Abstract
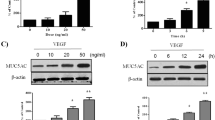
VE-cadherin and claudin-5 are major components of adherens and tight junctions of vascular endothelial cells and a decrease in their expression and an increase in the tyrosine-phosphorylation of VE-cadherin are associated with an increase in endothelial paracellular permeability. To clarify the mechanism underlying the development of edema in nasal polyps, we studied these molecules in polyp microvessels. Normal inferior turbinate mucosal tissues and nasal polyps from patients treated with or without glucocorticoid were stained for VE-cadherin or claudin-5 and CD31 by a double-immunofluorescence method and the immunofluorescence intensities were graded 1–3 with increasing intensity. To correct for differences in fluorescence intensity attributable to a different endothelial area being exposed in a section or to the thickness of a section, the relative immunofluorescence intensity was estimated by dividing the grade of VE-cadherin or claudin-5 by that of CD31 in each microvessel. Tyrosine-phosphorylation of VE-cadherin was examined by Western blot analysis. The relative intensities of VE-cadherin and claudin-5 in the CD31-positive microvessels significantly decreased in the following order; inferior turbinate mucosa, treated polyps and untreated polyps. The ratio of tyrosine-phosphorylated VE-cadherin to VE-cadherin was significantly higher in untreated polyps than in the inferior turbinate mucosa and treated polyps, between which no significant difference in the ratio was seen. Thus, in nasal polyps, the barrier function of endothelial adherens and tight junctions is weakened, although glucocorticoid treatment improves this weakened barrier function.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andriopoulou P, Navarro P, Zanetti A, Lampugnani MG, Dejana E (1999) Histamine induces tyrosine phosphorylation of endothelial cell-to-cell adherens junctions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:2286–2297
Argaw AT, Gurfein BT, Zhang Y, Zameer A, John GR (2009) VEGF-mediated disruption of endothelial CLN-5 promotes blood–brain barrier breakdown. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:1977–1982
Aslam M, Ahmad N, Srivastava R, Hemmer B (2012) TNF-alpha induced NFkB signaling and p65 (RelA) overexpression repress Cldn5 promoter in mouse brain endothelial cells. Cytokine 57:269–275
Aveleira CA, Lin CM, Abcouwer SF, Ambrósio AF, Antonetti DA (2010) TNF-α signals through PKCζ/NF-kB to alter the tight junction complex and increase retinal endothelial cell permeability. Diabetes 59:2872–2882
Bateman ND, Shahi A, Feeley KM, Woolford TJ (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor in nasal polyps: a comparison of asthmatic and non-asthmatic patients. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 29:677–681
Bikhazi NB (2004) Contemporary management of nasal polyps. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 37:327–337
Coste A, Lefaucheur JP, Wang QP, Lesprit E, Poron F, Peynegre R, Escudier E (1998) Expression of the transforming growth factor beta isoforms in inflammatory cells of nasal polyp. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 124:1361–1366
Coste A, Brugel L, Maître B, Boussat S, Papon JF, Wingerstmann L, Peynégre R, Escudier E (2000) Inflammatory cells as well as epithelial cells in nasal polyps express vascular endothelial growth factor. Eur Respir J 15:367–372
Dejana E, Orsenigo F, Lampugnani MG (2008) The role of adherens junctions and VE-cadherin in the control of vascular permeability. J Cell Sci 121:2115–2122
Dejana E, Tournier-Lasserve E, Weinstein BM (2009) The control of vascular integrity by enodthelial cell junctions: molecular basis and pathological implications. Dev Cell 16:209–221
Donners MM, Wolfs IM, Olieslagers S, Mohammadi-Motahhari Z, Tchaikovski V, Heeneman S, van Buul JD, Caolo V, Molin DG, Post MJ, Waltenberger J (2010) A disintegrin and metalloprotease 10 is a novel mediator of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced endothelial cell function in angiogenesis and is associated with atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30:2188–2195
Fawcett DW, Raviola E (1994) Bloom and Fawcett, a textbook of histology, 12th edn. Chapmann & Hall, New York
Förster C, Burek M, Romero IA, Weksler B, Couraud PO, Drenckhahn D (2008) Differential effects of hydrocortisone and TNF alpha on tight junction proteins in an in vitro model of the human blood–brain barrier. J Physiol (Lond) 586:1937–1949
Gosepath J, Brieger J, Lehr HA, Mann WJ (2005) Expression, localization, and significance of vascular permeability/vascular endothelial growth factor in nasal polyps. Am J Rhinol 19:7–13
Hashizume A, Ueno T, Furuse M, Tsukita S, Nakanishi Y, Hieda Y (2004) Expression patterns of claudin family of tight junction membrane proteins in developing mouse submandibular gland. Dev Dyn 231:425–431
