substance P in cutaneous, vascular and visceral sensory neurons of guinea pigs. Neurosci Lett 57:125–130
He CL, Soffer EE, Ferris CD, Walsh RM, Szurszewski JH, Farrugia G (2001) Loss of interstitial cells of cajal and inhibitory innervation in insulin-dependent diabetes. Gastroenterology 121:427–434
Heddle R, Collins PJ, Dent J, Horowitz M, Read NW, Chatterton B, Houghton LA (1988) Motor mechanisms associated with slowing of the gastric emptying of a solid meal by an intraduodenal lipid infusion. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:437–447
Heddle R, Dent J, Read NW, Houghton LA, Toouli J, Horowitz M, Maddern GJ, Downton J (1989) Antropyloroduodenal motor responses to intraduodenal lipid infusion in healthy volunteers. Am J Physiol 254:G671–G679
Huang PL, Dawson TM, Bredt DS, Snyder SH, Fishman MC (1993) Targeted disruption of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene. Cell 75:1273–1286
Karaosmanoglu T, Aygun B, Wade PR, Gershon MD (1996) Regional differences in the number of neurons in the myenteric plexus of the guinea pig small intestine and colon: an evaluation of markers used to count neurons. Anat Rec 244:470–480
Koch KL (1999) Diabetic gastropathy: gastric neuromuscular dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: a review of symptoms, pathophysiology, and treatment. Dig Dis Sci 44:1061–1075
Kunze WA, Furness JB (1999) The enteric nervous system and regulation of intestinal motility. Annu Rev Physiol 61:117–142
le Roux CW, Bueter M, Theis N, Werling M, Ashrafian H, Löwenstein C, Athanasiou T, Bloom SR, Spector AC, Olbers T, Lutz TA (2011) Gastric bypass reduces fat intake and preference. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301:R1057–R1066
LePard KJ (2005) Choline acetyltransferase and inducible nitric oxide synthase are increased in myenteric plexus of diabetic guinea pig. Auton Neurosci 118:12–24
Lin Y-Y, Tseng T-J, Hsieh Y-L, Luo K-R, Lin W-M, Chiang H, Hsieh S-T (2008) Depletion of peptidergic innervation in the gastric mucosa of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp Neurol 213:388–396
Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Furness JB, Gibbins IL, Costa M (1988) Quantitative ultrastructural analysis of enkephalin-, substance P-, and VIP-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the circular muscle of the guinea pig small intestine. J Comp Neurol 272:139–148
Madsen JL (1992) Effects of gender, age, and body mass index on gastrointestinal transit times. Dig Dis Sci 37:1548–1553
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Mearin F, Malagelada JR (1995) Gastroparesis and dyspepsia in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:717–723
Nam SM, Kim YN, Yoo DY, Yi SS, Kim W, Hwang IK, Seong JK, Yoon YS (2012) Hypothyroid states mitigate the diabetes-induced reduction of calbindin D-28k, calretinin, and parvalbumin immunoreactivity in type 2 diabetic rats. Neurochem Res 37:253–260
Ng Y-K, Zeng X-X, Ling E-A (2004) Expression of glutamate receptors and calcium-binding proteins in the retina of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Brain Res 1018:66–72
Papanas N, Ziegler D (2012) Prediabetic neuropathy: does it exist? Curr Diab Rep 12(4):376–383
Pereira RVF, Tronchini EA, Tashima CM, Alves EPB, Lima MM, Zanoni JN (2011) L-glutamine supplementation prevents myenteric neuron loss and has gliatrophic effects in the ileum of diabetic rats. Dig Dis Sci 56:3507–3516
Phillips RJ, Hargrave SL, Rhodes BS, Zopf DA, Powley TL (2004) Quantification of neurons in the myenteric plexus: an evaluation of putative pan-neuronal markers. J Neurosci Methods 133:99–107
Qu Z-D, Thacker M, Castelucci P, Bagyánszki M, Epstein ML, Furness JB (2008) Immunohistochemical analysis of neuron types in the mouse small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 334:147–161
Sang Q, Young HM (1996) Chemical coding of neurons in the myenteric plexus and external muscle of the small and large intestine of the mouse. Cell Tissue Res 284:39–53