Hellquist HB (1996) Nasal polyps update. Histopathology. Allergy Asthma Proc 17:237–242
Hofmann S, Grasberger H, Jung P, Bidlingmaier M, Vlotides J, Janssen OE, Landgraf R (2002) The tumour necrosis factor-alpha induced vascular permeability is associated with a reduction of VE-cadherin expression. Eur J Med Res 30:171–176
Ito A, Hirota S, Mizuno H, Kawasaki Y, Takemura T, Nishiura T, Kanakura Y, Katayama Y, Nomura S, Kitamura Y (1995) Expression of vascular permeability factor (VPF/VEGF) messenger RNA by plasma cells: possible involvement in the development of edema in chronic inflammation. Pathol Int 45:715–720
Kakoi H, Hiraide F (1987) A histological study of formation and growth of nasal polyps. Acta Otolaryngol 103:137–144
Kim TH, Lee SH, Lee HM, Lee SH, Jung HH, Cho WS, Cinn YG, Choe H, Kim MP, Yoo IO, Hwang HY (2007) D2-40 immunohistochemical assessment of lymphangiogenesis in normal and edematous sinus mucosa and nasal polyp. Laryngoscope 117:442–446
Komarova Y, Malik AB (2010) Regulation of endothelial permeability via paracellular and transcellular transport pathways. Annu Rev Physiol 72:463–493
Lampugnani MG, Corada M, Andriopoulou P, Esser S, Risau W, Dejana E (1997) Cell confluence regulates tyrosine phosphorylation of adherens junction components in endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 110:2065–2077
Lin SK, Shun CT, Kok SH, Wang CC, Hsiao TY, Liu CM (2008) Hypoxia-stimulated vascular endothelial growth factor production in human nasal polyp fibroblasts: effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha synthesis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:522–527
Moll T, Dejana E, Vestweber D (1998) In vitro degradation of endothelial catenins by a neutrophil protease. J Cell Biol 140:403–407
Muluk NB, Atasoy P, Arikan OK, Koc C (2007) Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the pathogenesis of nasal polyps. J Otolaryngol 36:357–366
Mygind N, Lildholdt T (1996) Nasal polyps treatment: medical management. Allergy Asthma Proc 17:275–282
Ohno I, Lea RG, Flanders KC, Clark DA, Banwatt D, Dolovich J, Denburg J, Harley CB, Gauldie J, Jordana M (1992) Eosinophils in chronically inflamed human upper airway tissues express transforming growth factor beta 1 gene (TGF beta 1). J Clin Invest 89:1662–1668
Park SK, Jang WH, Yang YI (2009) Expression of pro-angiogenic cytokines and their inhibition by dexamethasone in an ex vivo model of nasal polyps. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379:255–260
Predescu SA, Predescu DN, Malik AB (2007) Molecular determinants of endothelial transcytosis and their role in endothelial permeability. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 293:L823–L842
Roberts WG, Palade GE (1995) Increased microvascular permeability and endothelial fenestration induced by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Cell Sci 108:2369–2379
Sakai N, Chiba H, Fujita H, Akashi Y, Osanai M, Kojima T, Sawada N (2007) Expression patterns of claudin family of tight-junction proteins in the mouse prostate. Histochem Cell Biol 127:457–462
Shen W, Li S, Chung SH, Zhu L, Stayt J, Su T, Couraud PO, Romero IA, Weksler B, Gillies MC (2011) Tyrosine phosphorylation of VE-cadherin and claudin-5 is associated with TGF-β1-induced permeability of centrally derived vascular endothelium. Eur J Cell Biol 90:323–332
Slavin RG (2002) Nasal polyps and sinusitis. Clin Allergy Immunol 16:295–309
Vento SI, Wolff CH, Salven PJ, Hytönen ML, Ertama LO, Malmberg CH (2000) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor in nasal polyps. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 543:170–174
Wang F, Daugherty B, Keise LL, Wei Z, Foley JP, Savani RC, Koval M (2003) Heterogeneity of claudin expression by alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 29:62–70
Wittekindt C, Hess A, Bloch W, Sultanie S, Michel O (2002) Immunohistochemical expression of VEGF and VEGF receptors in nasal polyps as compared to normal turbinate mucosa. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 259:294–298
Xia XM, Wang FY, Zhou J, Hu KF, Li SW, Zou BB (2011) CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 modulates claudin expression and intestinal barrier function in experimental colitis. PLoS One 6:e27282
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was in part supported by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and the MEXT-Supported Program for the Strategic Research Foundation at Private Universities.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yukitatsu, Y., Hata, M., Yamanegi, K. et al. Decreased expression of VE-cadherin and claudin-5 and increased phosphorylation of VE-cadherin in vascular endothelium in nasal polyps. Cell Tissue Res 352, 647–657 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1583-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1583-0