Sang Q, Young HM (1998) The identification and chemical coding of cholinergic neurons in the small and large intestine of the mouse. Anat Rec 251:185–199
Schmidt H, Riemann JF, Schmid A, Sailer D (1984) Ultrastructure of diabetic autonomic neuropathy of the gastrointestinal tract. Wien Klin Wochenschr 62:399–405
Schmidt RE, Plurad DA, Roth KA (1988) Effects of chronic experimental streptozotocin-induced diabetes on the noradrenergic and peptidergic innervation of the rat alimentary tract. Brain Res 458:353–360
Schmidt MI, Duncan BB, Bang H, Pankow JS, Ballantyne CM, Golden SH, Folsom AR, Chambless LE (2005) Identifying individuals at high risk for diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes Care 28:2013–2018
Shotton HR, Broadbent S, Lincoln J (2004) Prevention and partial reversal of diabetes-induced changes in enteric nerves of the rat ileum by combined treatment with alpha-lipoic acid and evening primrose oil. Auton Neurosci 111:57–65
Shuttleworth CW, Murphy R, Furness JB (1991) Evidence that nictric oxide participates in non-adrenergic inhibitory transmission to intestinal muscle in the guinea-pig. Neurosci Lett 130:77–80
Smyth S, Heron A (2006) Diabetes and obesity: the twin epidemics. Nat Med 12:75–80
Spångéus A, El-Salhy M (2001) Myenteric plexus of obese diabetic mice (an animal model of human type 2 diabetes). Histol Histopathol 16:159–165
Spångéus A, Suhr O, El-Salhy M (2000) Diabetic state affects the innervation of gut in an animal model of human type 1 diabetes. Histol Histopathol 15:739–744
Surendran S, Kondapaka SB (2005) Altered expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the duodenum longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus of obesity induced diabetes mouse: implications on enteric neurodegeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338:919–922
Surwit RS, Kuhn CM, Cochrane C, McCubbin JA, Feinglos MN (1988) Diet-induced type II diabetes in C57BL/6J mice. Diabetes 37:1163–1167
Vincent AM, Hayes JM, McLean LL, Vivekanandan-Giri A, Pennathur S, Feldman EL (2009) Dyslipidemia-induced neuropathy in mice: the role of oxLDL/LOX-1. Diabetes 58:2376–2385
Voukali E, Shotton HR, Lincoln J (2011) Selective responses of myenteric neurons to oxidative stress and diabetic stimuli. Neurogastroenterol Motil 23:964–e411
Winzell MS, Ahrén B (2004) The high-fat diet-fed mouse: a model for studying mechanisms and treatment of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 53(Suppl 3):S215–S219
Woods M, Lan Z, Li J, Wheeler MB, Wang H, Wang R (2011) Antidiabetic effects of duodenojejunal bypass in an experimental model of diabetes induced by a high-fat diet. Br J Surg 98:686–696
Yamagishi S, Imaizumi T (2005) Diabetic vascular complications: pathophysiology, biochemical basis and potential therapeutic strategy. Curr Pharm Des 11:2279–2299
Yoneda S, Kadowaki M, Kuramoto H, Fukui H, Takaki M (2001) Enhanced colonic peristalsis by impairment of nitrergic enteric neurons in spontaneously diabetic rats. Auton Neurosci 92:65–71
Zanoni JN, de Miranda Neto MH, Bazotte RB, de Souza RR (1997) Morphological and quantitative analysis of the neurons of the myenteric plexus of the cecum of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 55:696–702
Zochodne DW (2007) Diabetes mellitus and the peripheral nervous system: manifestations and mechanisms. Muscle Nerve 36:144–166
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the University of Idaho WWAMI Medical Education program, Idaho INBRE (NIH Grants: P20 RR016454 and P20 GM103408) and a University of Idaho Start-Up fund. The authors would like to acknowledge Savannah Patterson and Joshua Cady for their help with staining and quantification procedures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stenkamp-Strahm, C.M., Kappmeyer, A.J., Schmalz, J.T. et al. High-fat diet ingestion correlates with neuropathy in the duodenum myenteric plexus of obese mice with symptoms of type 2 diabetes. Cell Tissue Res 354, 381–394 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1681-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1681-z